Where does fertilisation occur?
Ampulla of the fallopian tube

Name the stages of the ovarian cycle
Follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase
Name the hormones that control spermatogenesis.
Define infertility
Infertility is a disease of the male or female reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse (WHO)
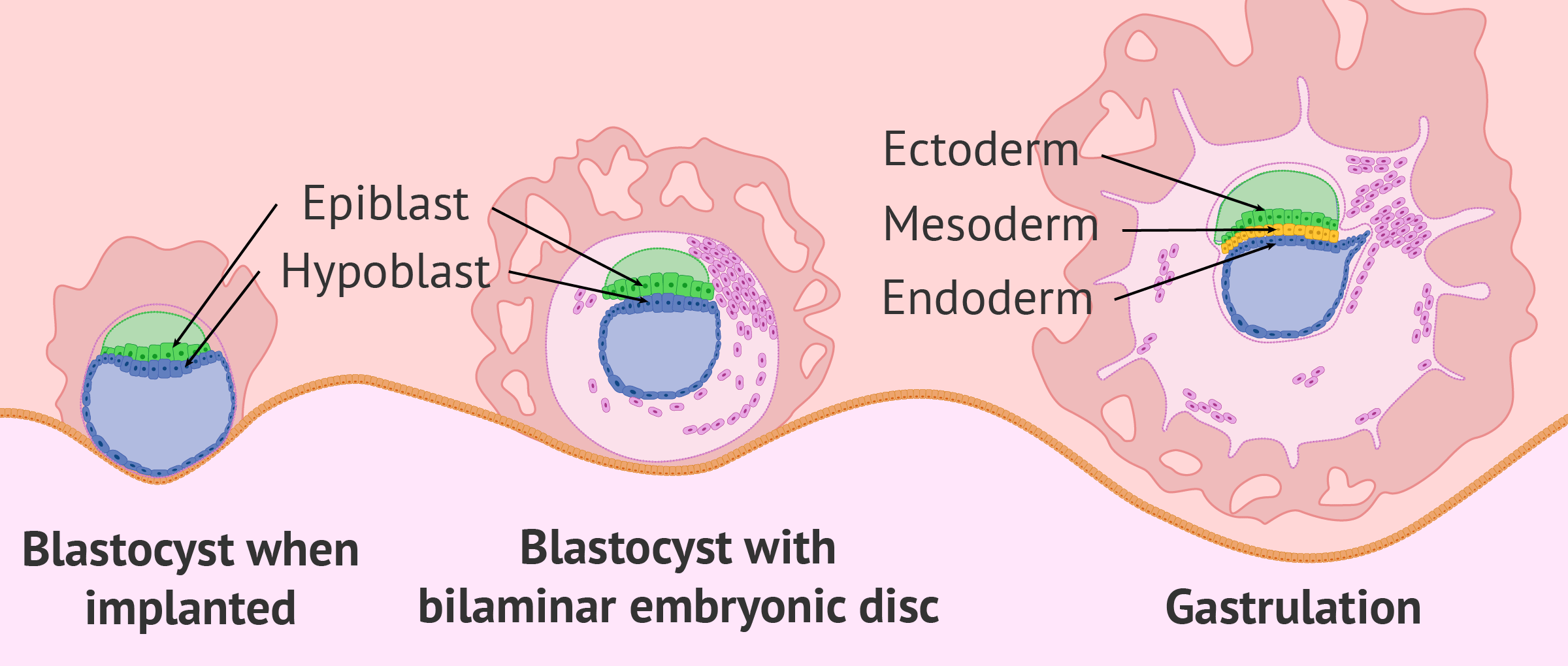
What are the three Germ Layers?
Endoderm, Mesoderm and Ectoderm

What happens to the corpus luteum after fertilisation?
Beta-hCG released by the embryo maintains the corpus lutem so that it continues to be a progesterone source for the uterus to remain stable in pregnancy
What causes progesterone release?
The formation of the corpus luteum, in the luteal phase
Which cell produces testosterone?
Leydig cells
Which a disease was Kylie screened for that can result in infertility in women?
Rubella
In which week of embryonic development do the 3 germ layers form?
Week 3
Name the main hormone change that induces labour?
What causes the LH and FSH surge?
Sustained oestrogen release from dominant follicle at high levels for 48 hours.
What does the midpiece do?
Contains mitochondria and provides energy for motility
What is the mechanism of how stress can cause a miscarriage?
Stress induces cortisol via Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, causing suppression of GnRH = reduced FSH and LH, impacting progesterone development
Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis by stress can also impact prolactin production (causing further reduced progesterone)
Embryologically what forms the epithelial lining of the GI tract?
The yolk sac
How does the combined pill work?
Suppresses the mid-cycle LH surge by inhibiting GnRH release via giving progesterone and oestrogen at a steady, controlled low dose - avoiding ovulation
Which cells do FSH and LH act on, and what does this produce?
FSH acts on granulosa cells, which secrete aromatase enzymes, that combine with androgens secreted by Theca cells, which are stimulated by LH.
This results in the production of oestrogen
What is the mechanism of how testosterone causes negative feedback in the hypothalamus?
Testosterone converts aromatase to extradiol, which binds to oestrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, inhibiting GnRH production. This impacts pituitary function as a result and the secretion of FSH and LH.
An early plateau of beta hCG (<8weeks) indicates a nonviable pregnancy
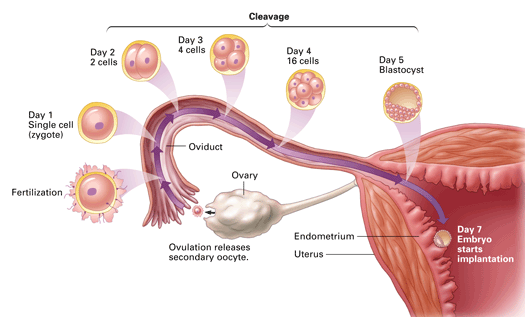
What does a fertilised egg turn into in order to be transplanted into the uterine wall?
A blastocyst
What is the impact of pregnancy on Respiratory function?
Progesterone also stimulates respiration, leading to hyperventilation
How do GnRH pulsations impact hormone release?
Low pulses stimulates FSH (which keeps negative feedback for most of the cycle)
High pulses stimulate LH (due to increased levels of oestrogen, enabling the switch from negative to positive feedback)
What is the name of the condition that shows poor sperm motility and can result in male infertility?
Asthenozoospermia
Name one way an ultrasound identifies early pregnancy problems.
- Locates gestational sac which is present in early pregnancy (if empty, indicates a nonviable pregnancy)
- Can identify ectopic pregnancy via no heart beat and large foetal pole
- Pregnancy failure when the yolk sac is too large (>7mm)
What is the process that turns a bilaminar disc into a trilaminar disc?
Gastrulation