Name two parts of the upper airway.
Nasopharynx (nose) and oropharynx (mouth).
Define ventilation.
Flow of air into and out of the alveoli.
What is hypoxemia?
Low oxygen in the blood.
What is oxygen therapy used for?
To treat or prevent hypoxemia.
Name one nursing action to improve oxygenation.
Encourage deep breathing and coughing.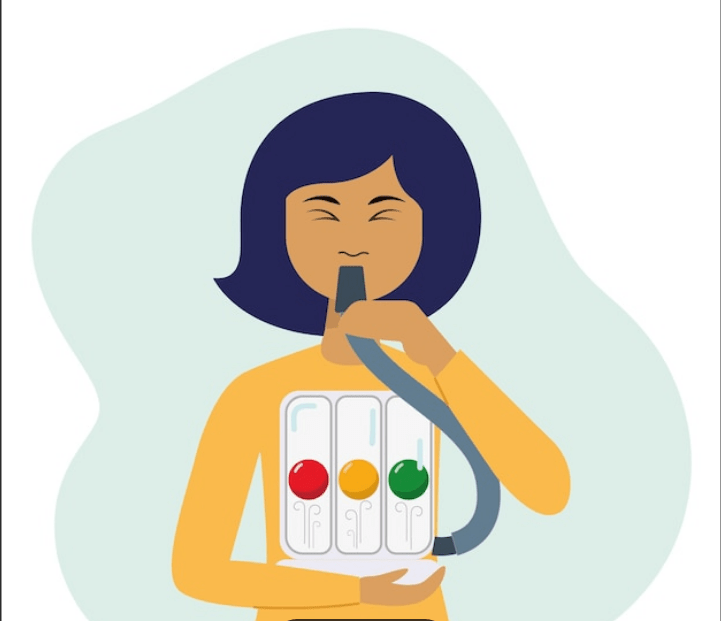
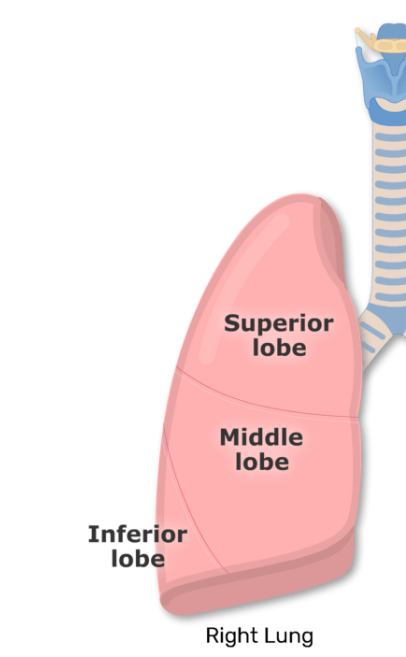
How many lobes does the right lung have?
Three
Define perfusion.
Flow of blood into alveolar capillaries.
What is hypoxia?
Lack of oxygen at the cellular level.
Name two oxygen delivery devices.
Nasal cannula and simple face mask.
What position promotes the best lung expansion?
Semi-Fowler’s or high-Fowler’s position.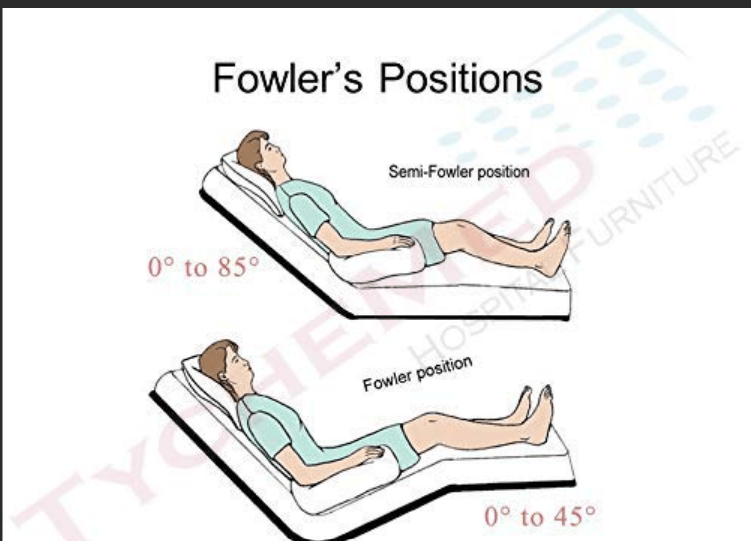
What is the function of surfactant in the lungs?
Keeps alveoli from collapsing.
What happens to the diaphragm during inhalation?
Contracts and moves downward to expand the thorax.
What are intercostal retractions a sign of?
Airway obstruction or respiratory distress.
What can happen if too much oxygen is given to COPD patients?
Carbon dioxide retention (hypercapnia).
What is the purpose of incentive spirometry?
Prevent atelectasis and improve ventilation
Define bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction.
Bronchodilation = airway expansion; Bronchoconstriction = airway narrowing.
What is the purpose of gas exchange in the alveoli?
Exchange oxygen into blood and remove carbon dioxide.
What are cardiopulmonary risk factors?
Smoking, obesity, inactivity, anemia, and chronic lung disease.
What is oxygen toxicity?
Lung damage due to prolonged high oxygen concentrations.
What should the nurse monitor for patients on oxygen therapy?
Skin breakdown around tubing and nasal dryness.
Which two nervous systems control the lungs?
Parasympathetic and sympathetic systems.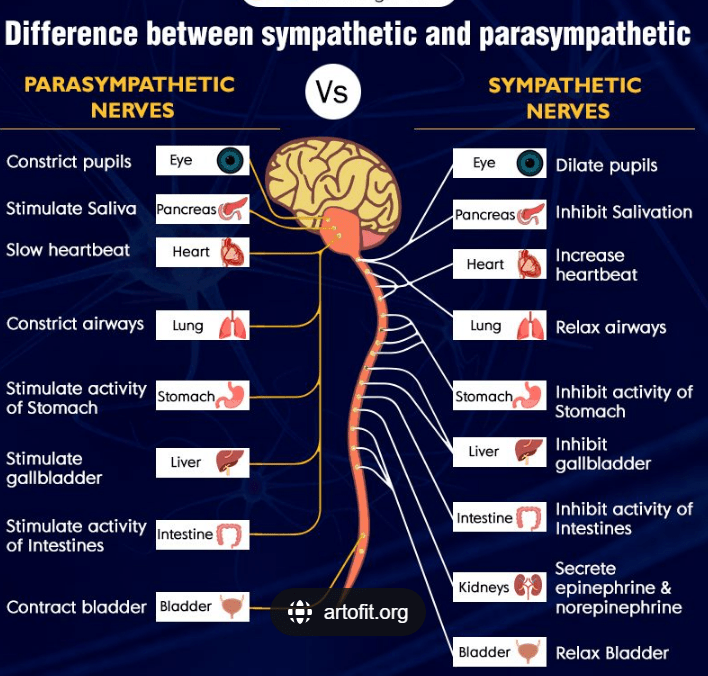
What are two factors that increase the work of breathing?
Decreased lung compliance and increased airway resistance.
Which muscles are used when a patient is in respiratory distress?
Accessory muscles.
What should always be assessed before and after oxygen therapy?
Oxygen saturation and respiratory effort.
What nursing intervention helps mobilize secretions?
Chest physiotherapy or hydration.