As frequency increases, the energy of the wave...
increases.
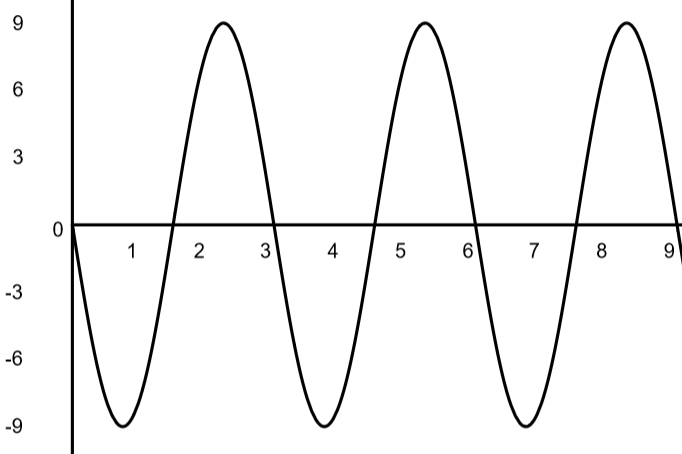 What is the amplitude of the wave?
What is the amplitude of the wave?
Amplitude = 9
Identify an energy example of a longitudinal wave
1. Sound waves
2. Ultrasound
3. Tsunami
Frequency of a wave is measured in?
Hz ( Hertz)
As amplitude decreases, the energy of the wave...
decreases.
What is the wavelength of the wave?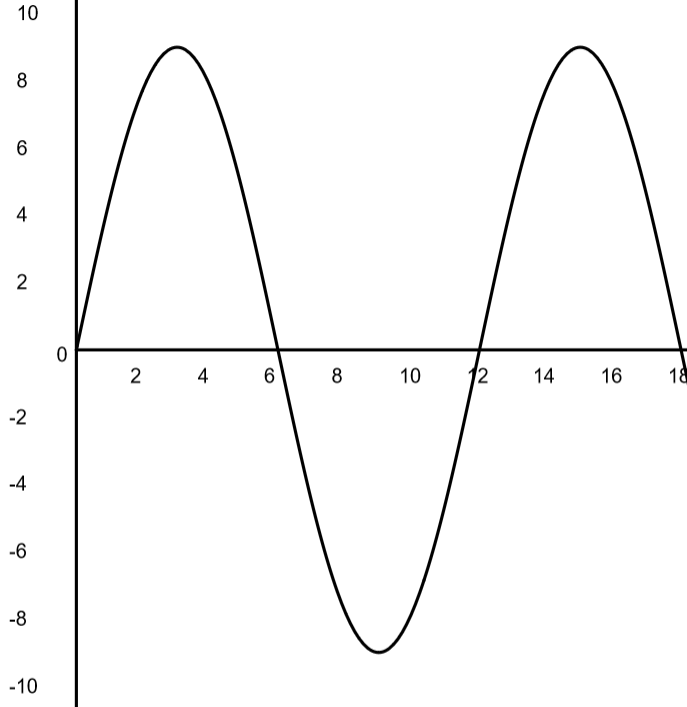
Wavelength = 12
State the direction that particles move in a longitudinal wave
parallel to the direction of travel
What part of a sound wave measures loudness?
Amplitude
If the energy of the wave increases, the amplitude....
What is the wavelength?

WL = 3
State the direction that particles move in a transverse wave
perpendicular to the direction of travel
A sound wave produced with an amplifier will have a _________ amplitude.
Higher
The distance between the identical point in two waves.
Wavelength
As amplitude decreases, the wavelength....
stays the same.
What is the amplitude of the wave?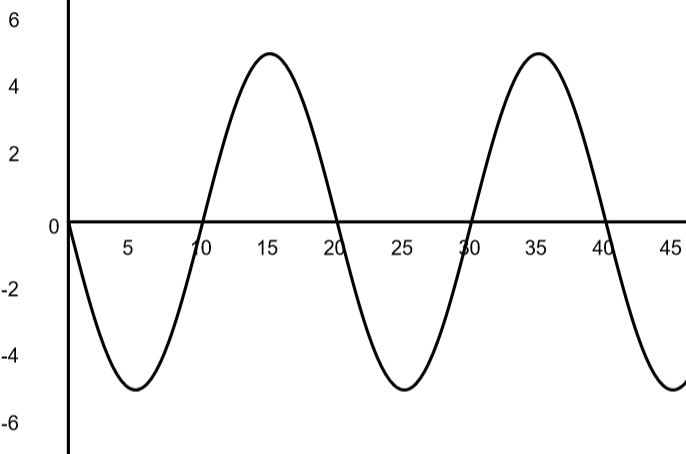
Amplitude = 5
The change in behaviour of light when moving through different densities is referred to as
the law of refraction
Sound waves more through a _________.
Medium
As the frequency increases, the wavelength.....
decreases.
What is the amplitude of the wave?

Amplitude = 9
The equation for calculating the frequency of a transverse wave is
𝑓 = 1/𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑
What is the difference between the wave height and the amplitude?
The wave height measures from crest to trough. The amplitude measures from the rest position to the crest OR the rest position to the trough