Define Anabolic Reactions
Reactions that make macromolecules (bigger molecules) from monomers (single units)
Which are weaker - hydrogen or covalent bonds?
Hydrogen bonds
What are the 4 biomolecules necessary for all living things?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins
To what element are the electrons in water more attracted to?
Oxygen
Anabolic reactions are also known as what kind of reactions?
Condensation reactions
Define Cohesion
The attraction of water molecules for other water molecules
How many bonds can Carbon have?
What kind of bonds are they?
Four covalent bonds
What are the 4 elements that 99% of all living things are made of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
What does it mean for something to be hydrophillic?
Ability to be attracted to polar water molecules
What kind of reactions are exergonic reactions?
Energy releasing reactions
Define Metabolism
Metabolism is the name we give to the chemical reactions of life.
What is the functional group of a biomolecule?
Functional Groups are parts of the molecule that determine its chemical characteristic and properties
 What is the name of this biomolecule?
What is the name of this biomolecule?
Phospholipid
Why is water's boiling point so high?
Hydrogen bonds require a large amount of heat energy in order to break.
More heat to break H bonds = higher temperature to boil water
Hydrolysis reactions are also known as what other kind of reactions?
Catabolic
Define hydrophobicity
The observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in an aqueous solution and exclude water molecules
What are the 2 pathways metabolic reactions can occur in?
Cycles and chains
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
–OH group attached to the first carbon atom in alpha glucose is located on the same side as the –CH2OH
–OH group attached to the first carbon atom of in beta glucose is located on the opposite side from the -CH2OH group
Where are hydrogen bonds located between water molecules?
Between the electronegative oxygen of one water molecule and one electropositive hydrogen of another water molecule.
The process that dissolves a piece of bread into simple nutrients your body can use, like glucose is considered what kind of reaction?
Catabolic
Define "atom"
The smallest particles of all elements. These are single units. A collection of the same atoms, makes an element.
What is he difference between a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid?
Saturated fatty acids lack double bonds between the individual carbon atoms, while in unsaturated fatty acids there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid chain
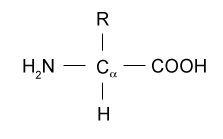 Name what kind of biomolecule this is.
Name what kind of biomolecule this is.
Amino acid
Explain why water is considered to be polar
The O (oxygen) is slightly more negative and the H (hydrogen) are slightly more positive which gives water molecules two opposite sides.
Which process is an example of catabolism?
A. Translation of mRNA
B. Replication of DNA
C. Hydrolysis of protein
D. Synthesis of a disaccharide