What are George's 2 options for arterial dominance and where does this originate?
Coronary arterial dominance is defined by the vessel which gives rise to the posterior descending artery (PDA)
Left dominant - PDA supplied by left circumflex artery
Right dominance - PDA supplied by right coronary artery
What are the 5 phases that George's heart would go through every time it beats?
Phase 4 - Resting phase (RMP)
- Cardiac cells remain in the phase until stimulated
- Assoc with diastole portion of heart cycle (refill)
Add current into cardiac muscle (stimulation) causes:
Phase 0 – opening of fast Na channels & rapid depolarization
- Drives Na+ into cell (inward current), changes membrane potential
- Transient outward current due to movement of Cl- & K+
Phase 1 – rapid repolarization
- Closure of fast Na+ channels
- Phase 0 & 1 together correspond to R & S waves of ECG
Phase 2 - plateau phase
- Sustained by balance between inward movement of Ca+ & outward movement of K+
- Has a long duration vs other nerve & muscle tissue
- Normally blocks any premature stimulator signals (other muscle tissue can accept additional stimulation & contractility in a summation effect)
- Corresponds to ST segment of ECG.
Phase 3 – repolarization
- K+ channels remain open,
- Allows K+ to build up outside the cell → cell to repolarize
- K + channels finally close when membrane potential reaches a certain level
- Corresponds to T wave on ECG
What is the purpose of doing the genetic testing on George/in general?
George - to test whether he had the Long QT gene
- Examines the genetic (DNA/RNA) information of an individual
- Determine if that person has or will develop a certain disease
- Or could pass a disease to his/her children
60% of population expected to develop a disease with a genetic contribution by 60 y.o.
- Increasingly important & vital role in mainstream health care
- Earlier & accurate diagnosis, increased patient outcome
- Rapidly changing the face of medicine
If we were to listen to George's heart sounds where is the auscultation site of the aortic valva, pulmonary valve, left atrioventricular valve, right atrioventricular valve
Aortic Valve - right 2nd intercostal space
Pulmonary valve - left 2nd intercostal space
Left atrioventricular valve - left 5th intercostal space
right atrioventricular valve - left 5th intercostal space
What is the mechanisms of the 4 Classes of Anti Arrhythmic drugs
Class 1 - Blocks fast Sodium channels
Class 2 - Beta blockers
Class 3 - Blocks potassium channels
Class 4 - Calcium channel blockers
What are the 3 types of genetic testing that the doctor could have done/ordered to be done for George?
1.Karyotyping (Chromosome Analysis)
•Chromosomes are examined microscopically & arranged in order
•Number & structure analysed
2.Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH)
•Uses complementary DNA probes to target specific regions of a patient’s genome
•Can be done on metaphase or interphase chromosomes
•Common for aneuploidies & microdeletion syndromes (>20kb)
3.Array Comparative Genomic Hybridisation (aCGH)
•Also known as a microarray
•Glass slide containing >100,000 region specific DNA probes
•Whole genome analysis of small (>60kb) duplications & deletions (intrachromosomal amplifications and deletions can be detected)
What are the 4 surfaces of George's heart? and the 3 borders?
4 surfaces
Sternocostal surface
Diaphragmatic surface
Base (posterior) surface --> left atrium
Pulmonary surface
Borders
Right border --> right atrium
Left border --> left auricle and left ventricle
Lower border --> mainly right ventricle + right atrium and left ventricle and apex
What other drug is in the same class that Atenolol (the drug George was prescribed) and what is its mechanism
Metoprolol
Mechanism - based on 2 major & 1 minor action
1.Competitively block catecholamine-induced stimulation of myocardial β-adrenergic receptors &
2.Depress phase 4 depolarization of pacemaker cells
- --> Inhibit sympathetic activation & cause indirect Ca2+ inhibition (on Phase 2)
- Slow sinus & AV conduction ® ¯ HR & prolongs PR interval (atrial depolarization)
- RP & prolongs duration of AP by ¯ conduction through AV node
- Some negative inotrope activity
3.(Some direct membrane-stabilising effects related to Na+ channel blockade)
What is DNA Sequencing? What are is the old and new type of DNA Sequencing
Process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a piece of DNA
Dideoxy (Sanger) Sequencing
- Developed in 1977, remained the major approach for the next 40 years
- Method used for sequencing the human genome
- Beginning to be superseded
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- Also known as high throughput sequencing or massively parallel sequencing
- Simultaneous sequencing of millions of overlapping DNA fragments
- Creates an enormous amount of data (terabytes!!)
- Identifies thousands of potential disease-causing variants
Draw the internal structure of George's right atrium - includes 5 things
Draw the internal structure of George's right ventricle - includes 3 things
Atrium include - fossa ovalis, crista terminalis, musculi pectinati
Ventricle include - chordae tendinae, papillary muscle, trabeculae carnae
What are the 2 drugs that aren't under the Vaughan Williams classification and their mechanisms?
Digoxin
Cardiac glycoside
- Cardiac slowing
- Reduce rate of conduction through AV node (refractory period of AV node
- decrease force of contraction – release of intracellular Ca2+
- Can cause ectopic pacemaker activity
- Useful in LV dysfunction, heart failure & AF
Adenosine
Mechanism
- Not in Vaughan Williams classification
- Purine nucleotide (activates adenosine receptors)
- Slows AV nodal conduction
- Also produces peripheral & coronary vasodilation.
If the doctor had decided to do the array comparative Genomic Hybridisation on George - what steps would this involve"
Steps 1-3: Patient and control DNA are labeled with fluoresecent dyes and applied to the microarray
Step 4: Patient and control DNA compete to atach or hybridise to teh microarray
Step 5: The microarray scanner measures the fluorescent signals
Step 6: Computer software analyses the data and generates a plot
Explain the function of the pericardium and draw it
- the pericardium is a fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels
- the pericardium has parietal and visceral layers
Why would you not prescribe sotalol or amiodarone to George? WHat is George had been pescribed these drugs, what would happen? What is the class of these 2 drugs and what are there mechanisms?
Sotalol and Amiodarone both prolong the QT interval - which would result in life-threatening polymorphic ventricular tachycardia for George
These 2 drugs are Class 3 drugs
Sotalol
Non-selective beta blocker & K+ channel blocker
- Combines Class 3 & 2 actions
- Prolongs AP & QT interval -lengthens refractory period
- Key sites = atria, ventricles & accessory pathways
- Used for SVT, AF & VA
Amiodarone
Mechanism
- Block outward K+ channels during Phase 3 (slowing repolarisation)
- Substantially prologs AP duration & refractory period in all cardiac tissues without affecting phase 0 of depolarization or resting MP
- Prolong RP and QT & PR intervals
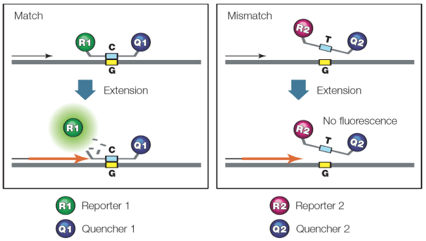
If the doctor were to order a real time (quantitative) PCR for George how would this be done? (Define terms like reporter and quencher)