This type of radiation is the main source of radiation exposure to the veterinary technician.
What is scatter radiation?
The distance between the target in the x-ray tube and the surface of the x-ray detector
What is focal film distance, or source image distance?
Equipment used for measuring thickness of your patient.
What are calipers?
3 most important parts of radiation safety.
What are time, distance, and shielding?
Caudal landmark of a thoracic radiograph.
What is the diaphragm?
2 examples of radiopaque (positive) contrast agents.
What is barium (oral), Gadolinium based (GBCAs) in MRI, and Iohexol (injectable) iodinated based contrast (CT, myelograms and arthroscopy)
Always place the thickest part of the area being radiographed toward the ______ side of the x-ray tube.
What is the cathode?
If you double the image receptor distance from the x-ray source, you will decrease the x-ray beam intensity to one-fourth of the original strength, what is the name of this "law"?
What is the inverse square law?
Units used for measuring patients for radiology.
What are cm?
ALARA
What is as low as reasonably achievable?
Positioning of hind limbs for an OFA pelvis radiograph.
What is Ventral/Dorsal with the stifles rolled inward and the hind limbs extended downward?
Example of radiolucent (negative) contrast agents/gases.
What are air, gas, carbon dioxide, and oxygen?
3 factors that must be correctly set for production of a diagnostic image.
What are kVp, mA, and time
kVp=Kilovolt peak
mA=milliamperage
Structures that are radiopaque on radiographs.
What are bones?
Most of the x-rays are absorbed due to its density, and bones appear white. Soft tissue or fluid is normally grey, as it is less dense than bone, so more x-rays pass through.
Where to measure a patient for a radiograph.
What is over the thickest area?
Maximum Permissible Dose of radiation yearly for occupational workers.
What is 0.05sV (sievert)/year?
1 Sv = 100 rem (roentgen equivalent man)
This must be included when radiographing a long bone.
What are the joint below and the joint above the bone?
Route in which contrast medium is injected for myelography.
What is intrathecally in the subarachnoid space?
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF
This setting controls the number of x-rays produced.
What is mA?
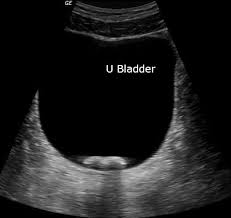
How urinary calculi (stones) appear on ultrasound image.
What is bright/hyperechoic?
Thickness above at which a grid should be used.
What is 10cm?
The purpose of a grid is to allow only the primary x-ray beam to pass through, thereby preventing scatter radiation from reaching the film
This type of grainy appearance can occur if your radiograph is ______exposed.
What is under exposed?
In a lateral pelvis radiograph, this limb should be pulled cranially.
What is the "down" leg?
Right limb in a right lateral radiograph, left limb in a left lateral radiograph.
Days of gestation at which fetus may be seen by radiography and ultrasonography.
What are 42-45 days (x-ray) and 25-35 days (u/s)?
The contrast of the film can be increased or decreased by changing the penetrating power or energy, or ______ of the x-rays.
What is kVp or Kilovolt peak?
The purpose of a ______ is to allow only the primary x-ray beam to pass through, thereby preventing scatter radiation from reaching the film
What is a grid?
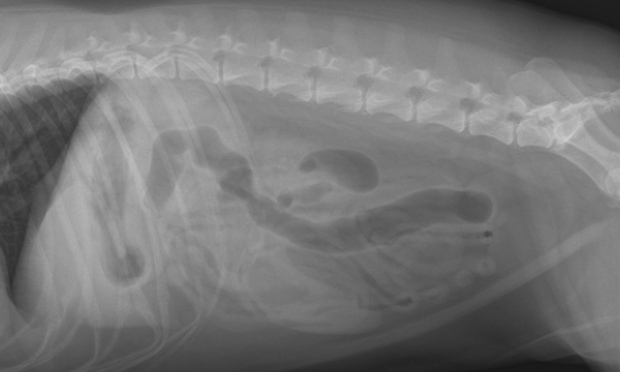
Which radiographic view is used to help diagnose a Gastric Dilitation/Volvulus? Describe what the radiograph would look like.
Right lateral:
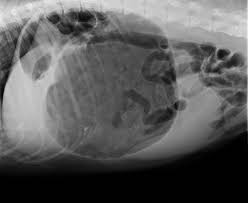
The artifact shown here, where a lucent halo is seen around metal implants.
What is the Uberschwinger artifact?
Cranial/rostral landmark of a lateral cervical spine radiograph.
What is the medial canthus of the eye?
The ionizing imaging modality used for moving structures, which provides a continuous image, and involves directing the x-ray beam through the patient and onto an image intensifier.
What is fluoroscopy?
Fluoroscopy can be used in GI studies, tracheal studies, and myelography and is essential for heart and vascular studies.