The highest part of a wave
crest
If the amplitude of a wave increases, what happens to the energy of the wave?
Energy increases
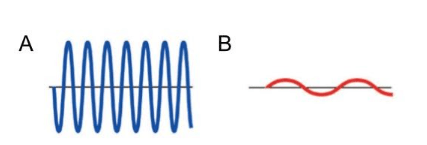
Which wave has a higher frequency?
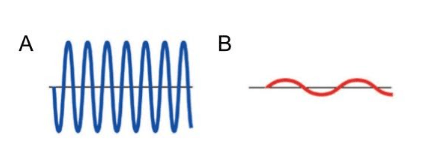
A
Which letter represents the trough?
B
Who is the best science teacher of all time? AKA the G.O.A.T.
Mr. Carreon
The lowest part of a wave
trough
If the amplitude of a wave decreases, what happens to the energy of the wave?
Energy decreases
Which wave has a longer wavelength?
B
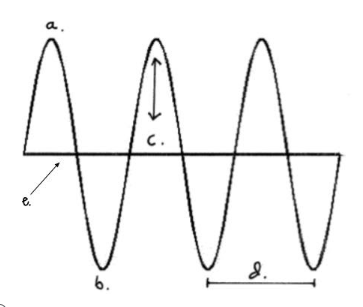
Which letter represents the amplitude?
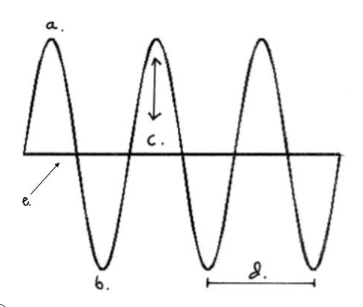
C
Transverse wave
The height of a wave (from line of origin to crest or line of origin to trough)
amplitude
Which wave has more energy?
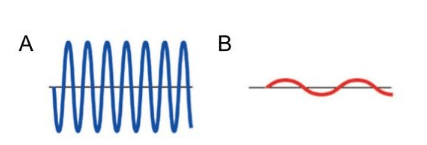
Wave A
If the wavelength of a wave increases, what happens to frequency?
Frequency decreases
Which letter represents the crest?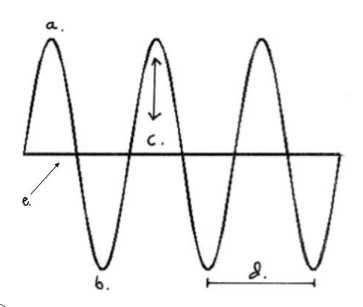
A
The material a wave travels through
Medium
The distance between two waves (from crest to crest or trough to trough)
wavelength
Which wave has more energy?
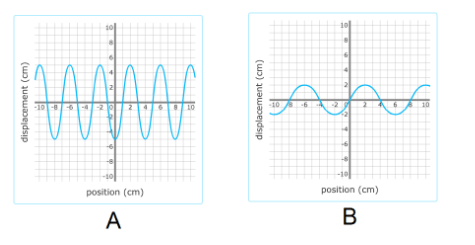
Wave A
If the wavelength of a wave decreases, what happens to the frequency?
Frequency increases
Which letter represents the line of origin?
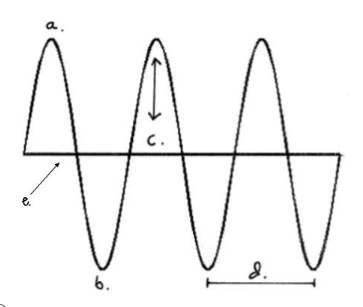
E
True or False: Sound waves can travel through empty space
False
The middle of a wave where the wave is at rest
line of origin
If the amplitude of a wave increases, how does it affect the frequency of the wave?
No effect
The number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time (one second)
Frequency
Which letter represents the wavelength?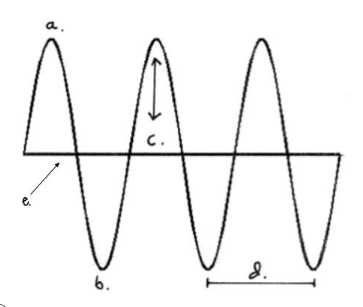
D
True or False: Light waves require a medium to travel through
False