Saliva empties into the oral cavity from the largest salivary gland through this duct.
What is the Stensen's duct?
(Parotid Gland)
The cranial nerve responsible for the sense of smell.
(Name and number)
What is the olfactory nerve (CN I)?
Term used to explain farther from the point of attachment of a limb to a body trunk.
What is Distal?
Located behind the sternum in the thoracic cavity and is the size of the human fist.
What is the heart?
Part of the autonomic nervous system, it's responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
A muscle of facial expression that functions to pull the mouth laterally, thereby shortening the cheek, and as an aid in keeping food on the chewing surfaces of the teeth.
What is the buccinator muscle?
This cranial nerve provides motor innervation to the muscles of mastication.
(Name and number)
What is the trigeminal nerve (CN V)?
Cranial bone that contains the foramen magnum, allowing the spinal cord to connect to the brain.
What is the occipital bone?
These vessels carry blood away from the heart to the body.
What are arteries?
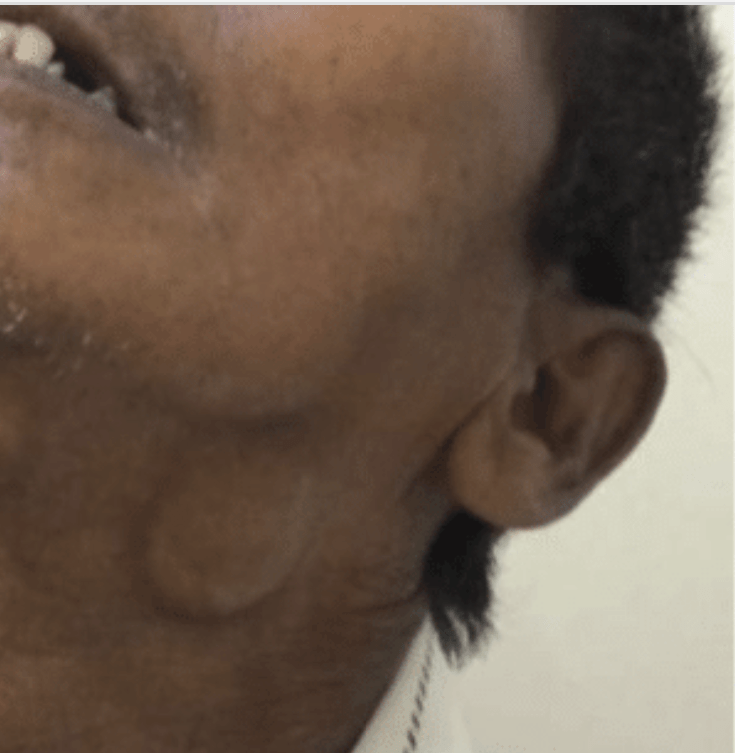
What are the submandibular nodes?
This single bone articulates with the frontal, parietal, ethmoid, temporal, zygomatic, maxillary, palatine, vomer, and occipital bones.
What is the sphenoid bone?
This cranial nerve innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
(Name and number)
What is the accessory nerve (XI)?
Major salivary gland that produces the highest proportion of mucous secretions.
What is the sublingual gland?
Microscopic vessels that connect arterioles to venules.
What are capillaries?
Structure in the lymphatic system responsible for the production and maturation of T-lymphocytes.
What is the thymus gland?
It supplies blood to the principal areas of the oral cavity and face by branching off anteriorly, medially, posteriorly and terminally.
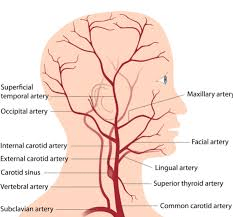
What is the external carotid artery?
It's the cranial nerve is involved in both hearing and balance.
(Name and Number)
What is the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII, 8)?
The landmark and nerves for the mental block injection.
What are the mental foramen/inferior alveolar nerve; mental and incisive nerve branches of V3?
This "master gland" has a stem-like stalk and serves as a storage site for anti-diuretic hormone and oxytocin.
What is the pituitary gland?
The two types of immunity, one that provides general defense that acts against anything foreign, and one that that recognizes specific threatening agents.
What are nonspecific (innate) immunity and specific (adaptive) immunity?
Muscle of mastication that orginates at the inferior border of the zygomatic arch, inserts on the lateral surface angle of the mandible, and acts to elevate the mandible.
What is the masseter muscle?
Damage to this cranial nerve would result in ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid), mydriasis (dilated pupil), and the eye being positioned "down and out."
What is the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
Bone forming cells that deposit calcium for remodeling.
What are osteoblasts?
Horomones released by the adrenal medulla in response to sympathetic stimulation.
What are epinephrine and norepinephrine?
These "ductless glands" are made of glandular epithelium whose cells manufacture and secrete hormones.
What are endocrine glands?