The three layers of embryonic development
Mesoderm, Ectoderm, Endoderm
Animals that walk one all their toe bones vs an animal that walks on only the most distal toe bone.
Digitigrade and Unguligrade
Two types of ossification.
Intramembranous ossification (flat bones)
Endochondral ossification (long bones)
"A"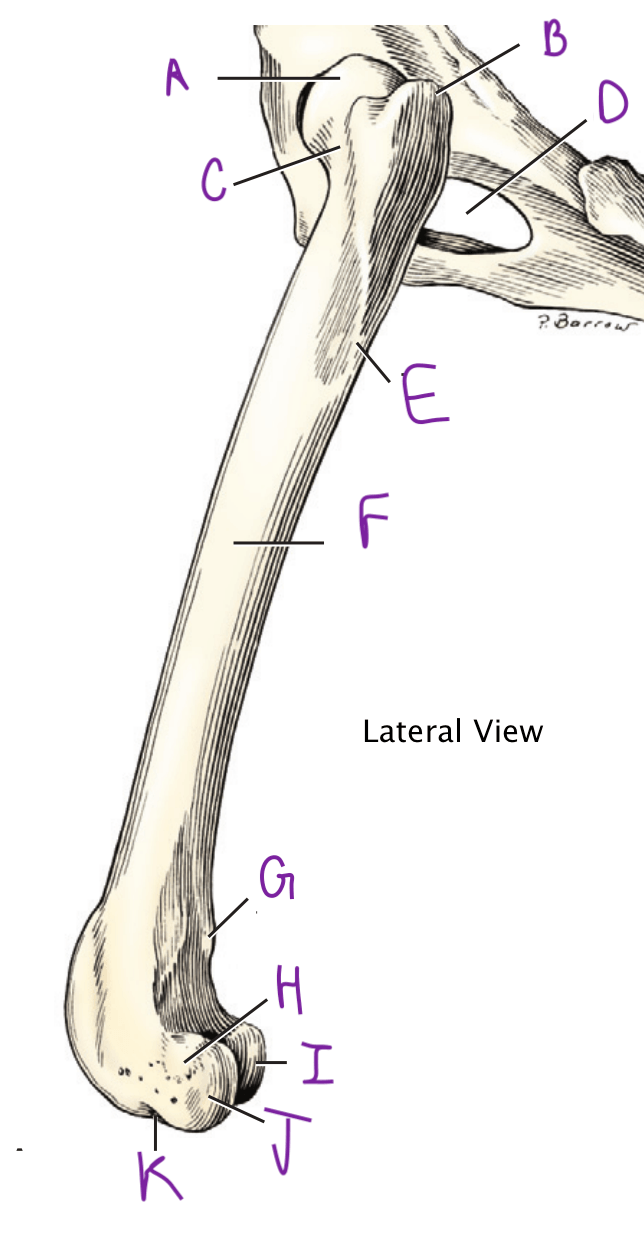
Greater trochanter
The spinal segments of the pelvic intumescence.
L4 to S3
1) Carpal/Trasal pad
2) Metacarpal/trasal pad
3) Digital pads
The embryological cell layer making up the neural tube.
Ectoderm.
Evolution left horses with only one primary metatarsal(carpal) and digit bones. (Hint: it's a number)
Third/Three
Joint classification based on function. (3)
1) Diarthroses (aka synovial) - freely moveable
2) Synarthrosis - immoveable
3) Amphiarthroses - slightly moveable
"-arthroses" = greek, Joint
"di-" = greek, through
"syn-" = greek, together
"amphi-" = greek, both sides
The purple promience.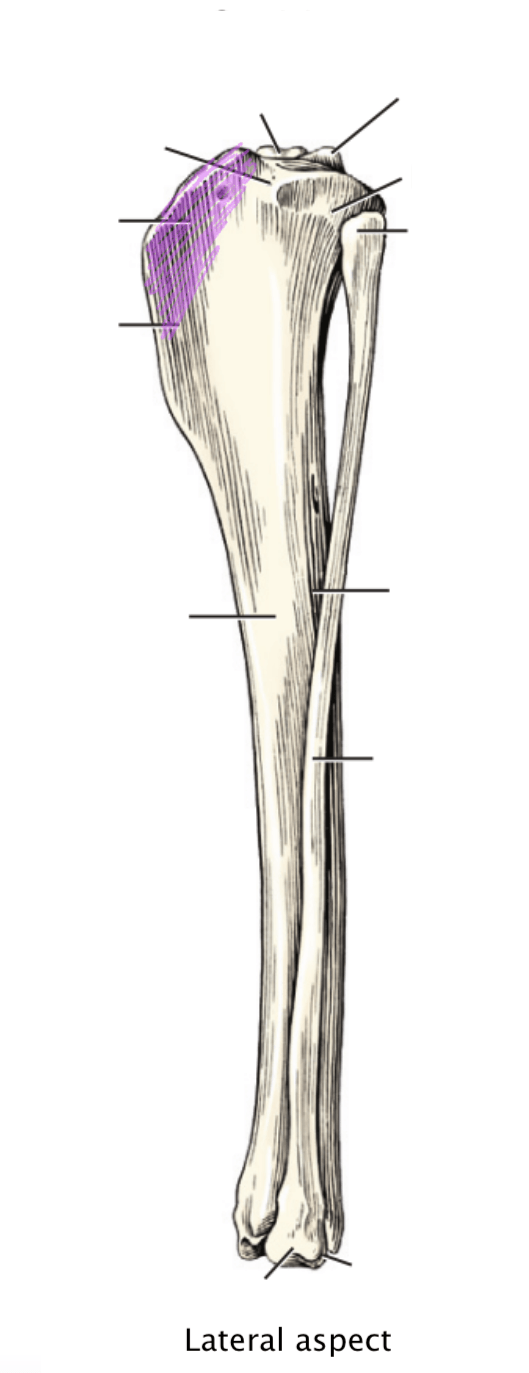
"B"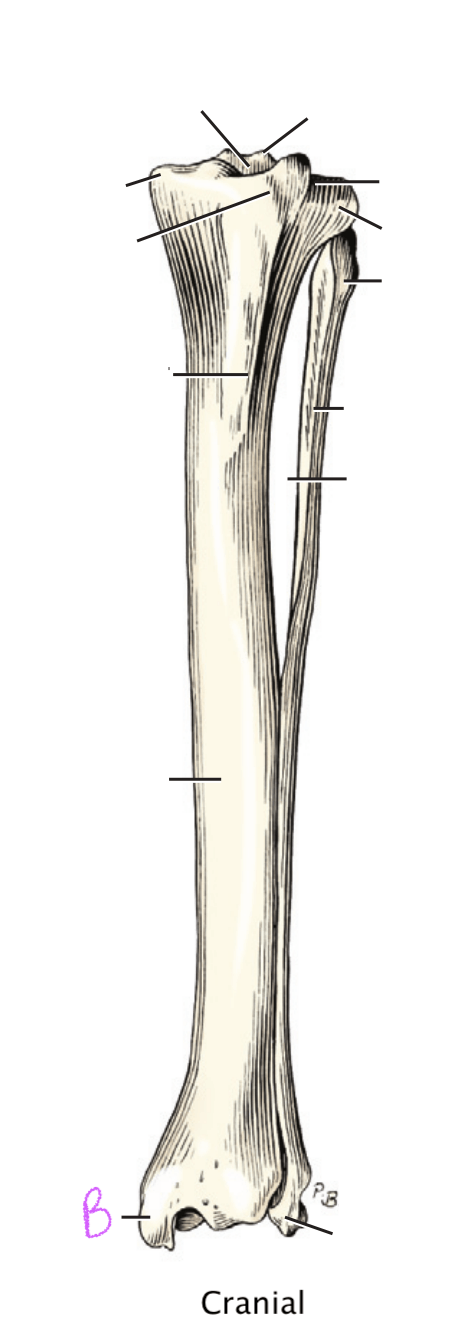
Purple: Tibial tuberosity
B: Medial malleolus
The nerve that runs on the dorsal aspect of the equine hindlimb along the cannon bone (M3).
Dorsal metatarsal n. (medial/lateral)
Two types of glands found in the skin.
Sweat glands
Sebaceous glands
The neural groove deepens as the neural folds grow up and towards each other. At the apex of each fold is a differentiating group of cells.
Neural crest (cells)
Name the red and blue colored parts.
Red = Peroneus tertius m. (Fibularis tertius m.)
Blue = Superficial digital flexor m.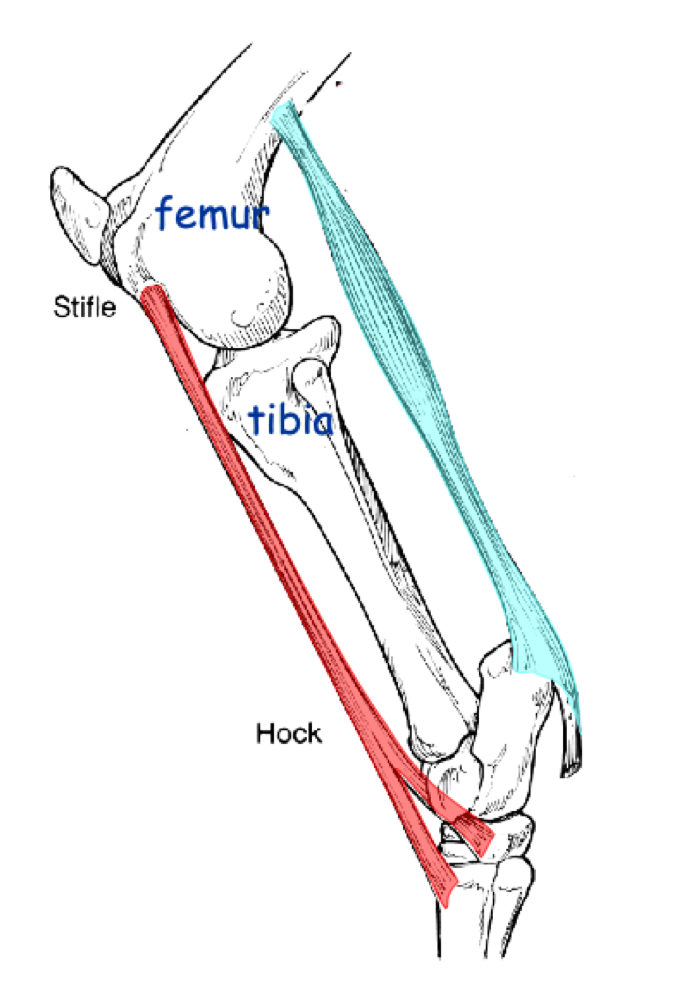
Ligament(s) within the joint space that assists with control of the joint movement.
Intracapsular ligaments
Three pelvic limb palpable landmarks proximal to the shaft of the femur.
1) Crest of the ilium
2) Greater trochanter
3) Ischial tuberosity
Iliopsaoas m. and Sartorius m. are innervated by this nerve.
*also innervates the Quadriceps mm.
Gland located along the medial pelvic fold, most commonly found in sheep and rabbits.
Inguinal glands.
Three functions of the mammalian yolk sac.
1) Nutrient and gas transfer prior to complete placental development
2) where blood elements are formed prior to live development
3) generation of primordial germ cells for future fetal gonads
Function of the reciprocal apparatus.
Prevents collapse of the hindlimb while supporting the weight of the animal via a locking mechanism; also guarantees that when the stifle is in extension the hock will also be in extension.
A fibrocartilage or dense fibrous tissue that increases congruency between articular cartilages. Also helps absorb concussion loads.
Articular discs and/or menisci
Three aspects of the femur where the patella sits.
1) Medial trochlea ridge
2) Trochlea
3) Lateral trochlea ridge
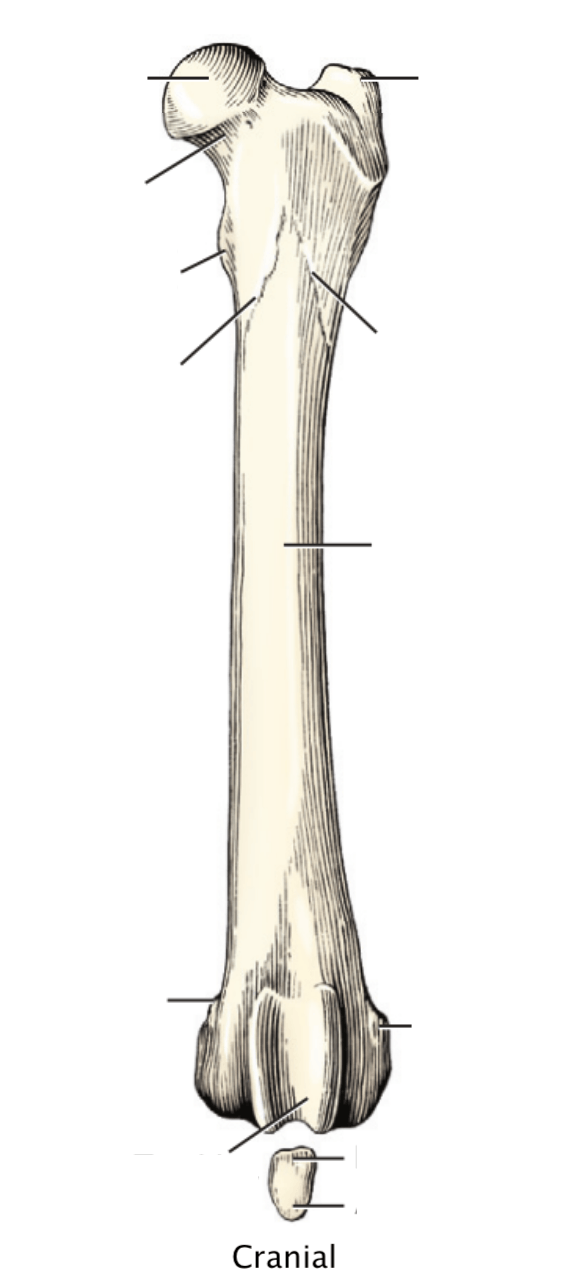
The Sciatic n. innervates these muscles.
Biceps femoris m.
Semimembranosus m.
Semitendinosus m.
Connective tissue that is primarily collagen with some elastic fibers, and a similar connective tissue that is continuous with the periosteum.
Superficial fascia
Deep fascia
The column of paraxial mesoderm divides itself into small, paired blocks along the cranial-caudal axis. These small aggregates are visible on the dorsum of the embyo and are made of a specific embryological cell layer.
Somites and mesoderm
1) suspensory ligament
2) proximal sesamoid bones
3) distal sesamoidean ligaments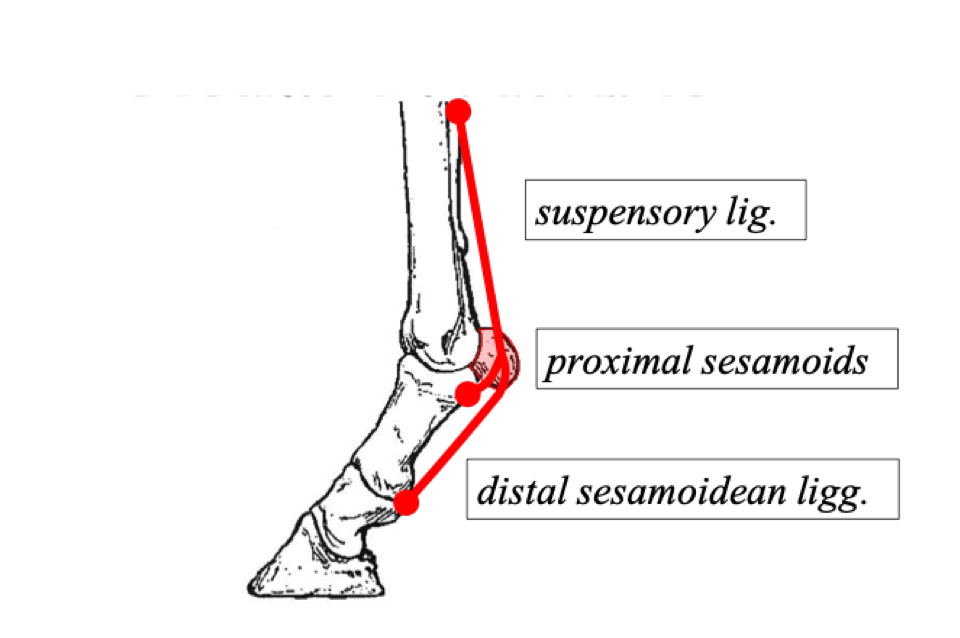
Thickened facia that anchors and/or stabilizes tendons, but still allows them to move.
Retinaculum
The origin and insertion of the gastrocnemius m.
Origin: Lateral and Medial supracondylar tuberosities (femur)
Insertion: Calcaneal tuber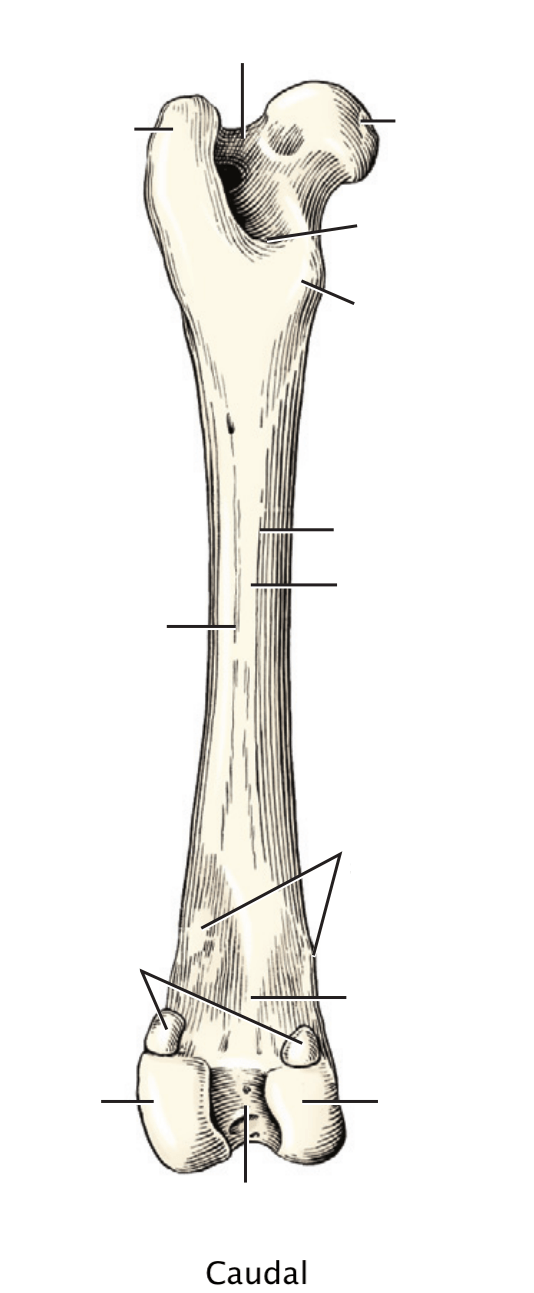
The Cranial gluteal n. spans these spinal segments and innervates at least one muscle.
L6-S1
Middle gluteal m.
Deep gluteal m.
Tensor fascia lata m.
The layers of epidermis.
Stratum basal
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum corneum
The development of the extra-embryonic coelom divides the mesoderm into two separate layers: the Somatic Mesoderm and the Splanchnic Mesoderm, each of these two layers join with another tissue/layer creating...
(Troph)Ectoderm + Mesoderm = Somatopleure
Endoderm + Mesoderm = Splanchnopleure
The proximal anatomical parts that allow a horse to lock it's stifle in extension. (3)
Proximad draw of the patella so that the parapatellar cartilage and medial patellar tendon can be hooked over the femur's medial trochlear ridge.
Synarthroses joints, aka Fibrous joints + cartilaginous joints. (6)
Fibrous Joints:
1) syndesmosis: united by white fibrous or elastic connective tissue (metacarpal bones, costal cartilage)
2) sutures: narrow fibrous uniting of bone, skull plates
3) gomphosis: collagen fibers to bone, periodontal ligaments
4) synostosis: fusion of bone, sacrum*
Cartilaginous joints
4) synchondrosis: hyaline cartilage joint, epiphyseal junction
5) symphysis: fibrocartilage joint, pubic and mandibular symphysis
Name A through G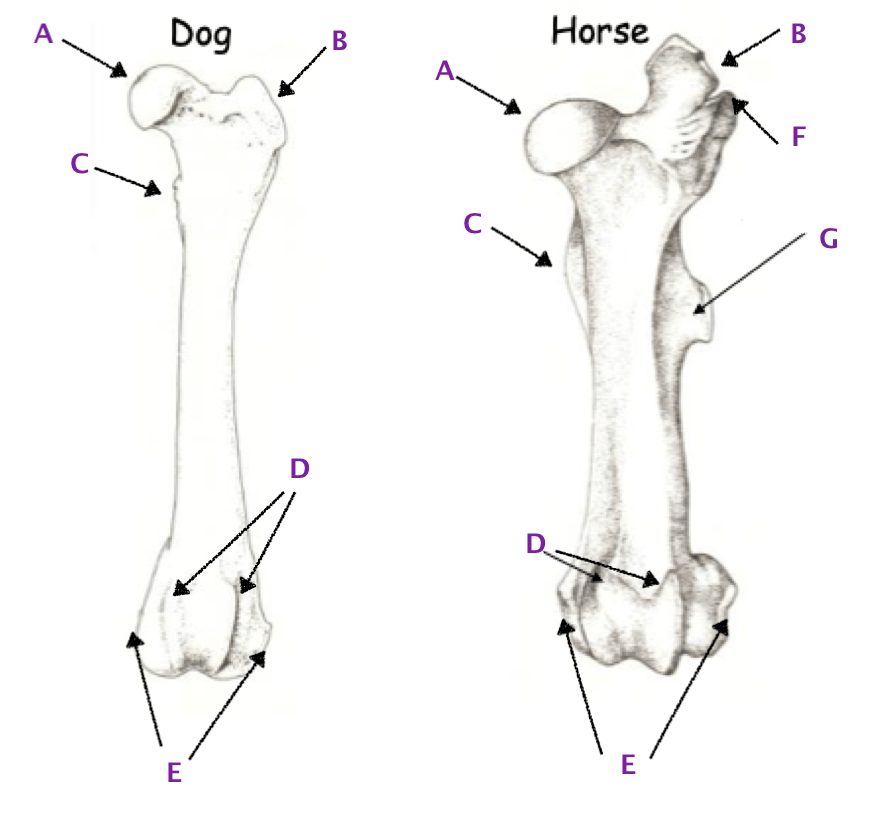
A: Head of the Femur
B: Greater trochanter
C: Lesser trochanter
D: Medial and Lateral trochlear ridges
E: Medial and Lateral epicondyles
F: Greater trochanter notch
G: 3rd trochanter
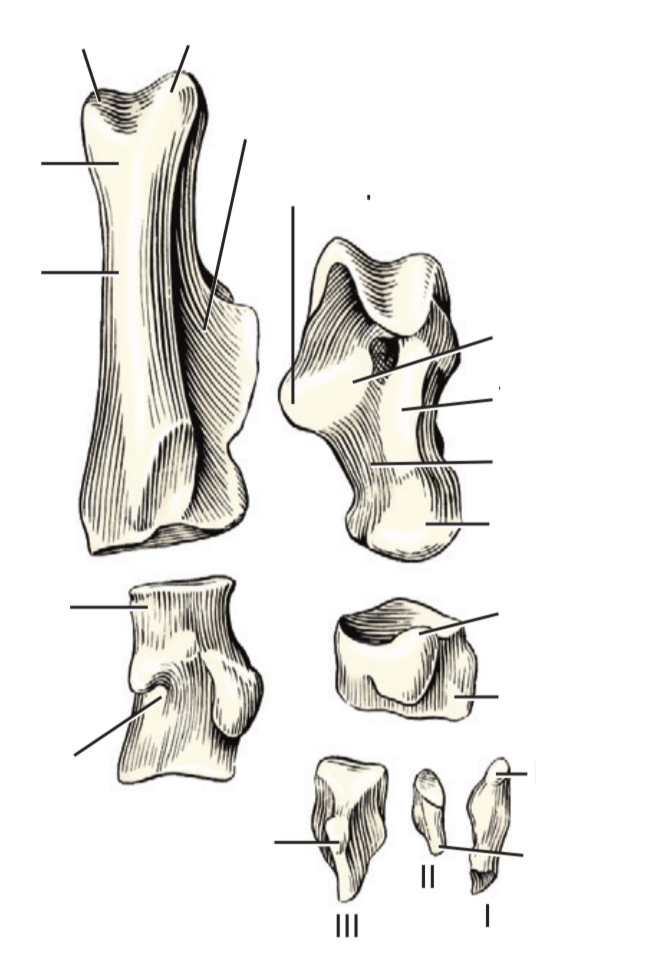
Name: A, B, C, D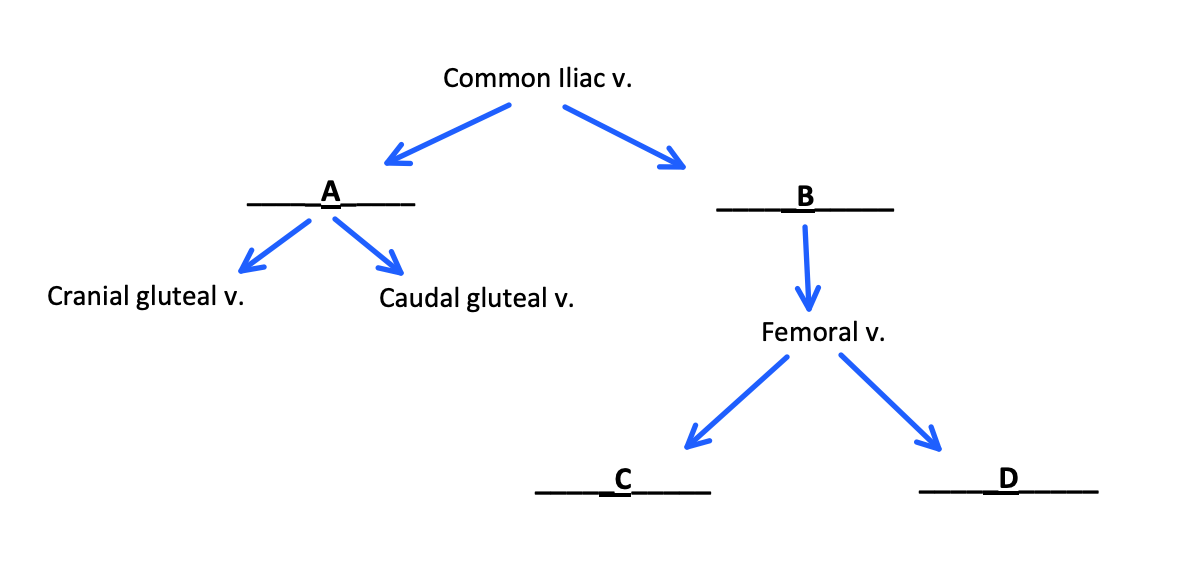
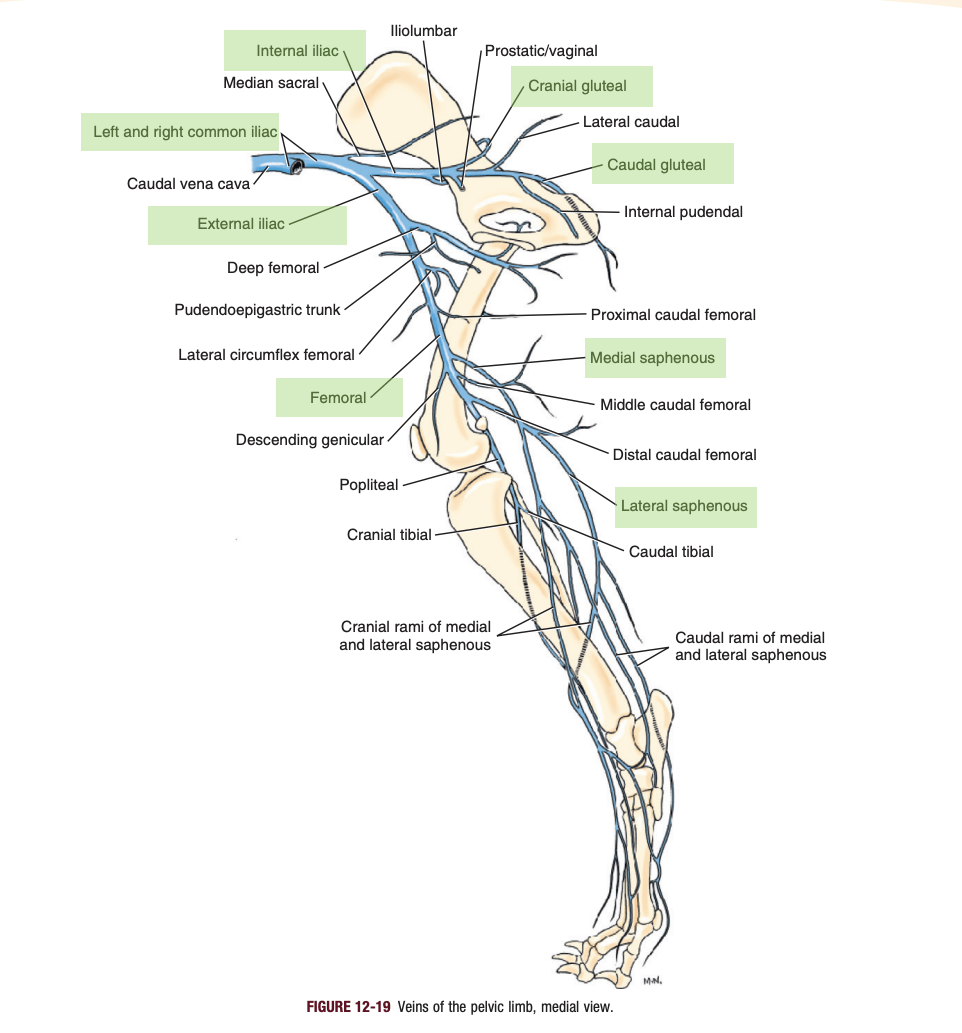
The two interdigitating, connective parts of a hoof wall and the dermis/periosteum.
Epidermal lamellae (insensitive)
Dermal lamellae (sensitive)