The nurse should trend this lab (the most critical) in acute kidney injury client.
What is potassium? potassium kills
remember expected labs for this diseased is elevated CR and BUN; decreased GFR what we do not know is how are the electrolytes that are cleared by the kidney doing such as K+, Phos, Mag,
Na is usually balanced due to the volume overload; Ca++ will be low due to increased Phos
The client has low CVP, Low PAWP, Low Stroke volume, low CO.
What is hypovolemic shock?
The acronym AVPU assesses this part of the primary survey.
or what is airway?
This is 2 shocks in 1.
What is burn shock - hypovolemic and distributive shocks?
The health care provider prescribes 1000mL of IV solution at 40 mL/hr. The tubing used is 15 drops/mL. How many drops/min should the client receive?
What is 10?
pH 7.31, CO2 33, HCO3 18, paO2 80
What is metabolic acidosis with partial compensation?
This is the most important lab to monitor in a client with liver failure.
What is INR/PT?
This is the first medication in the treatment of decreased preload due to hypovolemia.
What is isotonic fluid (LR or NS)?
additional information -if the client is actively hemorrhaging - Fluids then blood products then vasopressors; no blood loss then vasopressors
To protect the spinal cord, this is completed at the scene of the accident?
what is spinal backboard/cervical immobilization?
MAP - ICP =
What is CPP (cerebral perfusion pressure)?
This phase of a seizure the client is tired and confused.
What is post ictal?
This type of vomitus inidciates blood has been in the stomach for some time.
What is "Coffee-grounds"?
This type of AKI is caused by shock?
What is Prerenal?
Normal BP, high sodium, increased HR, Respiratory alkalosis.
What is compensatory shock?
This acronym is used to assist with the secondary survey.
What is SAMPLE? symptoms, allergies, medications, past med hx, last oral intake, events
Client has burns on face, upper 1/2 anterior torso, anterior right arm.
What is 18% TBSA burned?
The health care provide prescibes 1.25g/kg of mannitol IV over 60 minutes TID. Client weight is 80 kg. How many grams is the client receiving per dose?
100 g
1.25 x 80 = 100
Blood glucose >300, Polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, head ache, blurred vision
What is DKA - diabetic ketoacidosis?
This is the first action to correct hypotension.
What is lay flat?
This fluid should not be administered for initial treatment of dehydration.
What is hypotonic solution? hypotonic solutions may be used after vascular volume has been replaced; hypotonic is used to replenish depleated cellular volume
This type of injury is venous bleeding between the dura mater and the arachnoid layer of the meninges.
What is subdrual hematoma?
These three assessment findings = late signs of increased ICP.
What are widen pulse pressure, bradycardia, and irregular breathing? (Cushings triad)
Health care provide prescribes insuline infusion at 0.15 units/kg/hour. The insulin infuson bag has 100 units regular insulin in 100 mL normal saline. Cleint weigh is 166 lbs. How many mL/hour should the nurse program the infusion pump? (Round to the 1oth)
What is 11.3?
These type of ulcers are common in clients that are critically ill (burns, trauma, mechanical ventilators).
What are stress-related mucosal disease?
Toxins, vancomycin, contrast dye
What are things that cause inter renal AKI?
This intervention is completed in progressive shock to support the respiratory system.
What is RSI? Rapid sequence intubation
This is the anticipated assessment findings of a client with a complete spinal cord injury on the initial trauma assessment.
What is no movement or sensation below the level of injury? on the intial trauma assessment D = disability is neuro focus.
Using the Parkland formula 4mg/kg x TBSA% Calculate the 24-hour volume replacement required if the client is burned on their 50% and weight is 90kg.
What is 18,000 mL?
The nurse has a standing order for 10 mg IV labetalol to treat blood pressure greater than 180/100. The client BP is 181/110. Pharmacy supplies labetalol 100mg/20 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer?
What is 2 mL?
20mL x 10mg
________
100mg
This is the main difference between diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome?
What are ketones?
A nurse is caring for client with hepatitis B and notices red dots on the clients torso and legs.
What is petechiae?
To maintain arterial line patency the nurse should preform this every 1-4 hours.
What is manually flushing?
The nurse should do these two actions to prevent hypothermia in a trauma client.
What are apply warm blankets and warmed IV fluids?
A parent of acute brain injury patient states, "I don't understand why my son does not use the call light to get out of bed." What is the nurse's best response?
1. "The injury has affected the client's parietal part of his brain which controls judgement."
2. "The client's unawareness is temporary and will improve after the neurogenic shock resolves."
3. "The client has injury at the frontal lobe and results in impulsiveness."
4. "The client thinks they are at home and forgets to push the call light."
What is #3?
Rational: parietal lobe process sense of touch and assembles input from other senses; frontal lobe manages thinking, emotions, judgment, self-control, neurogenic shock results in dis-contention of epinephrine causing bradycardia and hypotension and temp disregulation; the client may think they are at home; but damage to the frontal lobe is a better response - family need to process the location of injury and the affect
The nurse should have ________and ________ at the beside of a client who is admitted post seizure.
What are seizure pads, suction equipment, oxygen and bag-valve-mask device? could have any of these 4 answers
This diagnostic tool is the primary source for diagnosing an upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
What is an upper endoscopy?
A nurse receives a client post hemodialysis treatment. What actions should the nurse take?
The nurse needs to perform a volume assessment - VS, weight, mentation, dizzyness; assess for Disequilibrium
Lactic acid, cultures, antibiotic, fluid bolus, vasopressor
What is the sepsis bundle?
Dark colored urine, low urine output, elevate creatine kinase
What is rhabdomyolysis?
Assessment - beefy red face with blisters.
What is a chemical exposure?
The nurse should level the external ventricular drain (EVD) to this landmark.
What is tragus? (level of the foramen of Monro or tragus of the ear)
This must occur in order to stop the insulin infusion.
What is closure of the anion gap?
This medication is prescribed to a client with esophageal varices that are bleeding and requires this additional intervention for the nurse to complete.
What is octreotide and blood glucose monitoring?
This is the external landmark to place the transducer for an arterial line.
What is phlebostatic axis? (4th intercostal space midaxillary)
Onset is charaterized by loss of consciousness at the scene followed by brief period of lucidity.
What is an epidural hematoma -arterial?
A client with a severed spinal cord at T6 is classified as __________ injury.
Complete injury
They will have no feeling or movement below the level of injury and no hope for improvement.
The goal of drug therapy is to _________ seizures with _________ drug side effects.
What is prevent and minimal?
The nurse needs to monitor a client with a GI bleed for this complication.
What is hypovolemic shock?
D50 1 amp
10 units regular insulin IV
Calcium gluconate
Sodium Bicarbonate
What are the medications in the hyperkalemia cocktail? remember that Ca is administered first as it is to stablize the heart rhythm, then the D50 to increase glucose prior to administering the insulin; Sodium bicarbonate may or may not be prescribed; if it is prescribed it will help push K+ back into the cells; clients with AKI are in metabolic acidosis
Pale, cool, clammy, decrease blood pressure, decreased cardiac output, increased heart rate, decreased UO, decreased mentation, increased respirations
What are signs of shock?
Note the client's symptoms will progress as the client goes from compensatory to refractory stages of shock. compensatory shock is respiratory alkalosis and progressive shock is respiratory acidosis
Evalution - should see the signs reverse
This type of respiratory trauma causes paradoxical breathing.
What is a flail chest?
Burn clients with these risk factors may have a poor prognosis for recovery.
What is preexisting heart, lung, or kidney disease, diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, malnutrition
remember burns is a shock and will cause organ dysfunction, heart will be stressed with CV volume shift, lungs are at risk of ARDS, this clients are at risk of AKI. Diabetes will increase their risk of infection, peripheral vascular disease will alter wound healing, malnutrition will alter wound healing as these clients will need 5000 kcal/day
A nurse is caring for a client with an external ventricular drain (EVD). What should the nurse document in the client's healthcare record regarding the EVD?
Dressing - is there any drainage if there is the color; Site - any redness or drainage; The color/clarity of the EVD drainage and amount; any odor; location,
if there is any suspicion of an infection based on the site assessment -check the client's CBC and VS for fever.
Hyperglycemia Hyperosmolar Syndrome clients must be monitored for this serious complication during volume resuscitation. How will the nurse know?
What is volume overload? what are crackles on asculation?
This procedure may be required for a client prior to endoscopy to control bleeding.
What is intubation?
The nurse will increase the client's vasopressor, if the MAP is less than this value.
What is 65 mm Hg?
The nurse assessing a new traum client racoon eyes and blood drainage coming from the right nares. What action should the nurse do next?
Complete a halo test - need to confirm if there is cerebral spinal fluid. Remember if there is any indication of a basilar skull fracture a NG tube is contrainidacted.
A nurse is caring for a client with a T4 incomplete spinal cord injury. The client complains of a headache and not feeling right. On assessment the nurse notices the BP has increase and the client is bradycardia. The skin is flushed above the injury and cool below the level of injury. What is the first action the nurse should take?
What is sit the client up? This action will cause the BP to decrease. The next action is to find the cause. 85% of Autonomic Dysreflexia is caused by bowel implaction/distended bladder.
These 2 nursing actions can protect a client's airway during a seizure.
What is turn the client to their side and suction the airway?
This laboratory result is elevated in a client with an upper GI bleed but not low GI bleed.
What is BUN? This lab will increase as the blood a protein is digested.
The most important nursing action when caring for a client with an electrolyte imbalance.
What is cardiac monitoring? These clients have a high risk of cardiac dysrythmias.
Narrow pulse pressure and distant heart tones.
What is cardiac tamponade?
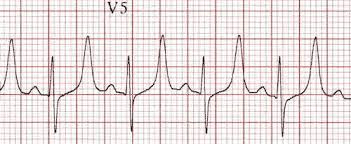
What are peaked t waves?
A nurse assessing a client who was in a house fire has these systems: headache, tachycardia, dizziness, nausua
What is carbon monoxide posioning?
These assessment findings indicated a possible basilar skull fracture.
What are raccoon eyes and battle sign?
The proper method to stop the insulin infusion on a DKA client.
What is administer basal insulin and wait 2 hours?
Assessment: normal liver enzymes, severe ascites, jaundice, low albumin, elevated INR and ammonia level, low urine output
What is end stage liver failure?
In a client's volume status the nurse should focus on these assessments.
What is VS (especially blood pressure), orthostatic VS, central venous pressure (CVP, high with volume access and low with volume depletion) Pulmonary artery presssure, breath sounds, oxygen saturation, skin turgor, edema, weight.
A nurse is assessing a client in the trauma ICU. The client has a circumferential dressing on their right arm. Right radial pulse is +2, left radial pulse +3; right fingers cool to touch; left fingers warm to touch; client states pain 8/10. Last medicated with 1 mg hydromorphone 1 hour ago. What should the nurse hypothesize?
What is compartment syndrome?
This device may used to help manage pain on a spinal cord injury client.
What is a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulaton unit (TENS)?
This medication is the first medicaiton given during a clonic-tonic seizure. (Provide the drug category and name)
What is benzodiazepine and lorazepam?
This is the first medication administered to a client with Addisonian Crisis.
What is hydrocortisone?
A nurse is assessing a client post hemodialysis. What assessment findings should the nurse anticipate? 1. crackles bilaterally 2. decreased weight 3. decreased potassium 4. increased BUN 5. increased heart rate
What is #2 and #3? bilateral crackles = volume overload would not anticipate this finding, HD removes volume so anticipate normal to slightly low volume, HD will clear the blood of potassium and lower BUN, too much volume removed would cause tachycardia.
Manifestations of this shock include elevated BNP, decreased CO, elevated CVP/PAWP, cardiac dysrythmias, cool/clammy skin, hypoactive bowel sounds.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Identify the components of the primary survey. ABCDEFG
A - airway; B = breathing, C = circulation, D = disability, E = exposure, F = full set of VS/family, G = get resuscitation adjuncts
The respiratory system is vulnerable to these 2 types of injury.
What are upper airway burns and lower airway injuries/burns? (assessment of burns that can affect breathing - nasal hair synged, hoarsness, drooling, brown particles in sputem (soot), burns on chest/neck/face)
The healthcare provider prescribes norepinephrine 5mcg/min for a client with hypotension. Pharmacy supplies 4mg norepinephrine in 250 mL normal saline. How many mL/hour should then program the infusion pump. Round to the nearest 1oth.
What is 18.8?
This medication can impair the release of insulin and increase insulin resistance.
What are calcium channel blockers?
A nurse is caring for a client with endstage liver failure who has an elevated PT/INR. What additional action does the nurse need to add to the client's plan of care?
Protect from injury - automatic fall precautions; apply additional pressure to stop bleeding from any venous pokes.
Note -INR is going to be the most concerning labs for this disease because just a little bump can create a huge bleed. We know the client is going to have altered liver enzymes until endstage and the levels go back to normal - this is an expected finding
These 2 complications can occur on an arterial line if the tubing connections are loose.
What is clotting and bleeding?
A nurse caring for a client post motor vehicle accident with multiple fractures notes petechia on the client's chest. The client complains of severe dyspnea. Oxygen saturations 85%. In an SBAR report, the nurse should anticipate orders for what complication?
What is fat emboli syndrome?
Why do spinal cord clients have to so much pain?
the damage to the nerves at the point of injury. These patient will have neuropathic pain; plus pain from posture changes and muscle spasms. clients will be on gabapentin, opioids, benzo, muscle relaxants/antispasmotics , botox injections,
A client admitted with a history of seizures asks the nurse, "why do I have an IV catheter in place, if I am not getting any intravenous medications". What is the nurse's best response?
If you have any seizure activity, the IV catheter will provide immediate access to administer medication to stop the seizure.
A client is admitted to progressive care with light headedness and black tarry stools. The HCP can order this nursing action to assess the clients volume deficit.
What are orthostatic vital signs?
This is a priority nursing assessment during hemodialysis?
Blood pressure - this assess volume status.
A nurse is admitting a client with hypovolemic shock. The nurse she make sure the client has _________ so that ___________ can be adminitered prior to the administration of _______________.
What is 2 large bore IVs?
What is volume replacement (first is isotonic followed by blood products if needed)?
What are vasopressors to maintain MAP > or equal to 65 mmHg?
Using the emergency Severity Index (ESI). A client with cardiac ischemia would triaged at what level.
What is ESI -2?
A nurse should assess for these 3 complications as a result of a lightening strike injury.
What are wounds, fractures, lethal dysrhythmias?
To decrease ICP, this is how the nurse should position the client.
What is head of bed 30 degrees and midline? Remember clients with elevated ICPs will have higher ICP as the client is layed flat and trendelenburg is contraindicated.
The nurse should add this to the client's IV fluids when serum glucose reaches 250 mg/dL? (There will be a standing order for this action)
What is D5W? The client will already have 0.9% Saline or 0.45% Saline infusing with 30 mEq of KCL per liter.
This is the recommended infusion rate for a client with a GI bleed with hypotension.
What is a rate that supports blood pressure?
A chest x ray post central line insertion is completed for these 2 reasons.
What is a pneumothorax? and what is to confirm the line placement/location.
Headache, flushing, bradycardia, hypertension
What is autonomic dysreflexia?
These are signs of early increase intracranial pressure (select all that apply): 1. projectile vomiting, 2. brady cardia, 3. ipsilateral pupil dilation, 4. widen pulse pressure, 5. altered mentation, 6. irregular breathing, 7. Seizure activity
1, 3, 5, 7 are correct
2, 4, 6, are all late signs - cushings triad; if not immediately corrected the client will have a cranial herniation
A nurse is caring for a client who just received 2 mg IV lorazepam to stop a tonic - clonic seizure. What is the nurses next action?
Monitor the client for impaired breathing.
The nurse should have this device at the client's bedside incase the client starts to hemorrage and plan for endoscopy to ________ the hemorrhaging vein.
What is balloon devices to tamponade (Blakemore or Minnesota tube) and banding?
This treatment is recommended for clients in the ICU who are volume overload, hypotensive, metabolic acidosis, abnormal electrolytes?
What is CRRT - Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy?
This type of shock prevents forward movement of blood through the heart chambers. Clients will have a narrow pulse pressure.
1 - name the shock
2 - provide examples of causes
1. Obstructive shock
2. Cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax, Pulmonary embolism are the main causes. These are medical emergencies and must recognized for early treatment.
A nurse assessing a trauma client who is gasping for air. How should the nurse open the airway?
What is the jaw thrust?
A client is burned on their full anterior torso. This procedure is completed when the client develops increased intraabdominal pressure?
What is an escharotomy?
BP 200/55; HR 45, RR irregular
What is Cushing's Triad? Widen pulse pressure/hypertension, bradycardia, and Cheyne- stokes respirations
This is the first priority of treatment for a client with DKA.
What is volume resuscitation?
A client with esophageal varices may be on these medications to reduce portal pressure.
What are vasopressin, octreotide, beta-blockers, nitrates?
This is the reason contnous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) is the preferred form of hemodialysis in the critically ill client.
Fluid control is more natural compared to intermittent hemodialysis, enhancing fluid volume removal without compromising vascular circulation.
This type of traction using and external fixation device.
What is skeletal traction?
Hypotension, Bradycardia, tempearture instability
What is neurogenic shock?
The HCP prescribes 150mg IV phenytoin to a client. Pharmacy supplies 50mg/1mL vial. How many mL will the nurse administer?
3 mL
Assessment findings: Low sodium, high potassium, low glucose, hypotension, low back pain, N/V, fever.
What is Addisonian Crisis?
Prior to starting a client on CRRT, this procedure will need to be completed.
What is a temporary hemodialysis catheter?
This is the goal for all shocks.
Maintaining adequate circulation to get oxygenated blood to the tissue. (elevated latic acid is oxygen debt at the tissue level)
Part 1: This 2 labs are the most critical to monitor after a crushing injury.
Part 2: These are the 2 complications these lab values indicate.
What is potassium and creatine kinase?
What is hyperkalemia and rhabdomyolysis?
If the client receives this fluid for volume resuscitation, the client will develop this complication.
What is NS?
What is metabolic acidosis from too much chloride?
Part 1: pH 7.33, CO2 66, HCO3 25, PaO2 55 (client is on a mechanical ventilator)
Part 2: Recommendation?
What is respiratory acidosis and hypoxemia?
What is increase respiratory/TV rate and oxygen? increased CO2 will cause cranial vasodialation increasing ICP; need to immediately hyperventilate the client to decrease ICP; hypoxia also causes cranial vasodialation increasing ICP; will also need t increase the FiO2 on the ventilator.
A client in HHS has bilateral crackles and echocardiogram shows EF of 30%. The nurse should anticipate this medication to be prescribed. (name the medication category and 1 example)
What are + inotropes? milrinone, dobutamine and digoxin
After a paracentesis, the nurse must do this intervention to monitor for this complication.
What are post op vital signs and hypotension?
A nurse caring for a client diagnosed with cardiogenic shock and is concerned the client is in volume overload. What hemodynamic readings and assessment findings would support the nurses hypothesis?
hemodyamic - elevated CVP, elevated PAWP, decreased CO, decreased SVO2/ScVO2
Assessment - decreased urine output, bilateral crackles, edema, +JVD, tachypnea
The 2 focuses of autonomic dysreflexia treatment.
What is lower blood pressure and find the cause? the first action is to sit the client up - this is to drop their BP the second action is to find the cause and if able to find quickly then relieve the painful stimulus - BP will quickly return to normal; unable to find the cause then focus on the bp to prevent epidural bleed
The client with a spinal cord injury has no feeling or movement below the level of injury on admission and 2 days later has pain in their feet.
What is spinal shock? This shock will resolve in days to weeks and is related to the secondary injury-inflammation putting pressure on the spinal cord.
During the discharge teaching, the nurse should emphasize these 4 discussion points regarding the client's medications.
1. compliance, 2. the need for drug level monitoring, 3. report side effects to the HCP, 4. all drugs have a black box warning to report suidicial thoughts or worsening depression to the HCP immediately
In a client with a GI bleed, this is the first fluid of choice and to stop the bleeding this is the first-line management.
What are isotonic fluids? and what is endoscopy?