Through which material can sound waves travel the fastest? (Solid, Liquid, or Gas)
Solid
If you increase the amplitude of a sound wave, what happens?
The sound gets louder
What are the low points in a transverse wave called?
The number of vibrations in a period of time is defined as the __________ of a wave.
frequency
Area of longitudinal wave where the coils are close together.
Compression
What is "D"? 
Trough
Sound cannot travel through a vacuum and needs a medium to travel through. True or False?
True
If the amplitude of a wave is decreased, what will the change in its energy?
lower
What is this distance? 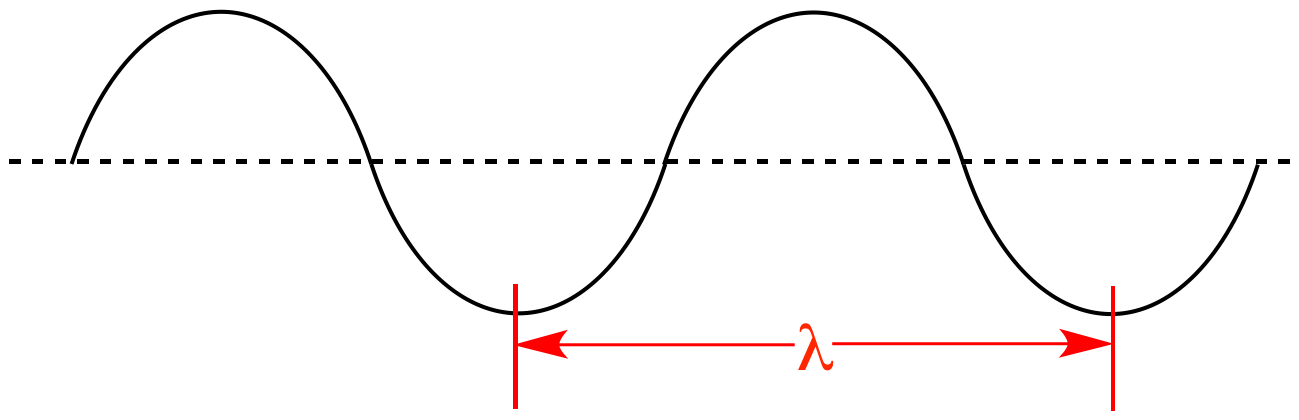
wavelength
Occurs when light rays bounce off of a surface back to your eyes (ie when you look in a mirror).
Refection
Disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another.
Waves
Area of longitudinal wave where the coils are spread out.
Rarefaction
If there is larger amplitude, how does this affect the energy levels?
higher
The maximum distance the particles of the medium carrying a wave move away from their rest position
Amplitude
The matter through which wave energy travels is called a
Medium
When looking through water, light waves can appear "bent." (Like a straw in water.) What is this called?
Refraction
What are the high points in a transverse wave called?
crests
What is "B" and "F"?

Crest
When light bends moving from one medium to another.
Refraction
When amplitude is increased in light waves, what changes do we see? Think of a light bulb
Increase in brightness (intensity)