Difference between RA and OA.
What is:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic, inflammatory autoimmune disease distinguished by joint swelling, tenderness, and destruction of synovial joints leading to disability.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of age-related joint disease involving the synovial joints characterized by pathologic changes in cartilage, bone, synovium, ligament, muscle, and periarticular fat. These changes lead to joint dysfunction, pain, stiffness, functional limitation, and loss of activities.
Pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia (in general).
(What is it / what causes it?)
What is:
1). decreased platelet production
2). increased destruction
3). Both of the above.
Low Platelets- The condition may be either congenital or acquired and may be either primary or secondary to other acquired or congenital conditions.
Platelet count below 50,000 platelets/μL
Excess amounts of thyroid hormone are secreted from the thyroid gland in this disease.
What is hyperthyroidism ?
Primary hyperthyroidism results from thyroid gland dysfunction and is most commonly caused by Graves disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and solitary toxic adenoma.
Central (secondary) hyperthyroidism (less common) and is caused by TSH-secreting pituitary adenomas.
Facts about Osgood-Schlatter disease
What are:
Repeated stress/force of quadriceps pulling on patella, patellar tendon and tibial tubercle causing inflammation or partial separation of the tibial tubercle.
Tendinitis of the anterior patellar tendon
Osteochondrosis of the tubercle of the tibia
Prominent tibial tubercle that is tender to direct pressure
Weight loss, bruising and bone pain.
What are early signs of acute leukemias?
Facts about von Willebrand disease.
Mostly an autosomal dominant inherited condition with variable findings resulting from a deficiency or dysfunction in von Willebrand factor (a protein that binds factor VIII) and affects platelet function and part of the clotting process.
Endothelial cells contain intracellular structures that contain von Willebrand factor (vWF, clotting factor VIII), which is released during vascular injury and activates platelets for hemostasis. This deficiency impacts the intrinsic clotting pathway.
Premature accelerated destruction of erythrocytes, either episodically or continuously.
What is hemolytic anemia?
Clinical manifestations of Cushing disease.
What are:
Excess cortisol is stimulated by pituitary
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which also stimulates androgen production.
Weight gain is the most common feature and results from the accumulation of adipose tissue in the trunk,
facial, and cervical areas. These characteristic patterns of fat deposition have been described as truncal [central] obesity, moon face, and buffalo hump.
Transient weight gain from sodium & water retention may be present because of the mineralocorticoid effects of cortisol, exhibited when cortisol is present in high levels.
Glucocorticoids also increase catabolism of proteinaceous tissues such as collagen, causing skin atrophy fragility with striae and easy bruising and acne.
Common term for ligament tears.
What are sprains?
Ligaments connects ‘Like to Like’ (i.e. ropelike bundles of collagen fibrils that connect bone to bone)
Ligaments connects and STABILIZE - No force transmission
Facts about Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
What are:
Local symptoms caused by pressure & obstruction of lymph nodes are the result of the lymphadenopathy.
Malignant lymphoma that progresses from one group of lymph nodes to another and includes the development of systemic symptoms and the presence of multinucleated cells derived from B lymphocytes called Hodgkin & Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells.
One of the most common cancers diagnosed in young adults
Meaning of epigenetics.
What are chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences that alter the expression of genes, resulting in disease and phenotypic variations (upon genetics).
Ways to prevent sickle cell crisis.
PREVENTION OF CRISES
AVOID TRIGGERS: Fever, infection, acidosis, dehydration, constricting clothes, and exposure to cold
Routine childhood immunizations, annual influenza vaccine, pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines
The role of calcitonin in calcium regulation.
What is:
Calcitonin suppresses osteoclast activity (osteoclasts are cells that resorb bone & release the calcium from resorbed bone). The end result is the reduction in serum calcium concentration.
Inflammatory response to excessive quantities of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) and in other body fluids, including synovial fluid.
These elevated levels lead to the formation of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in and around joints and forms insoluble precipitates of MSU that are deposited in connective tissues throughout
the body called tophi.
The result of crystallization in synovial fluid is acute, painful inflammation of the joint called ____
What is Gout?
TNM cancer staging system abbreviation.
What is the tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) classification?
T - Extent of the primary tumor
N - Nodal involvement
M - Extent of metastasis
Condition associated with increased blood volume and viscosity.
What is Polycythemia Vera?
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic pathway activation
What are:
Intrinsic: (Inside vessels, longer pathway – ‘Left side of the house’) - Activated through exposed endothelial collagen / Contact activation
Extrinsic: (External damage, shorter pathway, ‘Right side of the house’) - Activated through TISSUE FACTOR (TF) released by endothelial cells after external damage (trauma/inflammation)
Difference between DM 1 and DM2
Type 2 DM - Progressive loss of b-cell mass & function causing a deficiency in insulin secretion & insulin resistance by insulin-sensitive tissues. Obesity is common & frequent contributing factor to precipitate type 2 diabetes among those susceptible.
Type 1 DM - Pancreatic beta cells are destroyed. No insulin secretion. Common theory: Autoimmune - genetic & environmental factors, resulting in gradual process of autoimmune destruction in genetically susceptible individuals. Autoantibodies to insulin & glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65).
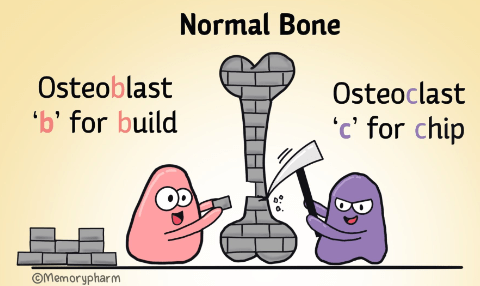
Type of bone cell that resorbs bone and has a major role in bone homeostasis
What is an osteoclast?
Common GI side Effects of BOTH chemo and radiation therapy.
What is:
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract: Rapidly proliferating cells of the GI tract are particularly sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy, leading to oral ulcers (stomatitis), malabsorption, and diarrhea, as well as increased risk for infection from the individual's own microbiome.
Anorexia nervosa complications.
What are:
Bradycardia, Dysrhythmia, Left ventricular atrophy, Sudden cardiac death (place on heart monitor!)
Lab abnormalitiees: hypokalemia -life threatening with cardiac rhythm problems (place on monitor!), hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia
Also, hair thinning, xerosis (dry skin), amenorrhea, constipation related to slowed peristalsis, liver function test abnormalities related to malnutrition; anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Osteoporosis
Platelet counts less than 10,000 platelets/μL can result in these skin manifestations.
What are petechiae, ecchymoses, and larger purpuric spots, or obvious frank bleeding from mucous membranes.
Severe spontaneous bleeding may result if the count is less than 10,000 platelets/μL and can be fatal if bleeding occurs in the GI tract, respiratory tract, or CNS. Protect patient from Trauma / Falls !
Pathophysiology of thyrotoxic crisis (thyroid storm).
Rare but life-threatening, acute complication of hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis).
TH levels rise dramatically and death can occur within 48 hours without treatment.
The condition may develop spontaneously, but usually occurs in individuals who have undiagnosed or partially treated Graves disease and who are subjected to physiologic stress, such as infection, pulmonary or cardiovascular disorders, trauma, seizures, surgery (especially thyroid surgery), obstetric complications, or dialysis.
Clinical signs and symptoms: hyperthermia; tachycardia (especially atrial tachydysrhythmias), heart failure; agitation or delirium; and nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea contributing to fluid volume depletion.
Specialized mesenchymal cells that synthesize bone matrix and coordinate the mineralization of the bones.
What are osteoblasts?
OsteoBlasts - Build Bone
Facts about chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
What are:
Chromosomal translocation called the Philadelphia chromosome aka BCR-ABL gene) - which involves chromosomes 9 and 22. The Philadelphia chromosome accelerates cell division and inhibits DNA repair. It is commonly present in 95% of patients with CML.
CML is a slowly progressing disease with increased numbers of maturing granulocytic precursors in the bone marrow, which usually includes elevated proportions of eosinophils and basophils.
The peripheral blood reveals a leukocytosis, often exceeding 100,000 cells/mm.
Associated factors with the development of obesity.
What is:
Obesity produces a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation.
Changes in the intestinal microbiome also are associated with and are a contributing cause of obesity.
Gene-environment interactions are associated with the development of obesity.
Insulin resistance develops.
A patient has hemophilia, which 'side of the house' or which clotting pathway is mostly affected?
What is the intrinsic pathway?
The majority of hemophilia disorders involve deficiencies of factors VIII, IX, or XI
Risk Factors for DM
What are the most well-recognized
risk factors: age, obesity, hypertension, physical inactivity, and family history?
Common term for a tear or injury to a tendon.
What is a strain?
Tendons - Fibrous connective tissue that:
Connects ‘Two types of Tissue’ (i.e. muscle to bone) and transmits forces from muscle to the skeletal system.
Facts about chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
What are:
CLL is the most common leukemia in the Western world.
CLL is a slow-growing cancer.
CLL has the highest incidence of familial association, with first-degree relatives having more than an eight-fold higher likelihood of developing the disease.
CLL has a low incidence among Asians/Pacific Islanders, particularly Japanese, and incidence does not increase when living in the U.S.
Exposure to pesticides, deltamethrin, and herbicides has been associated with the development of CLL.
CLL involves malignant transformation and accumulation of B lymphocytes
CLL rarely involves chromosomal translocations.
Binge eating criteria for bulimia.
What are:
Recurrent episodes of binge eating. An episode of binge eating is characterized by both of the following:
Eating, in a discrete period of time (e.g., within any 2-h period), an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat during a similar period of time and under similar circumstances.
A sense of lack of control overeating during the episode (e.g., a feeling that one cannot stop eating or control what or how much one is eating).
A patient has the following clinical manifestations: weakness, fatigue, paresthesia of feet and fingers, difficulty walking, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, weight loss, and a sore tongue that is smooth and beefy red (glossitis). Name this condition and cause.
What pernicious anemia (PA)?
PA is a type of megaloblastic anemia and is caused by vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency due to intestinal malabsorption.
Parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, vitamin D
What are hormones involved with calcium and phosphate balance?
Term for increased pressure (due to swelling swelling or bleeding) inside a muscle space (enclosed by fascia, a tough membrane) which compresses blood vessels and nerves.
What is compartment syndrome?
Early (within days to a few weeks) clinical manifestations of ACUTE leukemia (bone marrow depression in general).
What are:
Fatigue caused by anemia. Fever caused by infection.
Bleeding (skin, gums, mucous membranes, and GI tract) resulting from thrombocytopenia.
Visible signs: petechiae and ecchymosis, discoloration of the skin, gingival bleeding, hematuria, and midcycle or heavy menstrual bleeding.
Facts about Virchow triad.
3 factors that influence the risk of developing spontaneous thrombi:
1.Vessel Injury
2.Reduced blood flow
3.HyperCoagulability of the blood
Example: Risk factors for VTE include conditions and disorders that promote blood clotting because of venous stasis (immobilization, heart failure), injuries to the endothelial cells that line the vessels (trauma, infection, caustic IV infusions), and hypercoagulability (inherited coagulation disorders, malignancy, hormone replacement therapy, pregnancy, oral contraceptives).
Facts about Rhabdomyolysis.
What are:
Rhabdomyolysis is the rapid breakdown of muscle that causes the release of intracellular contents,
including protein pigment myoglobin, into the extracellular space and bloodstream.
Myoglobinuria (presence of the muscle protein myoglobin in the urine) from crush injuries or in individuals found unresponsive and immobile for a long time.
A classic triad of muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine is considered typical of rhabdo.
After a patient has a thyroidectomy, you notice they start having sudden muscle spasms / twitching, what does this signify?
What is hypocalcemia?
Removal of the parathyroid glands (e.g., during total thyroidectomy) with the resulting loss of PTH causes hypocalcemia.
After a total thyroidectomy, a positive Chvostek's sign (twitching of the facial muscles when tapping the facial nerve) can indicate hypocalcemia (low blood calcium) due to hypoparathyroidism (damage to or removal of the parathyroid glands), which are responsible for calcium regulation.
What is the pathophysiology of osteoporosis?
There is Increased bone resorption from enhanced development of osteoclasts and decreased osteoclast apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Cortical bone becomes more porous and thinner, making bone weaker and prone to fractures due to dysregulation of OPG and RANKL.
Osteoprotegerin (OPG) - secreted by osteoblasts and also B lymphocytes & promotes bone formation & reduces bone loss.
RANKL - Activates osteoclasts (with hyperparathyroidism and /or declining estrogen levels (menopause).
= bone resorption → osteoporosis
Facts about multiple myeloma (MM).
What are:
MM is a proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow that arise from one clone of B cells that usually produce large amounts of immunoglobulin (IgG).
Increased osteoclasts are stimulated to reabsorb bone resulting in bone lesions (that appear as punched-out lesions on X-ray), hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood), renal failure, anemia, and immune abnormalities.
As the number of myeloma cells increases, fewer red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are produced.
It is slightly more common in men than in women.
Risk factors include overweight or obesity, Agent Orange, and in some irradiated populations including Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
------------------
Clinical manifestations (CRABBI)
•HyperCalcemia – From osteoclast (bone breakdown) - Watch confusion, drowsiness, weakness, loss of appetite, kidney stone formation, fall risk
•Renal failure – Bence jones proteins deposition in renal tubules
•Anemia
•Bone pain
•Bone / Lytic lesions (round, “punched out” regions of bone)
•Numbness – Spinal degeneration from lytic lesions impacting nerves
•Bleeding - Thrombocytopenia
•Infections – Leukopenia, loss of the humoral immune response
Specific environmental or nongenetic factors associated with epigenetic modifications.
What are diet, lifestyle and exposure to certain chemicals?
Name at least 2 types of Normocytic-Normochromic (normal size, normal color) anemias.
What are:
–Hemolytic
–Hemorrhagic (from trauma or surgery)
–Anemia of chronic disease
–Sickle cell (different shape)
Facts about Addison disease.
What is: Adrenocortical hypofunction?
Primary adrenal insufficiency (hypocortisolism and hypoaldosteronism) = Inadequate production of cortisol and aldosterone.
Characterized by inadequate corticosteroid and mineralocorticoid synthesis and elevated serum ACTH levels (loss of negative feedback).
Common cause (in US) is autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortex.
Occurs most often in adults 30 to 60 years of age, more common in women.
Collapse of bone caused by metastatic cancer or osteoporosis.
What is a pathologic fracture?
Facts about acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia (ALL).
What are:
The most common malignancy in children.
ALL is a progressive neoplasm defined by the presence of greater than 30% lymphoblasts in the bone marrow or blood.
ALL is an aggressive, fast-growing leukemia with too many lymphoblasts (immature lymphocyte with altered morphology) or lymphocytes in the bone marrow and peripheral blood.
ALL involves immature B (pre-B) or T (pre-T) cells called lymphoblasts. As leukemia develops, the bone marrow becomes dense with lymphoblasts that replace the normal marrow and disrupt normal function
Liver, spleen, and lymph node enlargement occurs more commonly in ALL than in AML.
Increased risk for ALL has been linked to exposure to x-rays before birth, being exposed to ionizing radiation (postnatally), past treatment with chemotherapy, certain chemical exposures (e.g., benzene, glues, detergents, art supplies, paint strippers), certain viral infections, age (children and adults over age 50), race/ethnicity (more common in whites), gender (more common in males), and certain genetic conditions.
The study of abnormal changes in body functions that are the causes, consequences, or concomitants of disease processes.
What is Pathophysiology ? !
Facts about Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
What are:
Widespread activation of coagulation resulting in formation of fibrin clots in medium and small vessels (microvasculature) throughout the body.
Hemorrhage and clotting occur simultaneously. Clotting may lead to blockage of blood flow to organs, resulting in multiple organ failure.
The magnitude of clotting may result in consumption of platelets & clotting factors leading to severe bleeding.
Decreased TH levels with decreased heart rate, low basal metabolic rate, constipation, cold intolerance, lethargy, and slightly lowered basal body temperature.
What is hypothyroidism?
What is the pathophysiology of a greenstick fracture?
A greenstick fracture is an incomplete fracture that tends to occur in more flexible, growing bones of children. This fx perforates one cortex and splinters the spongy bone. The name is derived from the damage sustained by a young tree branch (a green stick) when it is bent sharply. The outer surface is disrupted, but the inner surface remains intact. Greenstick fractures typically occur in the metaphysis or diaphysis of the tibia, radius, and ulna.
Facts about acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
What are:
AML is one of the most common leukemias in adults.
AML is a malignancy of the stem cell precursors of the myeloid lineage - red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells (except B and T cells).
Can spread quickly into the blood, and other organ systems.
Peripheral blood smear shows: Auer Rods (abnormal fusion of granules that are red/pink and needle or rod-shaped)
Risk factors
•Exposure to radiation, benzene, and chemotherapy
•Hereditary conditions
Pathophysiological effects of alcohol consumption
What is:
Classified as a human carcinogen.
Linked to cancers of mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, liver, colorectum.
Increased risk of pharynx cancer when used in combination with tobacco smoking.
No “safe limit” of intake or drink type - Acetaldehyde is most toxic metabolite & chief cause of carcinogenesis.
Folate deficiencies cause epigenetic changes in DNA methylation that promote tumor cell proliferation
Known to increase circulating unbound hormones & obesity.
Nutritional deficiencies reduce cancer-protective elements (i.e. retinol, retinyl esters, folic acid & other vitamins).
Clinical manifestations of iron deficiency anemia.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) begin gradually. Early: symptoms are nonspecific - fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath; pale earlobes, palms, & conjunctiva.
Later, structural and functional changes occur in epithelial tissue. The fingernails become brittle, thin, coarsely ridged, and spoon-shaped or concave (koilonychia) as a result of impaired capillary circulation. IDA also is associated with unexplained burning mouth syndrome and painful ulcerations of the buccal mucosa, Tongue papillae atrophy and causes soreness along with redness and burning (glossitis).
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is the most common type of nutritional disorder worldwide. IDA is common in USA, particularly in toddlers, adolescent girls, & women of childbearing age.
Name at least 3 clinical manifestations of DM and patho cause.
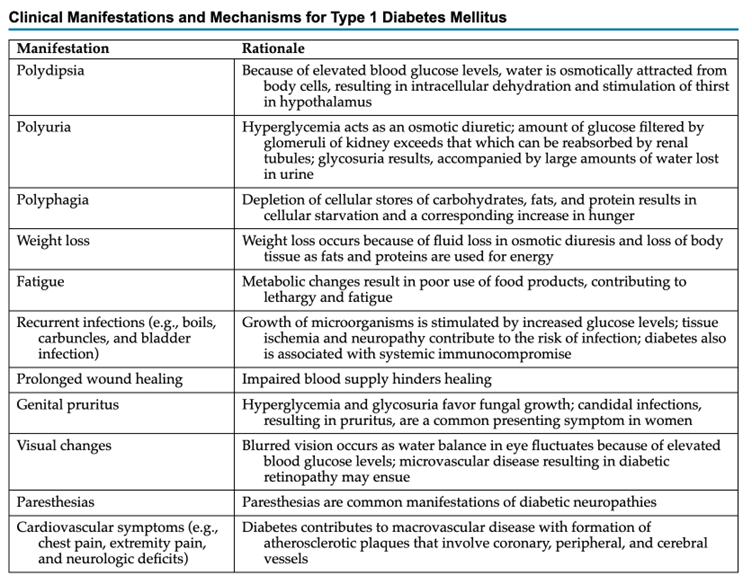
Name (at least 5) signs of compartment syndrome.
What are:
1). Pain (earliest sign)
~Out of proportion to injury
~Deep and constant
~Poorly localized
~ Pain with passive stretch (most sensitive finding before ischemia sets in)
~Not relieved with pain meds
2. Poikilothermia - limb that feels cooler than surrounding areas
3. Pressure (tight or full feeling)
4. Pulselessness (late sign)
5. Pallor (Not always pale. Affected area may be shiny, late sign)
6. Paresthesia (tingling, numbness, prickling - late, ominous sign)
7. Paralysis (very late, ominous sign – may be permanent)
Recent research has addressed low-intensity & radiofrequency radiation from devices i.e. cell phones, broadcast antennas, Wi-Fi, security monitors, baby monitors, wireless charging stations, routers, antennas, laptops, etc.
Name some recommendations to reduce exposure that can damage DNA, induce cancer, and impair reproductive health and may cause tumors (particularly in children).
Use text messaging when possible and use speaker or hands-free.
Hold phone an inch or more away from the head.
Make only short or essential calls on cell phones.
Avoid carrying your phone against the body, such as in a pocket, sock, or bra.
If watch a movie on phone, download it first, then switch to airplane mode while watching it to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure.
Monitor signal strength (i.e., how many bars); the weaker your cell signal, the harder the phone has to work and the more radiation it gives off; it is better to wait until there is a stronger signal before using the device.
Avoid making calls in cars, elevators, trains, and buses; the cell phone works harder to get a signal through metal, so the power level increases.