Sound is a _________________ wave.
(Longitudinal or transverse)
Longitudinal
Are light waves longitudinal or transverse?
Transverse.
The reciprocal of the period of a wave is its _________.
frequency
The kind of light directly below the visible spectrum (in terms of frequency)
infrared
The speed of light in meters per second
about 299 million
Higher pitch sounds have __________ wavelengths than lower pitch ones.
Red and green light combine to make ______________.
Yellow
What is the wave doing as it passes through the aperture in the image on the left?

Diffracting
Radio waves have _____________ wavelengths than visible light
longer.
Explain the image in terms of interference

Where the peaks of one wave and the peaks of the other line up, the water is highest. Peaks and troughs meet to cancel each other out. Troughs and troughs meet to make deeper troughs.
Shortening the length of the vibrating medium will _________ the pitch it creates.
increase
In the human eye, ____________ detect color, and _________ detect light and dark.
cones; rods.
Why is the wave in the image turning the direction that it is turning?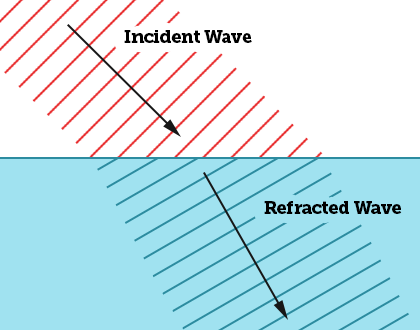
It is refracting to its own right because it travels slower in the blue medium.
What is the role of a "sound envelope" in AM radio?
With Amplitude Modulation, the radio waves' amplitude fills an "envelope" creating the shape of the sound wave.
The hight of a water wave is called its _______________.
amplitude
The sound that a stationary train's horn makes is __________ than that of a train moving away from you. This is known as the ______________.
higher; Doppler Effect
In this ray diagram for a ______________ mirror, the LOST are:
Convex
Location: behind the mirror
Orientation: upright / normal
Size: smaller / diminished
Type: virtual
The frequency, speed, and wavelength of waves are related by the equation ____________.
Speed = (Wavelength)*(Frequency)
This is an image of a radio telescope. Why is it shaped the way it is?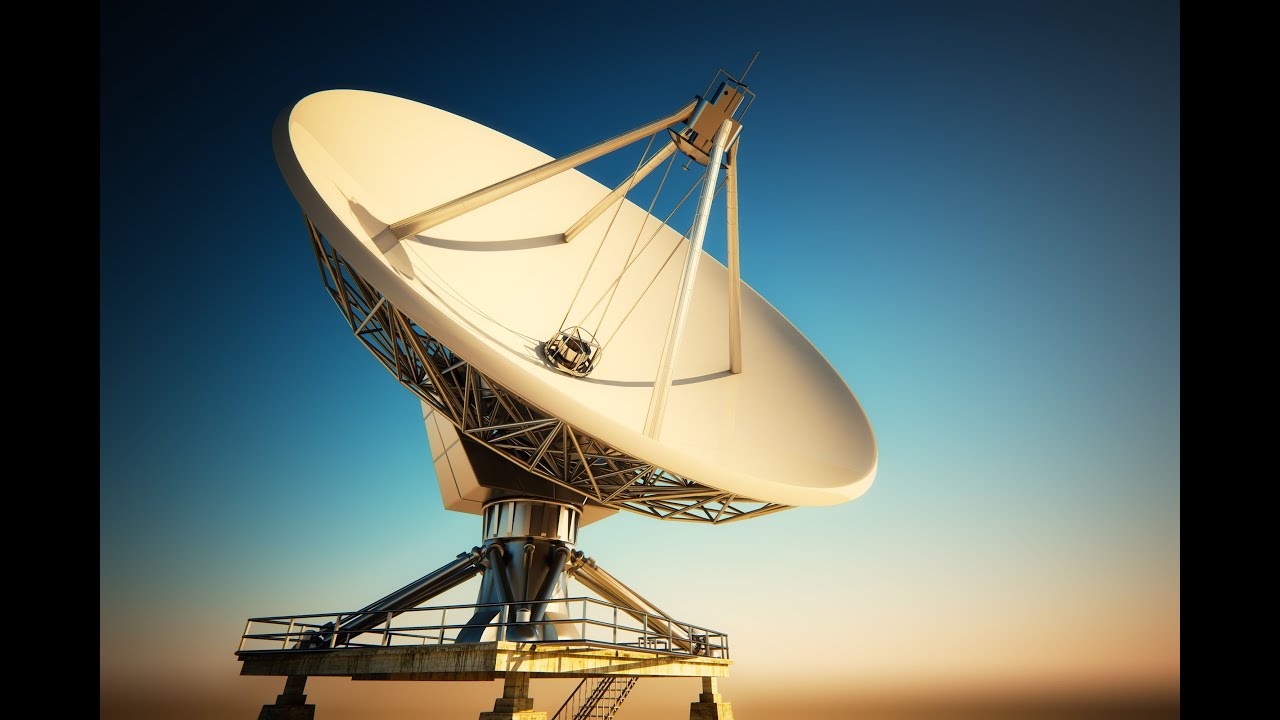
The dish acts as a concave mirror, directing radio waves to the focus (where the detector is).
Light passing through two vertical slits will create the following pattern of light dots. Why?

Light is diffracting through both slits, spreading out. The waves interfere with each other. Where they combine constructively, they create bright spots, and where they combine destructively, dark spots.
In the standing wave image, A, E, and F are at __________, and B, C, and D are at __________.

A, E, and F: anti-nodes
B, C, and D: nodes
A near-sighted person's eyes focus light in front of the __________ rather than on it. In order to correct this, they need ____________ (concave or convex) lenses.
retina; concave
Consider the image on the left. The black lines represent the path of sound waves in ocean water as they approach the surface (darker blue represents deeper water). What do the paths tell you? You must be very specific to be awarded points.
The speed of sound in the water is decreasing gradually as the waves approach the surface, so that they are refracting to their own right.
List all the main kinds of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing wavelength.
Gamma rays
X-rays
Ultraviolet
Visible light
Infrared
Microwaves (can be omitted because technically they are part of the radio band)
Radio waves
The center image shows the absorption spectra of light from our sun.
The top image shows the absorption spectra for the Andromeda galaxy. What can you say about the motion of Andromeda relative to the Earth?
It is blueshifted, meaning that Andromeda is moving towards the Earth.