The highest part of a wave
crest
If the amplitude of a wave increases, what happens to the energy of the wave?
Energy increases
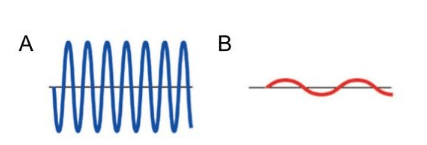
Which wave has a higher frequency?
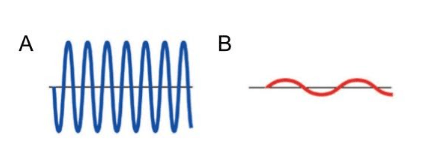
A
Which letter represents the trough?
B
A wave that has a disturbance that moves in the same direction as the wave travels
Longitudinal wave
To bounce off
reflect
What type of wave is this? 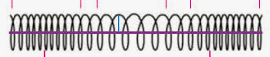
Longitudinal
When light hits a mirror, how does it interact with the mirror?
Reflects
The lowest part of a wave
trough
If the amplitude of a wave decreases, what happens to the energy of the wave?
Energy decreases
Which wave has a longer wavelength?
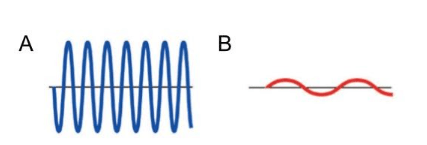
B
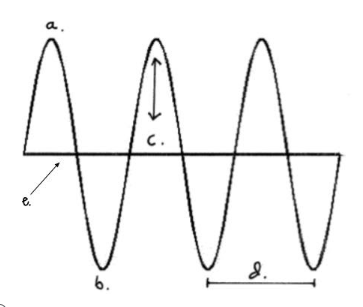
Which letter represents the amplitude?
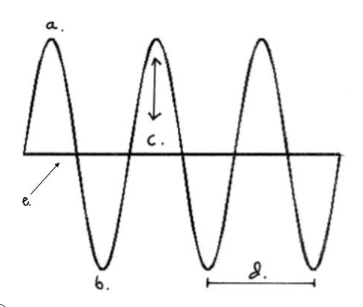
C
Transverse wave
To pass through
transmit
What type of wave is this? 
Transverse
When light hits a window, how does it interact with the window?
Transmits
The height of a wave (from line of origin to crest or line of origin to trough)
amplitude
Which wave has more energy?
Wave A
If the wavelength of a wave increases, what happens to frequency?
Frequency decreases
Which letter represents the crest?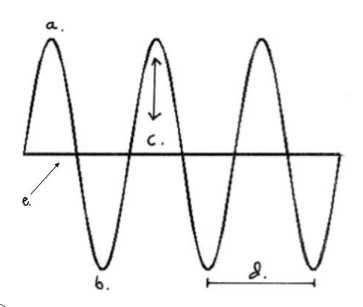
A
The material a wave travels through
Medium
To take in
absorb
Is sound a transverse or longitudinal wave?
Longitudinal
When all colors of light are reflected, what do we see?
White
The distance between two waves (from crest to crest or trough to trough)
wavelength
Which wave has more energy?
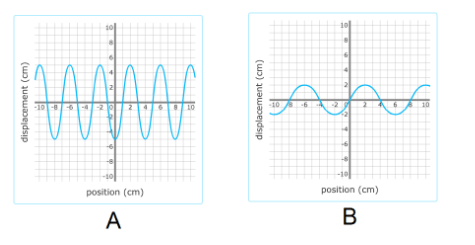
Wave A
If the wavelength of a wave decreases, what happens to the frequency?
Frequency increases
Which letter represents the line of origin?
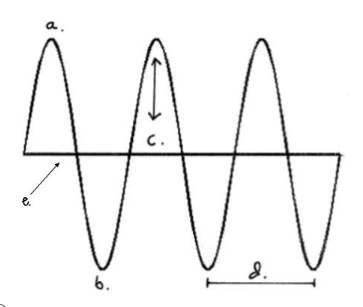
E
True or False: Sound waves can travel through empty space
False
To bend
refract
Is light a transverse or longitudinal wave?
Transverse
A special material is used in movie theaters, so we can hear the movie clearly without noise from outside. What is happening to the sound when it interacts with the material?
It's absorbed
The middle of a wave where the wave is at rest
line of origin
If the amplitude of a wave increases, how does it affect the frequency of the wave?
No effect
The number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time (one second)
Frequency
Which letter represents the wavelength?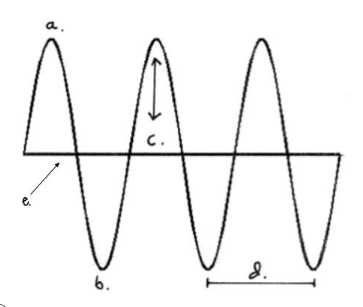
D
True or False: Light waves require a medium to travel through
False
When a material absorbs light, what happens to the material?
it changes
What do we call a sound that reflects?
Echo
Green light is reflected and all other colors are absorbed by the cucumber