Define Weathering
The weakening and breaking down of material in place.
Define Mass Wasting
The movement of material downslope under the force of gravity.
Define Erosion
The more distant removal of material by wind, water, and ice.
What is a floodplain?
an area of low-lying ground adjacent to a river, formed mainly of river sediments and subject to flooding
What are the two types of Weathering
Mechanical and Chemical weathering
What are at least three examples of effective mass wasting SOLUTIONS
Retaining walls, back fill w/gravel, drainage pipes, rip rap, gabion, cover crops, dams, etc.
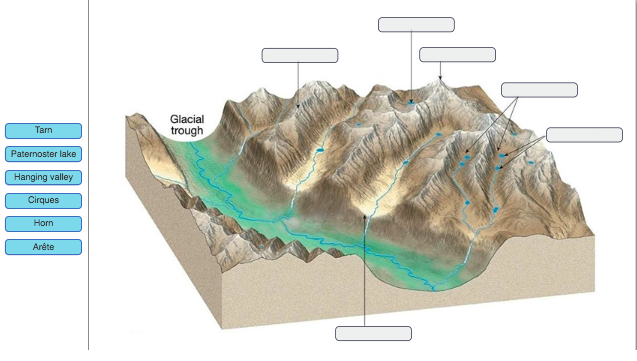
What are the two types of glaciers?
Alpine, Continental
Chemical weathering changes WHAT?
Mechanical weathering changes WHAT?
Chemical weathering changes COMPOSITION
Mechanical weathering changes SIZE
What are the five types of Mass wasting
Creep, flow, slump, slide, fall
What are the three types of erosion transportation we've covered?
River transportation, coastal transportation, wind transportation
What is a meander?
A series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse
What are the three types of chemical weathering?
Oxidation, hydrolysis, carbonation
Define slope stability.
What is the difference between driving and resisting forces?
Slope stability: Slope stability refers to the condition of inclined soil or rock slopes to withstand or undergo movement
Driving forces: positive forces to change
Resisting forces: opposing forces to change
Explain how longshore drift works.
Prevailing winds push waves onto shore. The water picks up sediments and moves them diagonally down the shore. Larger sediments are deposited at the top of the shore, smaller sediments are moved around much more. Opposing winds can wash away smaller sediments or reverse the flow of the waves.
Correctly differentiate between:
dissolved load, suspended load, bedload.
Dissolved load: the portion of a stream's total sediment load that is carried in solution
Suspended load:the amount of sediment carried downstream within the water column by the water flow
Bedload: the material carried by a river by being bounced or rolled along its bed.
Abrasion, Ice wedging, biological, exfoliating, thermal expansion/ contraction
How are the five types of mass wasting defined?
Creep, Flow, Slump, Slide, Fall
Creep: Very slow flow, which is usually only visible by the damage it causes to trees, fences, retaining walls, roads, etc.
Flow: Downslope movement of unconsolidated material in which particles move about and mix within the mass.
Slump: Slides along a curved slip plane, producing slump blocks and tongue.
Slide: The downslope movement of a coherent block of material.
Fall: The free fall of earth material.
What are the types of water erosion? List or describe them.
(Six types)
splash, sheet, rill, gully, channelized, costal