A lone pair, a single bond, a double bond, or a triple bond all count as THIS in VSEPR
Electron group
The fundamental concept of VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion = electron groups want to spread out as much as possible (repel each other)
Difference in electronegativities cause two atoms to share electrons ________
unequally
Bonds formed by head-on overlap of atomic orbitals and by side-on or lateral overlap of atomic orbitals respectively
Sigma bonds
Pi bonds
According to MO theory, overlapping of atomic orbitals from different atoms create these
new molecular orbitals
_____ is the sum of bonded and non-bonded electron groups on an atom.
Steric Number
The strongest repulsion force is due to the presence of THIS, which causes bond angle deviation
Lone pair of electrons
Two things required for a molecule to be polar
Polar Bonds
Asymmetry
How many and what type hybridized orbitals exist within:
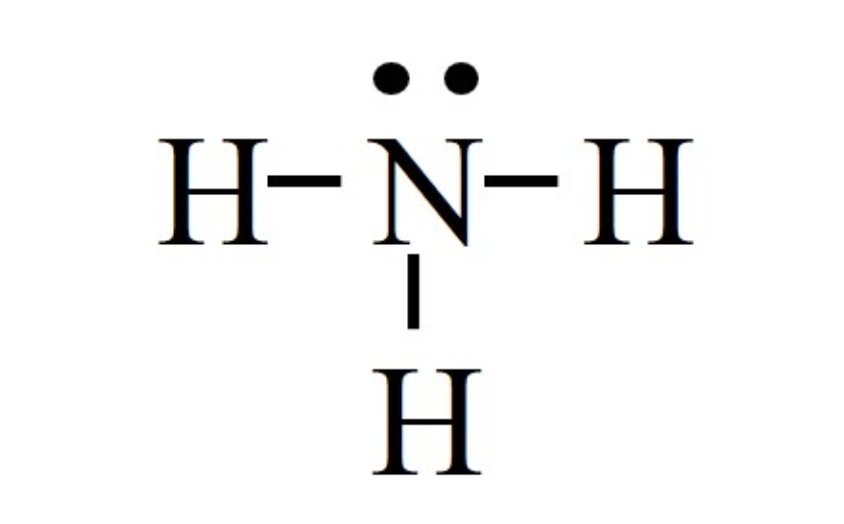
4 sp3 hybridized orbitals
The main difference between bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals
Energy
(bonding lower energy than original atomic orbitals, anti-bonding higher energy)
Water is _____ (polar/nonpolar) and therefore it attracts ______ (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) molecules.
Polar
Hydrophilic
Molecular geometry of chlorine trifluoride
T-shape
(5 total electron groups, 2 of which are lone pairs)
You have a molecule AX4 that has 2 lone pairs. X has greater EN than A. What is the molecular geometry and is the molecule polar?
Square planar
Nonpolar
The hybridization of the interior atoms in: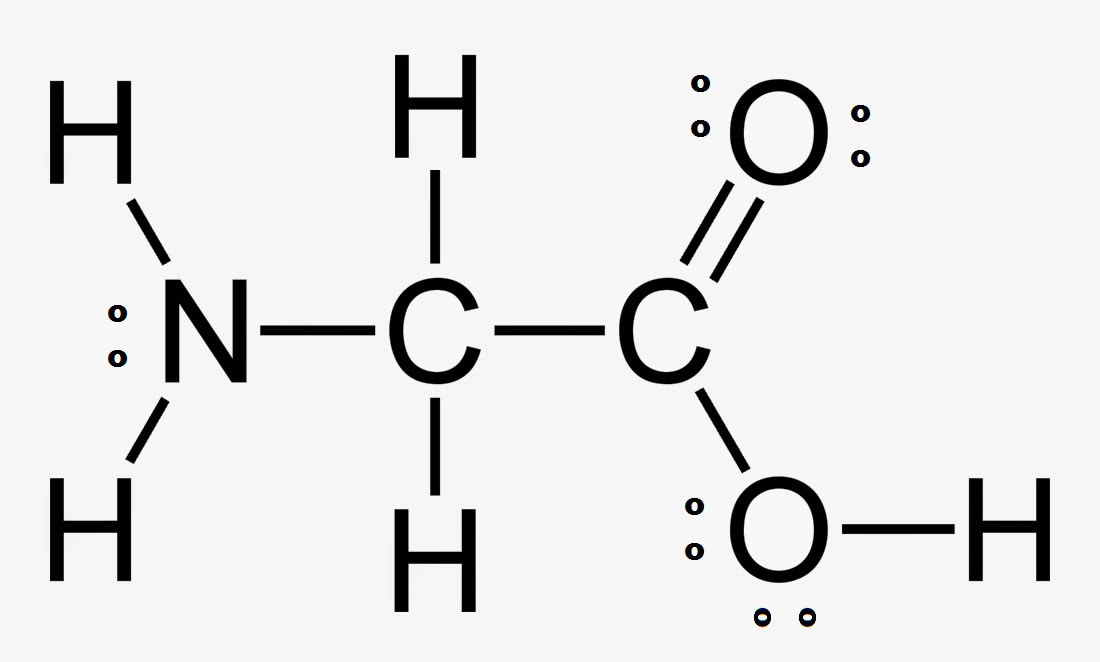
N - sp3
C1 - sp3
C2 - sp2
O - sp3
You make an MO diagram for two different atoms. There are 12 bonding electrons and 8 antibonding electrons. What type of bond will the two atoms form?
Double bond (bond order = 2)
When two or more atomic orbitals combine creating new orbitals with different shape and energy
Hybridization
Compare electron and molecular geometries for the compounds: XeF4 & XeOF4
Both octahedral e- geometry
Molecular geometry square planar (2 lone pairs), and square pyramidal (1 lone pair)
Give an example of a polar and nonpolar molecule.
Answers will vary
The hybridization about the bromine contained in the compound BrF4-
sp3d2
What are the bond orders of O2 and N2, and which is a stronger bond?
O2 bond order = 2
N2 bond order = 3 (Stronger bond)
A molecule is not attracted to a magnetic field and is considered THIS if the electrons are all paired in shared MOs
Diamagnetic
The steric number, electron geometry, and molecular geometry of TeCl4
electron geom - trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geom - seesaw
Is acetone (CH3COCH3) polar?
Yes

1. overlap of atomic orbitals
2. overall lowering of energy
What is the main advantage and drawback of using MO theory rather than Lewis Structures or VBT?
Adv: more accurate E and explanation of molecule propterties
Drawback: complicated, not standard order of MO energies