or Electromagnetic spectrum
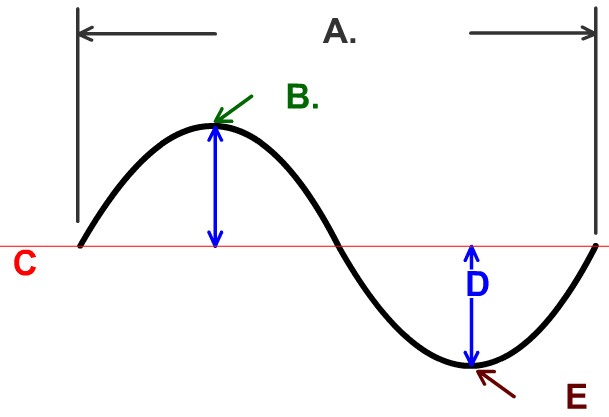
The name of Part B
What is the Crest
The name of part A
What is Wave length
something a mechanical wave needs to move
What is a medium
Description of how electromagnetic waves moving differently from mechanical waves
What is does not require a medium but can use a medium if needed, can move through space like a vacuum.
Has the longest waves, and are able to bend around objects
What are radio waves
The video that was watched to show when this particular item touches the water while vibrating
The types of waves Earthquakes produce
What are transverse and longitudinal waves?
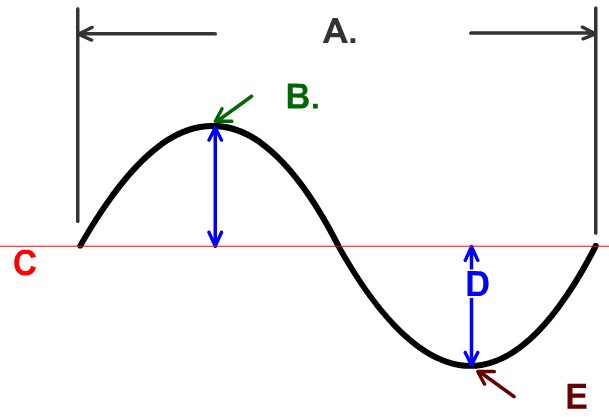
The name of part E
What is the Trough
The name of part B
What is Compression
The 2 types of waves that mechanical waves can produce.
What are the transverse and longitudinal waves?
These are the types of electromagnetic waves
What are: Radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light waves, ultraviolet light waves, gamma waves.
The uses of Microwaves in EM spectrum
Which are: heating up food, mobile phones, wi-fi, satellite communications.
Transmits Energy But not matter
What is sound waves
The direction energy moves during an earthquake
It moves away from the epicenter
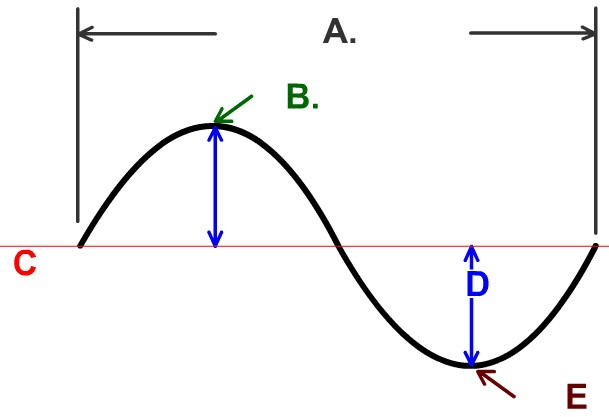
The name of part D
What is the Amplitude
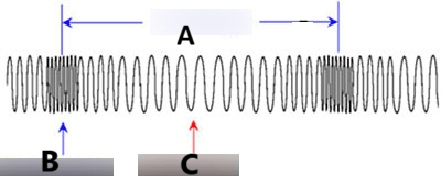 The name of part C
The name of part C
What is rarefaction?
This determines the speed of the mechanical waves
What is the type of medium that is used for the mechanical movement?
The speed in which electromagnetic waves move
What is the speed of light or "c"?
Uses of Infrared light waves
What are thermal (heat) images, remote controls, phototherapy, pain relief, study space using telescopes
The explanation of soundwaves moving in the water
By causing water molecules to vibrate back and forth in the direction of their travel.
How fast do the waves of the electromagnetic spectrum travel
What is the speed of light or "c"
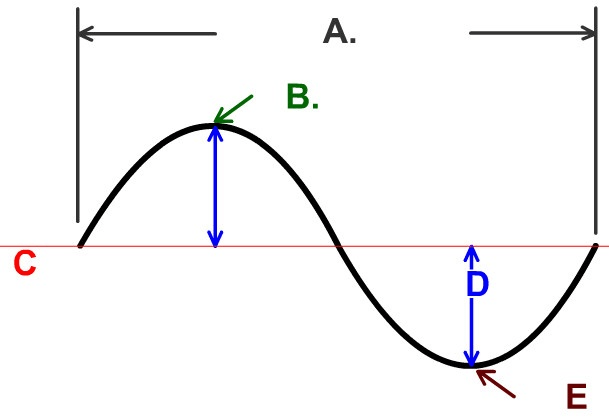
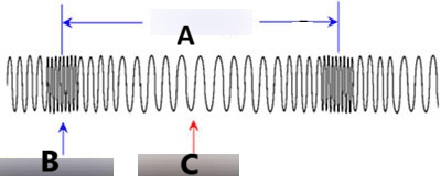
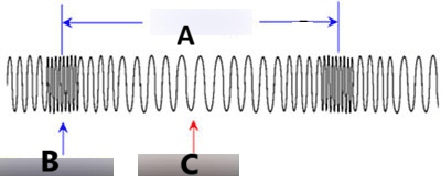
The Name of Part A
What is the wavelength
Description of how longitudinal waves move in correspondence to the movement of energy
What is the wave movement is parallel to the wave energy
or
What is the movement goes in the same direction as the energy?
How fast does the mechanical energy transfer
What is the speed in which the object moves (oscillates).
How do you describe the path of energy transfer for electromagnetic waves
What is the movement of electrical fields and magnetic fields being perpendicular to each other and simultaneously perpendicular to the wave direction?
The uses of Ultraviolet light
What are disinfectants, sterilization, treating skin conditions, black lights, glow in the dark objects, tanning beds
Producing a sound by the vibrating string that vibrates the surrounding air
Sound waves made by plucking string instruments
this is the reason why a high pitch sound is heard on the guitar string
It is a thinner strand that creates a faster frequency
The relationship of wavelength and frequency
What is the longer the wave length, the lower the frequency
or
What is the shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency
Pendulum, grandfather clock, marbles going down the stairs, tuning fork in the water
What is examples of Longitudinal Waves
Examples of Mechanical Waves
What are: Sound waves
Seismic waves
Waves on strings
Oceanic Waves
Examples of Electromagnetic waves
The wave characteristic used to make X-rays usable
What is High Energy
The type of wave a guitar string makes
A transverse wave
A low pitch sound is created