% of Earth covered by water
What is ..... 71%
Which property makes water the "universal" solvent?
What is its ..... polarity 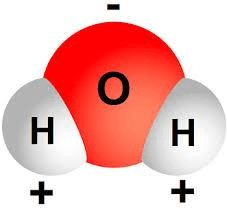 / + & -sides
/ + & -sides
Aquatic animals have evolved streamlined shapes due to water's high _____ (resistance to flow).
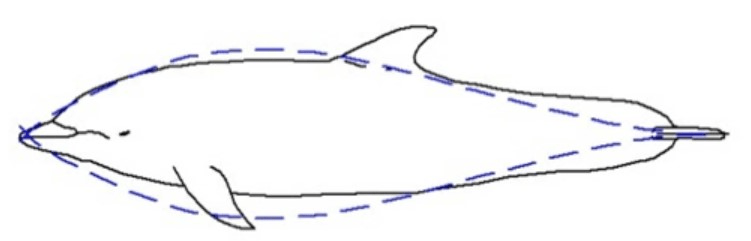
What is ... viscosity
Photosynthetic phytoplankton in which biome produce 50% of our atmospheric oxygen?
What is ... ocean
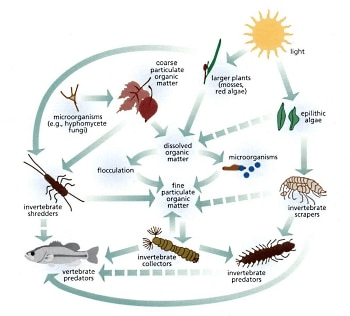
Leaf debris is the source of energy supplying which freshwater biome?
What is ... streams & rivers
% of Earth's water that is freshwater
What is ... 3 %
What property makes water slower to change temperature than many other substances? It also allows it to moderate local temperatures.
What is .... high specific heat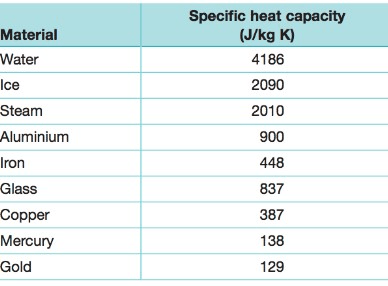
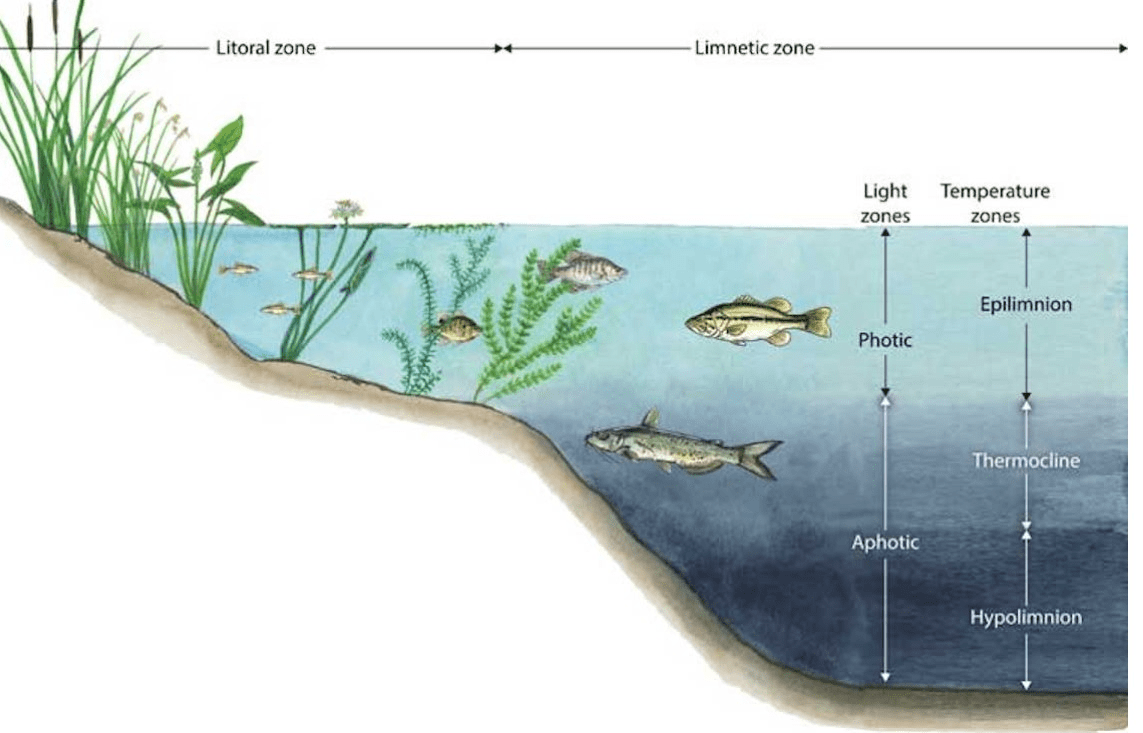
choices: littoral, limnetic, benthic
What is .... benthic (bottom dwelling)
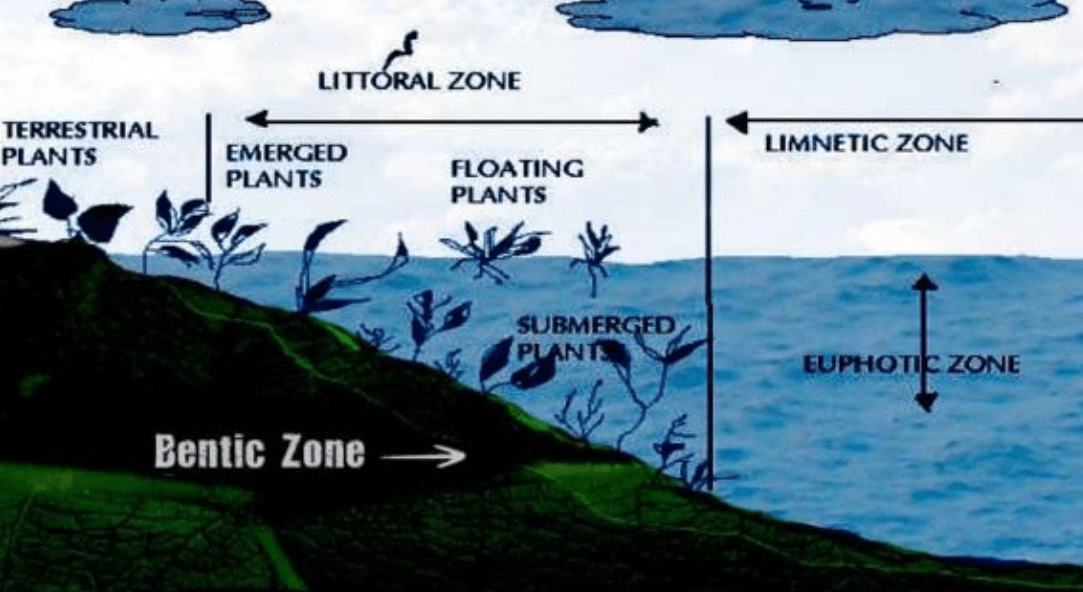
These detritivores are found in the benthic zone of this biome.

What is ... ocean
Wind during fall and spring cause "overturn" of layers of surface and deep water, oxygenating the depths of which biome?
What is ... lake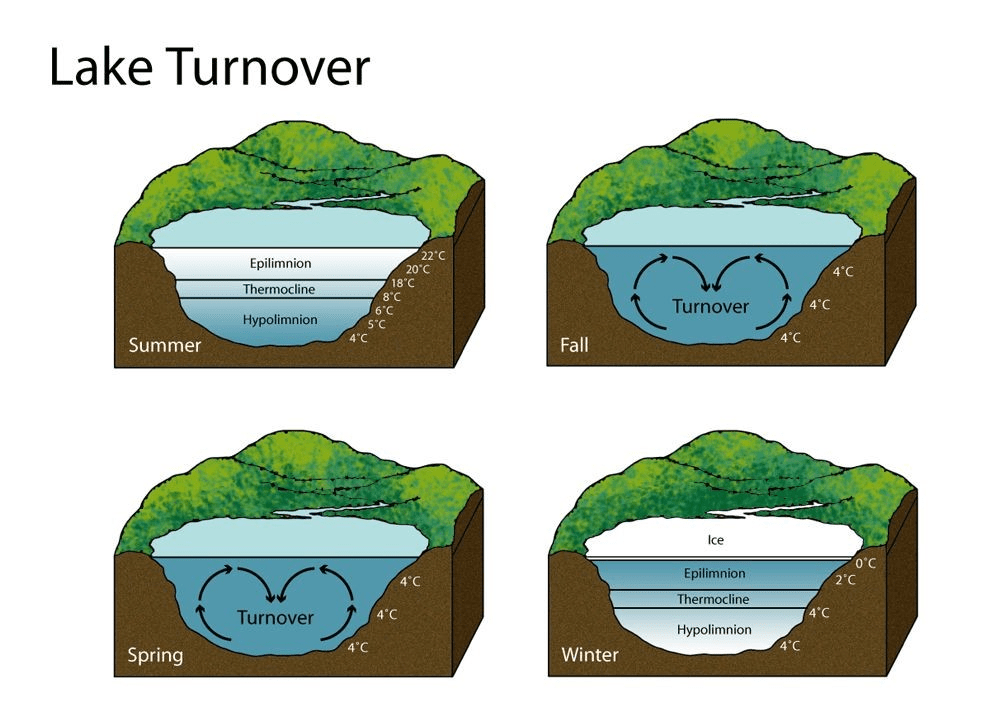
Ocean gyres move warm water away from which latitude line and cool water away from which latitudes?
What are...equator / poles
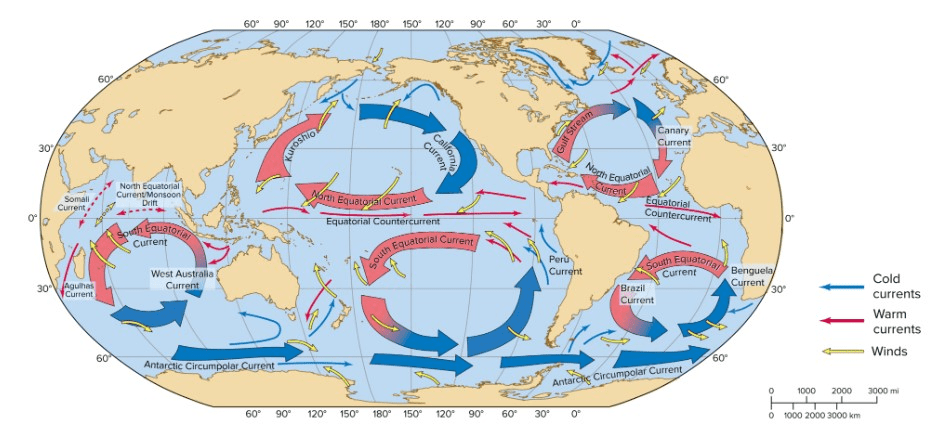
Which water is more dense and sinks? (choose 2)
lower temp vs. higher temp
lower salinity vs. higher salinity
What is ... lower temp and higher salinity
CRUSH YOUR ENEMIES! Take 20pts from another team if correct.
Many aquatic organisms are cold-blooded so their bodies don't need to burn energy to stay warm. Which water property makes organism lose body heat 3 times faster in water than in air?
What is ... conduction.
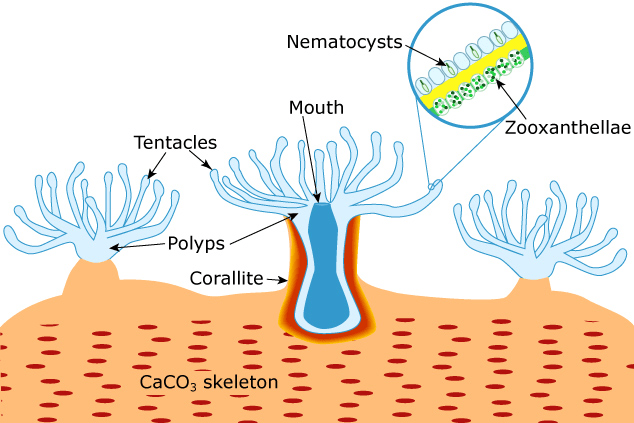
Shallow, biodiverse biome enabled by a symbiotic relationship relationship of a photosynthetic algae living inside tiny animals.
What is ... coral reef
In this biome, the littoral zone is shallow w/ plants & the lentic zone is deep.
What is ... lake
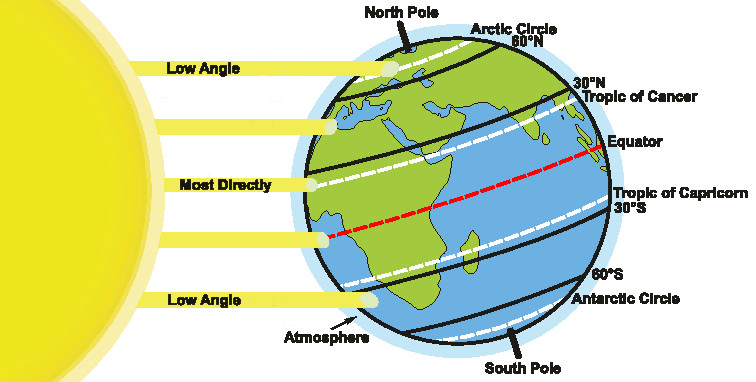
This is the initial energy source that drive global air and water circulation patterns.
What is ... solar energy (strongest at equator)
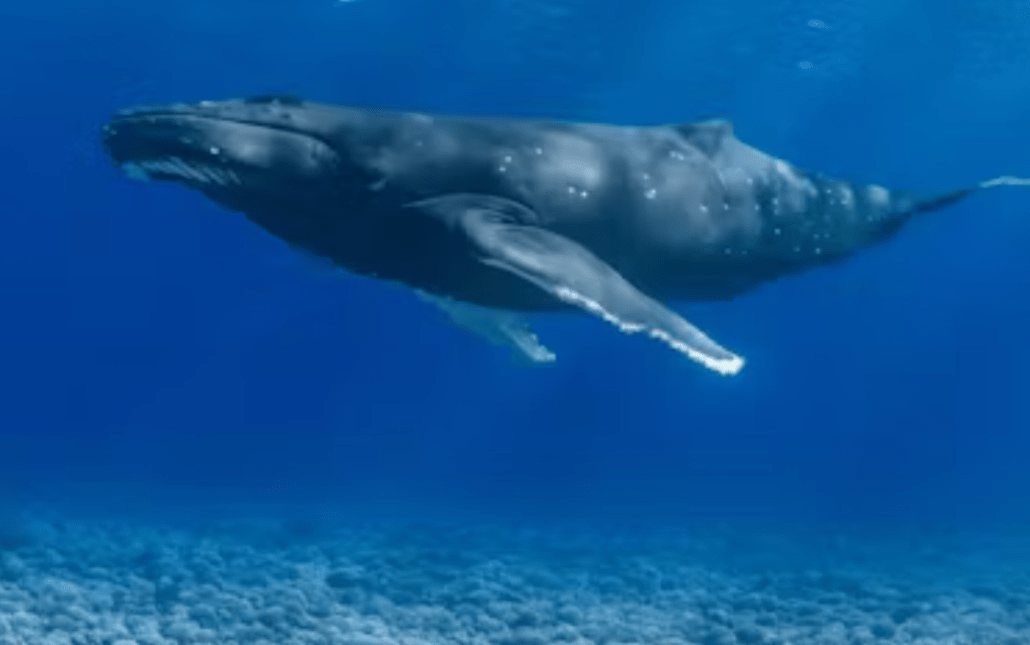
Property of water that allows organisms, even very heavy ones, to float.
What is ... buoyancy

All organisms need this molecule to conduct respiration, so how much of it is available is a limiting factor for aquatic life.

What is ... dissolved oxgyen

Shallow, biodiverse marine habitat in cool waters off the coast of California. Main producer is very tall form of algae.
What is ... kelp forest
Invasive zebra mussels were introduced into this North American freshwater biome from ballast water.
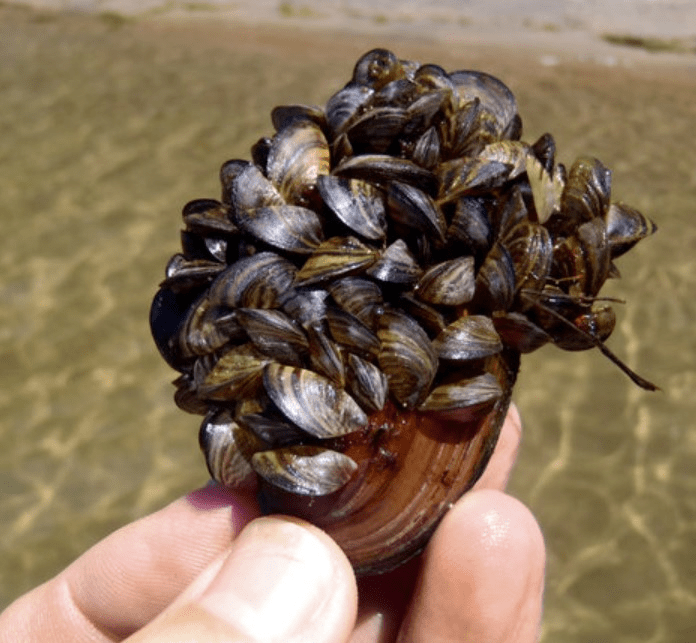

What is ... the Great Lakes

It drives the movement of water through the atmosphere and causes mixing of surface water into deeper water in the ocean and lakes.
What is .... wind
FP = 0C 32F BP = 100C 212F
The type and abundance of these benthic organisms is measured to assess stream health.
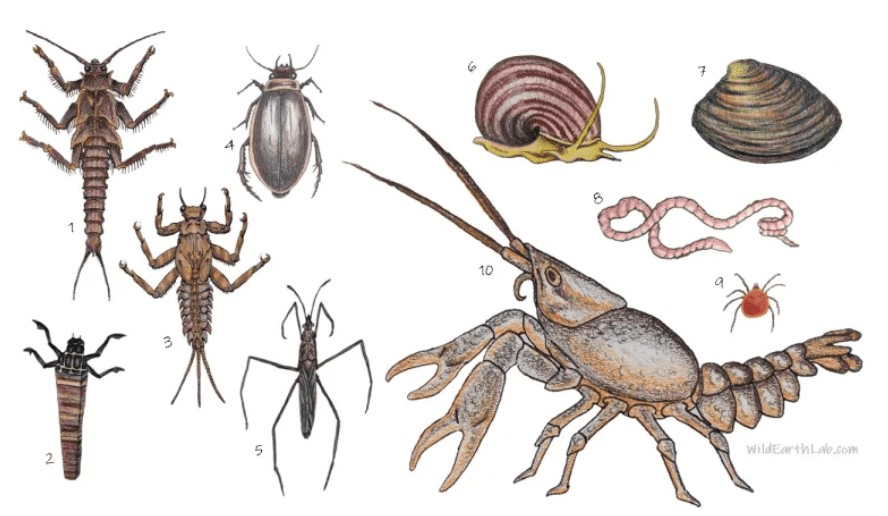
What are ... macroinvertebrates
(insects, insect larvae, clams, mussels, snails, crayfish etc.)
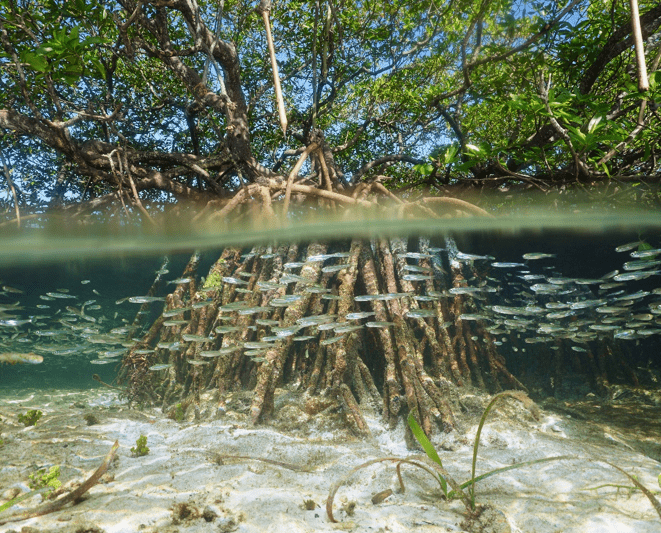
Shallow, tropical biome with tall-rooted plants that hold shoreline in place and give habitat to many organisms and their young.
What is .... mangrove

Freshwater biome that is lentic.
Freshwater biome that is lotic and well aerated.
Lentic = still = lake
Lotic = flowing (adds oxygen) = streams & rivers

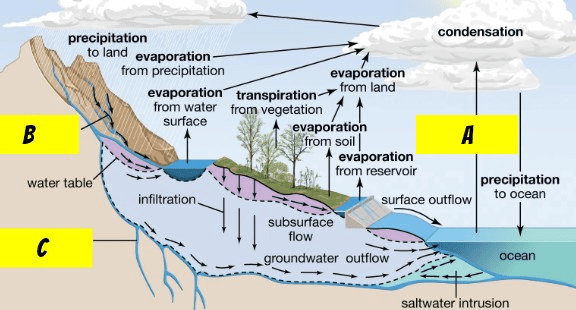
A,B, and C in the hydrologic cycle.
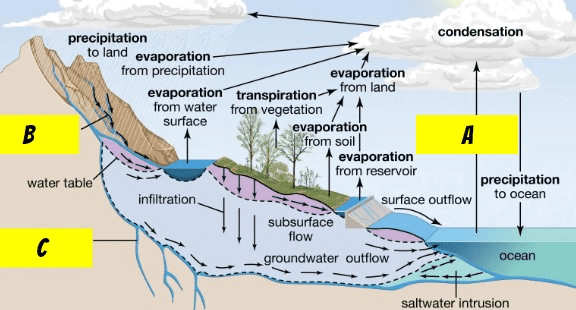
A = evaporation B = runoff C = percolation
Water "reservoirs" that are the fastest and slowest to turnover or recharge.
choices: lakes, rivers & streams, oceans, atmosphere, groundwater
fastest = atmosphere (9d) slowest = ocean (3,000y)
Name of survey system using number, type, and health of fish to assess lake and river health.
What is ... Karr's Index of Biological Integrity
CRUSH YOUR ENEMY! Subtract 20 point from the team of your choice if you answer correctly.
Four (4) shallow, marine habitats where organisms must be adapted to daily fluctuations in water level, salinity, light and temperatures.
What are ... intertidal zone, saltwater marsh, mangrove, estuary.
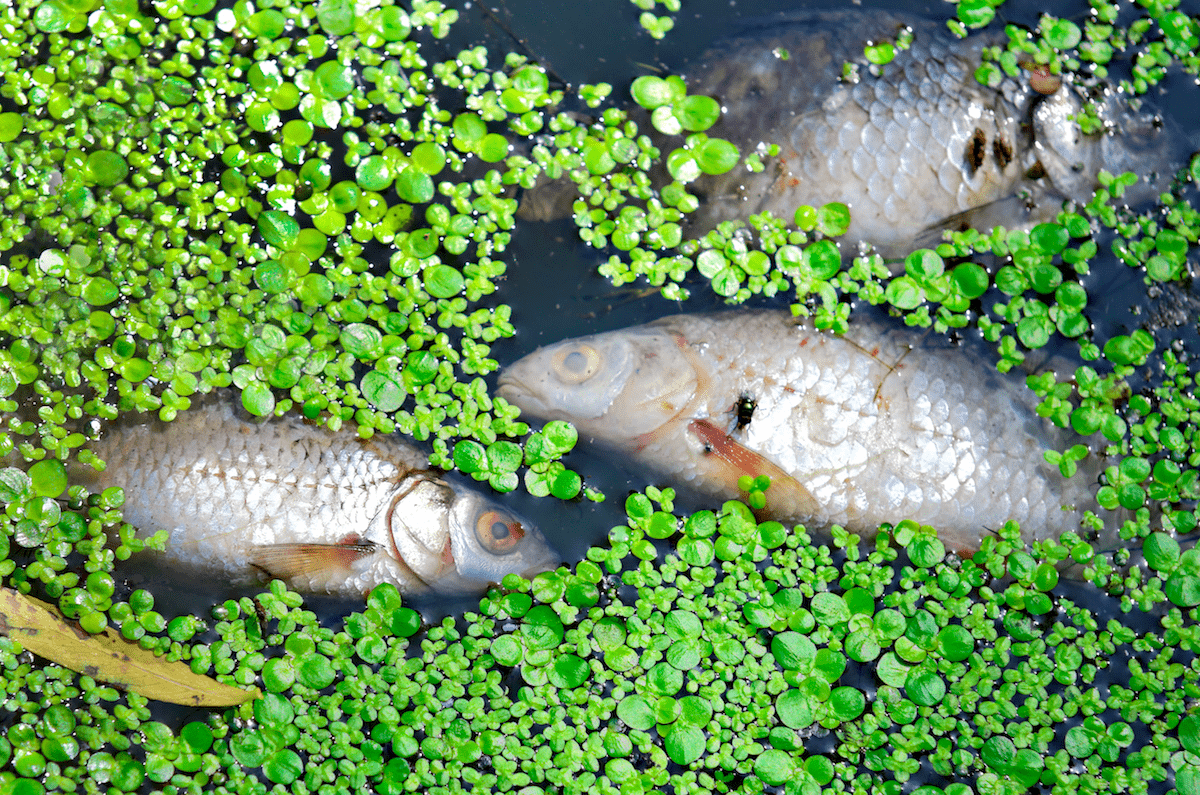
Eutrophication of this biome results from nutrient (N&P) overload that initially increases producer numbers, followed by producer die-off & decay that depletes the system of dissolved oxygen, causing fish die offs.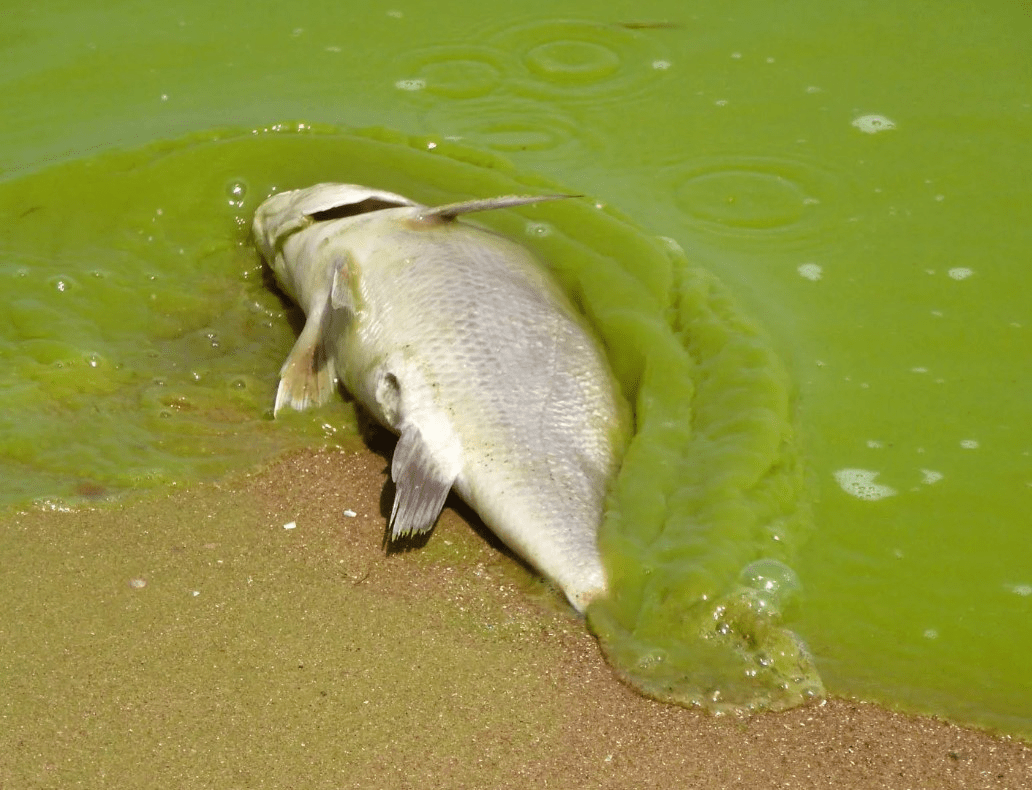
What is ... lake (but also happens in gulfs & bays)
