Pink eye
What is conjunctivitis?
This condition presents as white plaques on the bucal mucosa, palate, tongue or oropharynx and easily scrapes off most commonly affects infants, older adults with dentures and immunocompromised individuals.
What is Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)?
What is topical antibiotic ointment (Erythromycin ointment)?
This presents as an opacification of the lens that can lead to decreased vision and blindness.
What is a cataract?
This painful ulceration in the mouth can be triggered by stress?
What is an aphthous ulcer?
Infection of the lacrimal sac (tear sac) due to blockage in the nasolacrimal duct.
What is Dacryocystitis?
What is Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)?
Misalignment of the eyes
What is strabismus?

This type of diabetic retinopathy is characteristic of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, hard exudate, soft exudates, macular ischemia and macula edema.
What is Non-Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy.

A perception of abnormal ear or head noise.
What is tinnitus?
This wedge shaped growth start on the conjunctiva and may encroach onto the cornea.
What is Pterygium?
Presents as fever, sore throat, white patches on tonsils and cervical lymphadenopathy.
What is Pharyngitis?
This presents as unilateral supero-lateral orbital pain, redness, swelling with drooping eyelids.
What is Dacryoadenitis?
Inflammation of the lacrimal gland (tear gland)
In what stage of this condition that can cause central vision loss do you see neovascular degeneration, choroidal neovascularization hemorrhages, fibrosis.
What is Advanced/Late - Wet macular degeneration?
This clinical presentation is unilateral induration and erythema that extends from the cheek to the angle of the jaw and can cause dry mouth and decrease saliva.
 What is parotitis?
What is parotitis?
This condition is characteristic of optic disc swelling secondary to increased pressure in or around the brain?
What is papilledema?
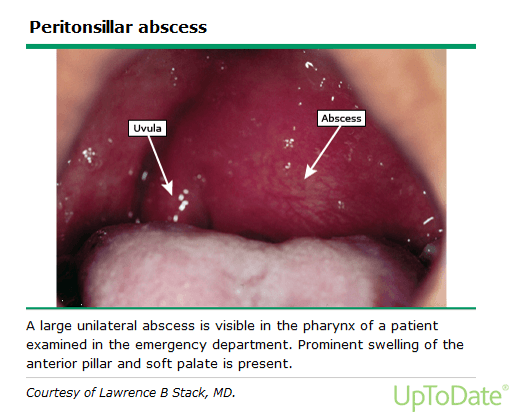
A complication of acute tonsillitis with extension into the peritonsillar space can cause what clinical presentation?
What are: muffled voice, drooling, uvula deviation, trismus, soft palate fullness.
This traumatic condition is characterized by bleeding into the anterior chamber caused by a ruptured iris root vessel.
What is a hyphema?

Fever, malaise, pain with extraocular movements, vision changes, proptosis (eyeball pushed forward)
This is a complication of an auricular hematoma (subperichondrial hematoma).
Involuntary eye movements
What is nystagmus?
Leuokplakia is white patches on the oral mucosa that can not be scraped out and are benign but can develop into what?
What is squamous cell carcinoma?
What is the optic chiasm?

What diagnostic study would you order if you suspected a orbital blowout fracture?
What is a CT scan of the face/orbital bones?
Symptoms present as low frequency sensorineural hearing loss, low blowing sound and sensation of unilateral aural pressure.
What is a transient loss of vision in one or both eyes?
What is Amaurosis Fugax?
This condition presents as a toothache, mouth or gum pain and could be secondary to poor hygiene.
What is a dental abscess?
Symptoms include throbbing headache, fatigue, visual disturbances and pain in the jaw muscles during chewing.
What is giant cell arteritis (temporal arteritis)?
Treatment - Corticosteroids
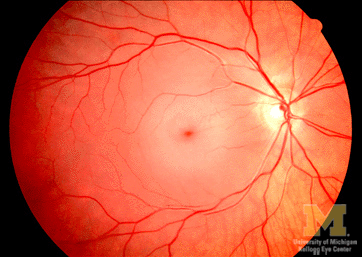
Fundoscopy shows a pale fundus with a cherry-red spot.
What is central retinal artery occlusion?
This abnormal growth of skin is located in the middle ear behind the ear drum and is caused by poor Eustachian tube function and recurrent ear infections.
What is a cholesteatoma?