When rocks break apart but don’t change in any other way...
Physical Weathering
Weathering of limestone by acid rain is an example of ____________________.

Chemical Weathering

These rocks were worn by
a. water
b. waves
c. wind

C. Wind

What property would a farmer use to identify earth materials?
a. size
b. color
c. weight
b. size
Which layer of the soil profile would be affected the most by weathering and erosion?
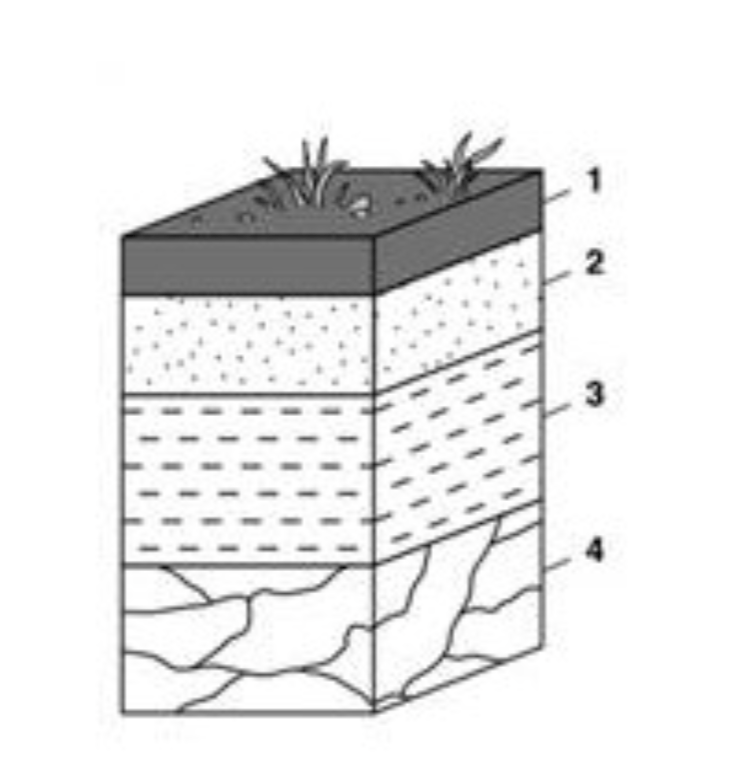
1 the top level exposed at the earths surface!

Ice expansion is an example of ___________________ weathering

Physical Weathering

In order wind to effect rocks it needs to pick up what to break down the soft rock?
a. sand
b. sticks
c. metal
a. sand
Is it more important for plants in have:
a. soil that has great weight
b. soil that has a great age
c. soil that has lots of humus
c. soil that has lots of humus
Settling of soil that often occurs when water flow slows down or stops, and heavy particles can no longer be supported by the river turbulence. What particles would you likely find at the bottom of the river?
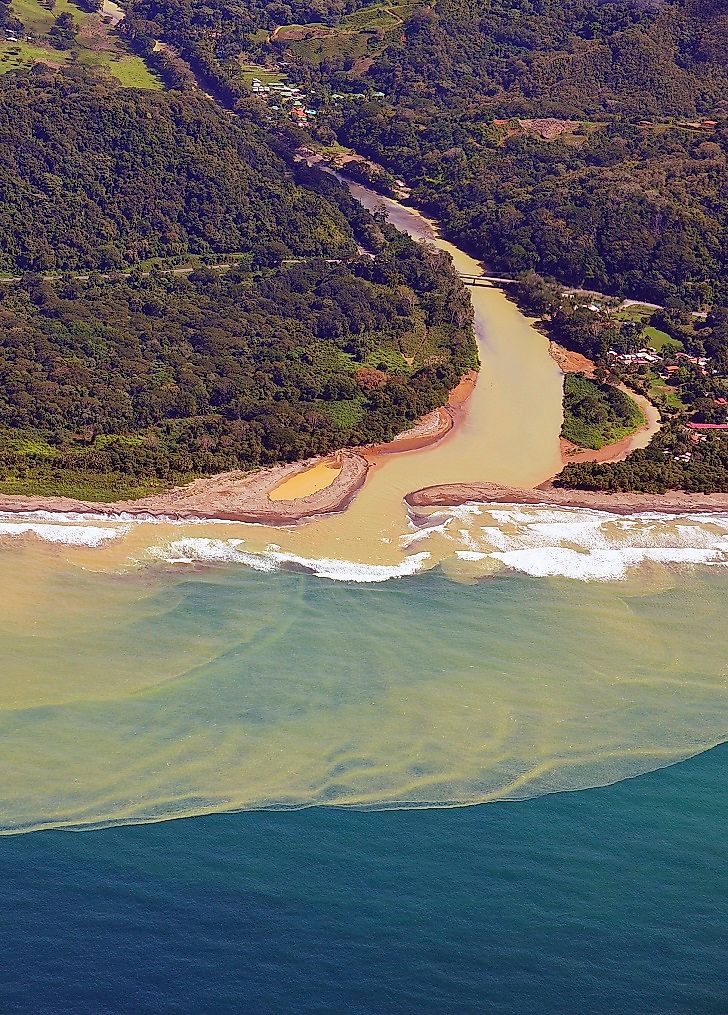

Small rock particles like clay or silt.
When water freezes it___

Expands/gets bigger

What NATURAL processes cause acid rain?
a. landslides
b. volcano eruptions
c. tornados
b. volcano eruptions
Use the picture below, when soil settles the particles go from _____ to ______.

Use the picture below, when soil settles the particles go from SMALLEST to LARGEST.

The process of breaking down rocks is called ______

Weathering

Chemicals from the environment can change rocks into new minerals or other materials.This prcess is called____

Chemical weathering.

What HUMAN processes cause acid rain?
a. car exhausts
b. factories
c. air pollution
d. all of the above
d. all of the above

Decayed plants and animals in the soil are called:

Humus is decaying plants and animals.

Which of the following aids in the weathering and erosion of rocks?
A. rain
B. water
C. wind
D. all are correct

D. all are correct
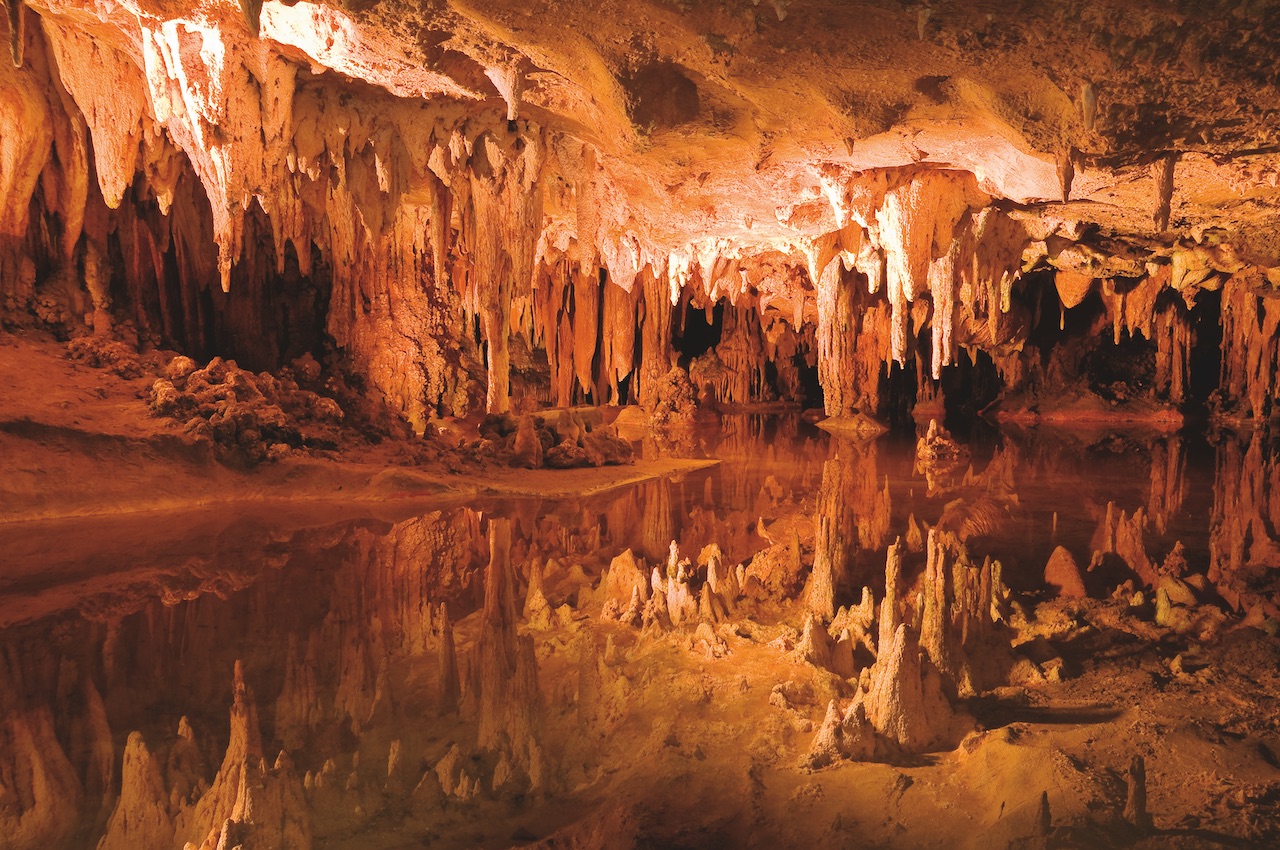
Chemical weathering changes the _____ in rocks

Chemical weathering changes the MINERALS in rocks.

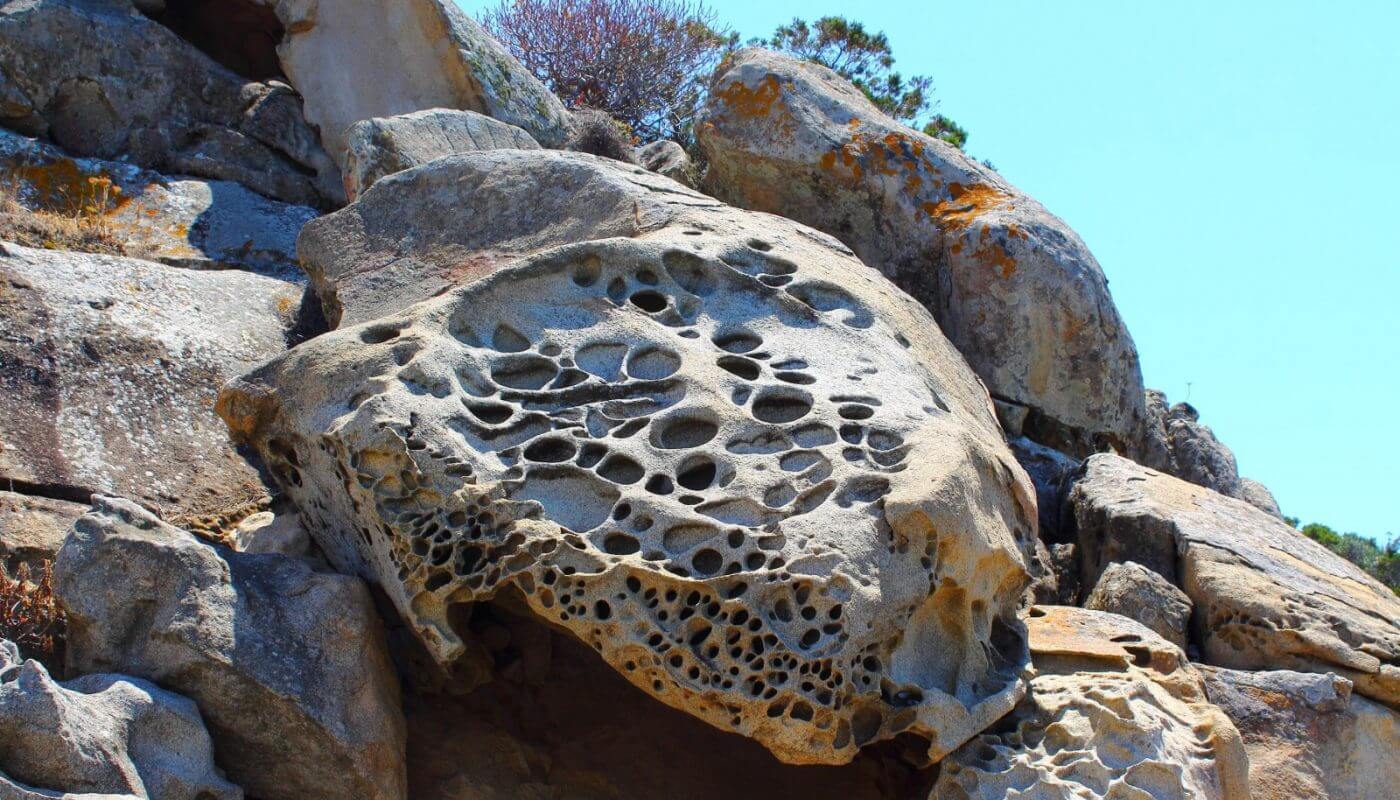
What caused these rocks to weather?
a. physical weathering
b. chemical weathering

b. chemcial weathering

Which environment would have soil with lots of humus?
a. mountains
b. forest
c. dessert
b. forest
________is the scrapping of rocks against each other to break down or round.
Abrasion
Which type of weathering is illustrated:

Physical
What rocks react most to acid rain?
a. basalt
b. sandstone
c. limestone
c. limestone

Healthy of soil relates to:
A. how the soil was formed over time
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth
C. the amount of water found in the soil
D. the amount of bacterias found in the soil
B. the amount of nutrients that allow plants to growth