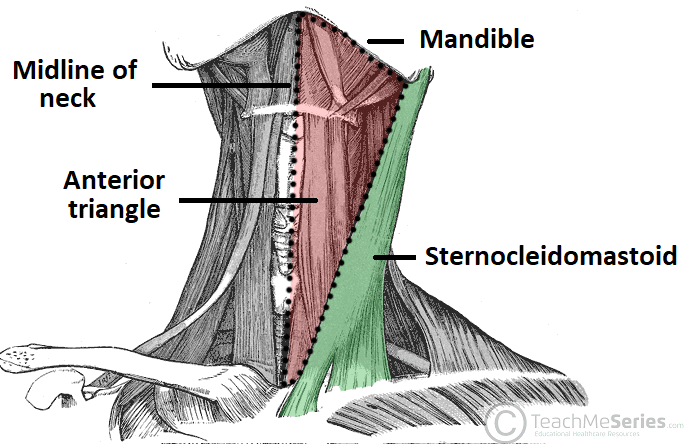
The boundaries of the anterior triangle are..?
Mandible, SCM, midline of neck
Superior meatus
What nerve passes through the cribriform plate?
Olfactory nerves
This is the ONLY muscle to ABduct the vocal folds
Cricothyroid m.

5 (1,2,3,4, and 6)
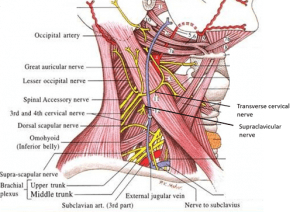
The boundaries of the posterior triangle are?
A. Trapezius, SCM, and clavicle
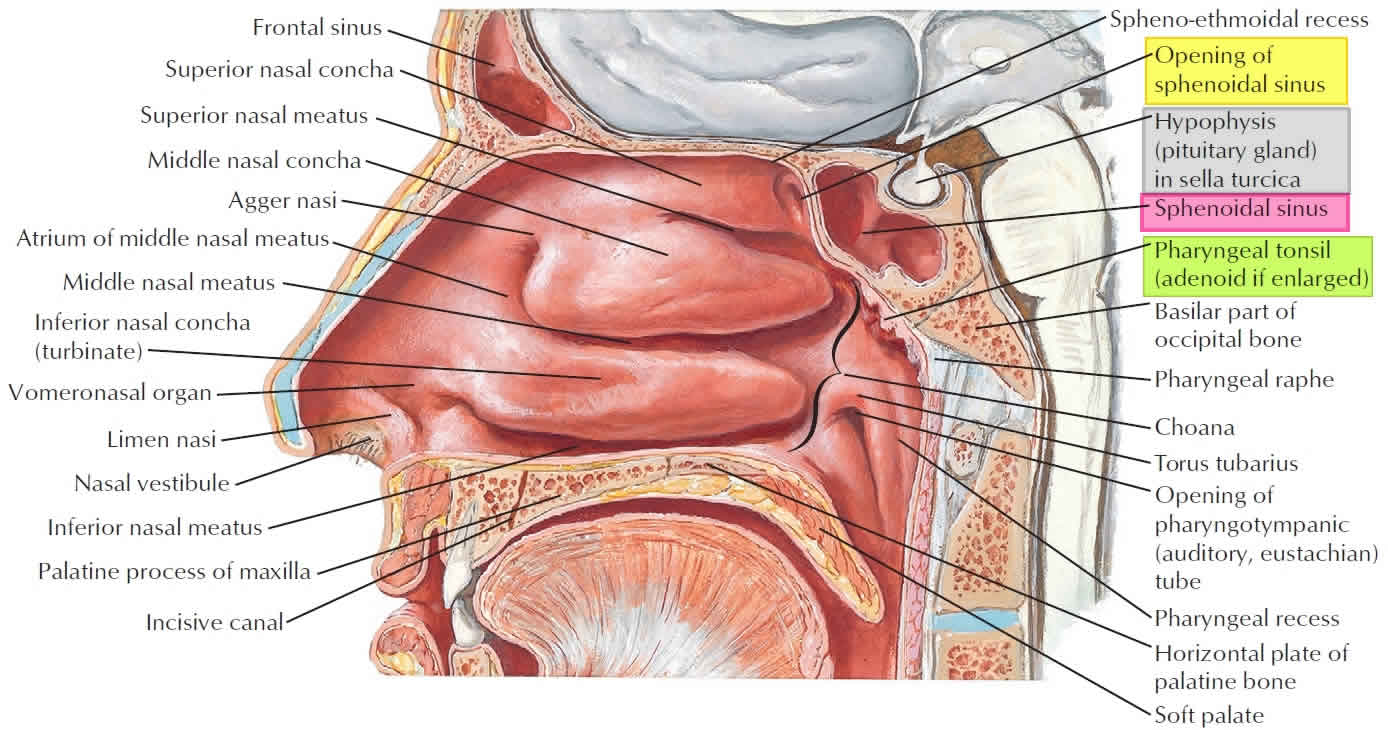
The pituitary gland can be accessed through this sinus
Sphenoid sinus
Can be accessed through transsphenoidal approach, which follows the nasal septum through the body of the sphenoid. Care must be taken not to damage the cavernous sinus and the internal carotid artery.
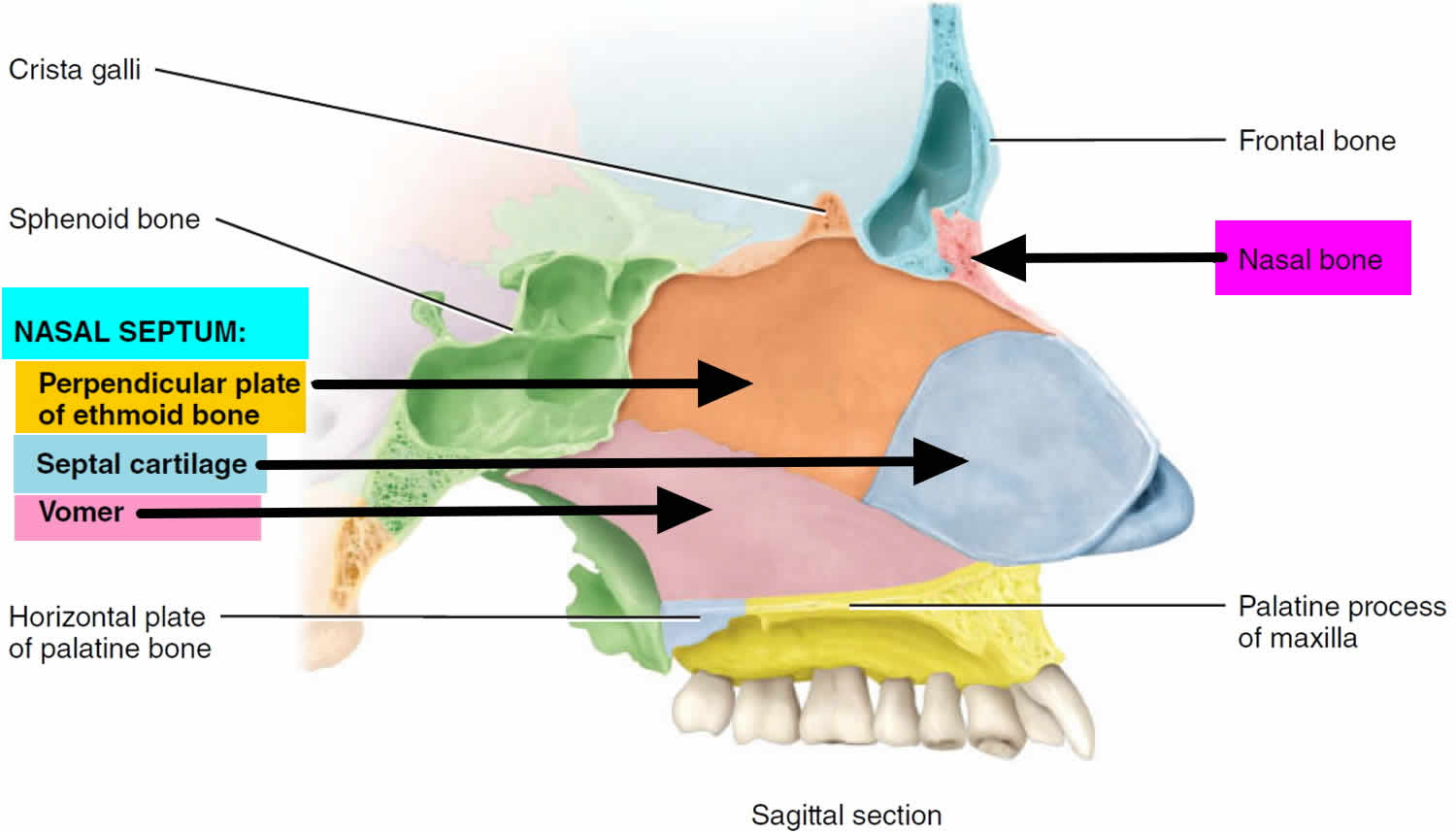
During a gang fight, a 17 year old boy is punched, and his nasal septum is broken. Which of the following structures would be damaged?
A. Septal cartilage and nasal bone
B. Inferior concha and vomer
C. Vomer and perpendicular plate of ethmoid
D. Septal cartilage and middle concha
E. Cribriform plate and frontal bone
C. Vomer and perpendicular plate of ethmoid
The nasal septum is formed primarily by the vomer, the perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone, and the septal cartilage. The superior, middle, and inferor conchae form the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. The ethmoid (cribriform plate), nasal, frontal, and sphenoid (body) bones form the roof. The floor is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of the palatine bone.
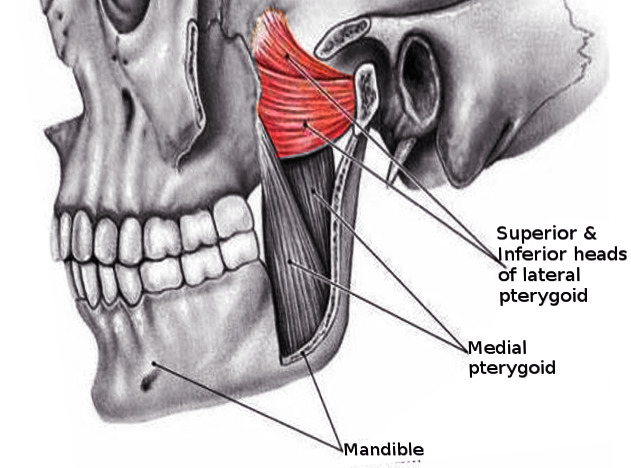
A 64 year old woman is unable to open her mouth or jaw because of tetanus resulting from a penetrating wound from a rusty nail. Which of the following muscles would most likely be paralyzed?
A. Masseter muscle
B. Medial pterygoid muscle
C. Lateral pterygoid muscle
D. Buccinator muscle
E. Temporalis muscle
C. Lateral pterygoid muscle
Opens the mouth by depressing the jaw. Masseter, medial pterygoid, and temporalis muscles close the jaw. The buccinator muscle is a muscle of facial expression.
Treacher-Collins (mandibulofacial dysostosis) syndrome results from embryological anomolies of this pharyngeal arch.
PA1
The anterior belly of the digastric m. is innervated by this nerve
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal n. (CN V3)
Tears will flow through the nasolacrimal duct into this structure
A. Sphenoethmoidal recess
B. Semilunar hiatus
C. Inferior meatus
D. Middle meatus
C. Inferior meatus
This structure receives the nasolacrimal duct
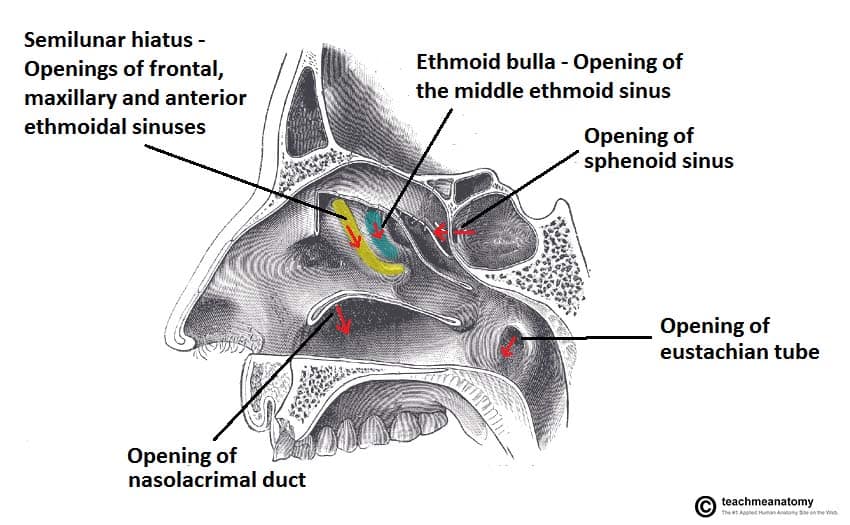
This is the opening to the nasopharynx
Choanae
During surgery for a malignant parotid tumor in a 69 year old woman, the main trunk of the facial nerve is lacerated. Which of the following muscles is paralyzed?
A. Masseter muscle
B. Stylopharyngeus muscle
C. Anterior belly of the digastric muscle
D. Buccinator muscle
E. Tensor tympani
D. The buccinator muscle is innervated by the facial nerve. The masster, anterior belly of the digastric, and and tensor tympani muscles are innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. The stylopharyngeus muscle is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
DiGeorge Syndrome is the diagnosis for failure of these pharyngeal pouches to differentiate?
PP 3 & 4
3 = inferior parathyroid gland and thymus
4 = superior parathyroid gland and ultimobranchial body
What is present in the posterior cervical triangle?
A. External jugular vein, brachial plexus roots, subclavian, suprascapular artery, transverse cervical artery
B. External jugular vein, brachial plexus trunks, digastric muscles, suprascapular artery
C. Internal jugular vein, transverse cervical artery, brachial plexus roots, subclavian artery
D. Trapezius, SCM, anterior omohyoid, posterior omohyoid, transverse cervical artery
A. Posterior cervical triangle is bounded by the trapezius, SCM, clavicle, and is subdivided by the posterior belly of the omohyoid into the occipital and subclavian triangles. It contains the spinal accessory nerve; external jugular vein; cervical plexus; roots and trunks of the brachial plexus; and subclavian, transverse cervical, and suprascapular arteries
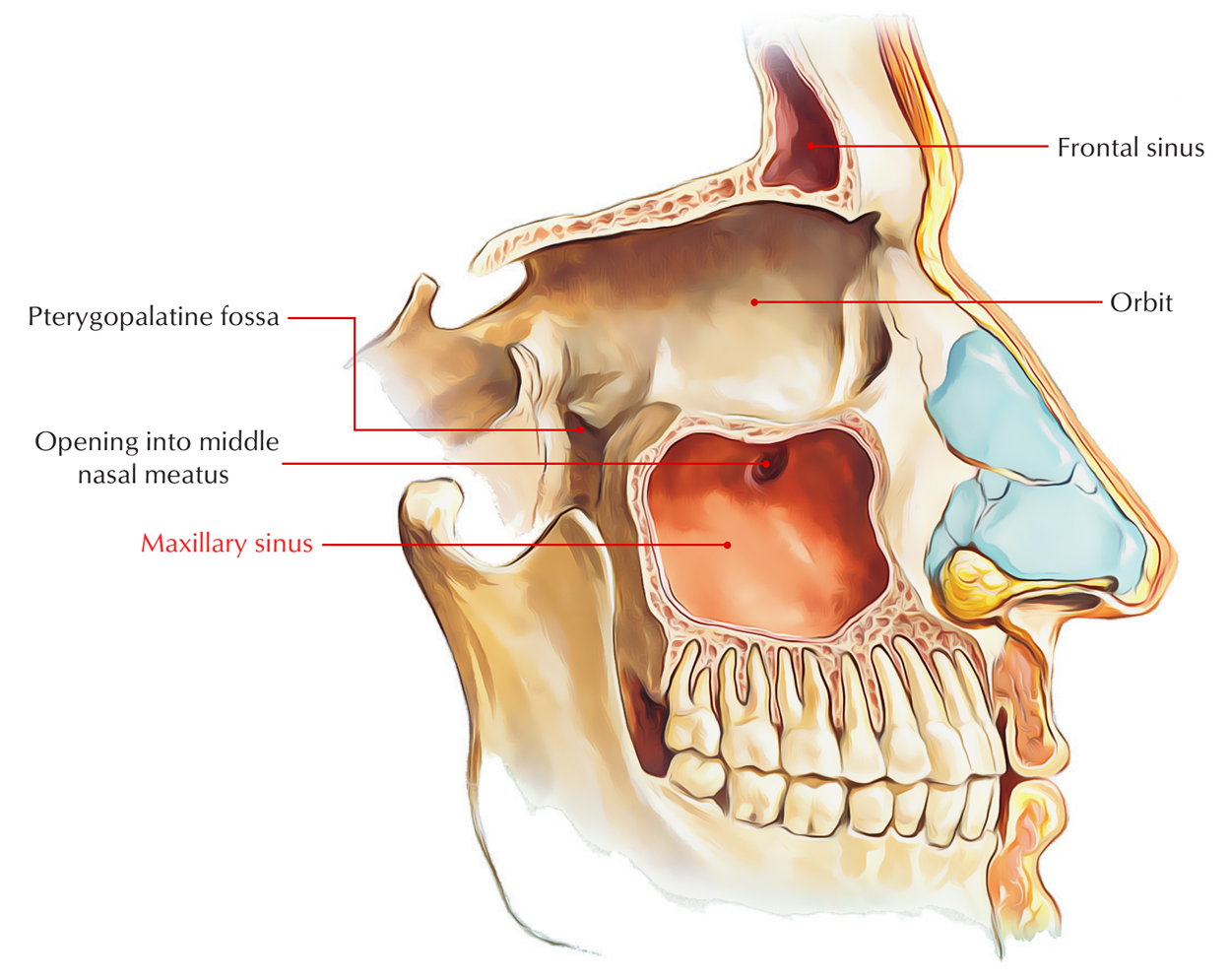
This is the only paranasal sinus that may be present at birth
Maxillary sinus
A 58 year old woman presents with progressive loss of voice, numbness, loss of taste on the back part of her tongue, and difficulty shrugging her shoulders. Her MRI scan reveals a dural meningioma that compresses the nerves leaving the skull. These nerves leave the skull through which of the following openings?
A. Foramen spinosum
B. Foramen rotundum
C. Internal auditory meatus
D. Jugular foramen
E. Foramen lacerum
D. Jugular foramen
An angiogram of a 45 year old man shows an occlusion of the costocervical trunk. This obstruction could produce a marked decrease in the blood flow in which of the following arteries?
A. Superior thoracic
B. Transverse cervical
C. Ascending cervical
D. Deep cervical
E. Inferior thyroid
D. Deep cervical
Costocervical trunk gives rise to the deep cervical and superior intercostal arteries. The superior thoracic artery arises from the axillary artery. The transverse cervical, inferior thyroid, and suprascapular arteries arise from the thryo-cervical trunk. The ascending cervical artery arises from inferior thyroid artery.

It is more common to find an ectopic inferior parathyroid gland than an ectopic superior parathyroid gland because...?
Both inferior and superior parathyroid glands can migrate insufficiently, but the inferior parathyroid is much more likely to migrate too far inferiorly because it co-migrates with the thymus from the PG3.
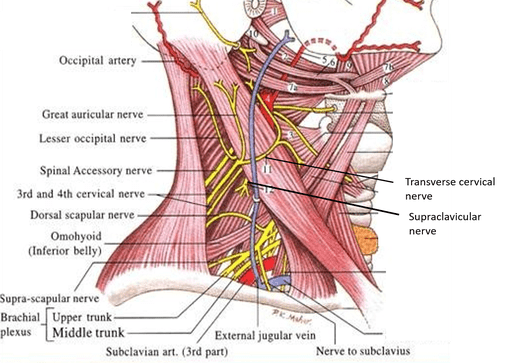
A 59 year old male complains of numbness in the anterior cervical triangle. Therefore, damage has occurred to which of the following nerves?
A. Phrenic nerve
B. Greater auricular nerve
C. Transverse cervical nerve
D. Supraclavicular nerve
E. Lesser occipital nerve
C. Transverse cervical nerve
This nerve turns around the posterior border of the SCM and innervates the skin of the anterior cervical triangle. The phrenic nerve, a branch of the cervical plexus, contains motor and sensory fibers but no cutaneous nerve fibers. The greater auricular nerve innervates the skin behind the auricle and on the parotid gland. The supraclavicular nerve innervates the skin over the clavicle and the shoulder. The lesser occipital nerve innervates the scalp behind the auricle.
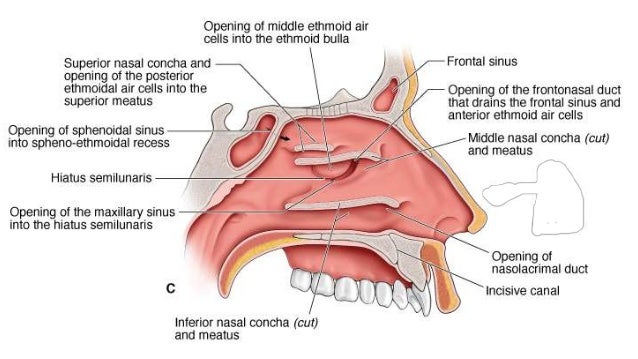
A 53 year old man has difficulty with breathing through his nose. On examination, his physician finds that he has swelling of the mucous membranes of the superior nasal meatus. Which opening of the paranasal sinuses is most likely plugged?
A. Middle ethmoidal sinus
B. Maxillary sinus
C. Posterior ethmoidal sinus
D. Anterior ethmoidal sinus
E. Frontal sinus
C. Posterior ethmoidal sinus
A 59 year old patient is unable to swallow because of a nerve injury. Which of the following nerves is UNaffected?
A. Hypoglossal nerve
B. Spinal accessory nerve
C. Vagus nerve
D. Facial nerve
E. Trigeminal nerve
B. Spinal accessory nerve supplies SCM and trap.
Swallowing involves movements of the tongue to push food into oropharynx, elevation of soft palate to close entrance of the nasopharynx, elevation of the hyoid bone and larynx to close opening into the larynx, and contraction of pharyngeal constrictors to move food through to pharynx.
A. Hypoglossal nerve supplies all of the tongue muscles except the palatoglossus (vagus nerve).
C. Vagus nerve innervates muscles of palate, larynx, and pharynx.
E. Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve supplies suprahyoid muscles (ant. belly of digastric and mylohyoid muscles)
A 38 year old man has had thryoid surgery to remove his papillary carcinoma. The external laryngeal nerve that accompanies the superior thyroid artery is damaged during the surgery. This injury could result in a severe impairment of function of which of the following?
A. Relaxing the vocal folds
B. Rotating the arytenoid cartilages
C. Tensing the vocal cords
D. Widening the rima glottidis
E. Abducting the vocal cords
C. Tensing the vocal cords
A 3 year old girl is admitted to the hospital with pain and hearing defect. An MRI examination reveals that she has developmental defects in the auditory tube and middle ear cavity. Which of the following pharyngeal pouches is most likely developed abnormally?
A. First pouch
B. Second pouch
C. Third pouch
D. Fourth pouch
E. Second and fourth pouches
A. First pouch
The 1 Pharyngeal pouch gives rise to the auditory tube and middle ear cavity. Second pouch forms palatine tonsils. Third gives rise to inferior parathyroid gland and thymus. Fourth develops into superior parathyroid gland and ultimobranchial body of thyroid