What gives us detailed information about the depths of the Earth? 518
P and S wave seismic data
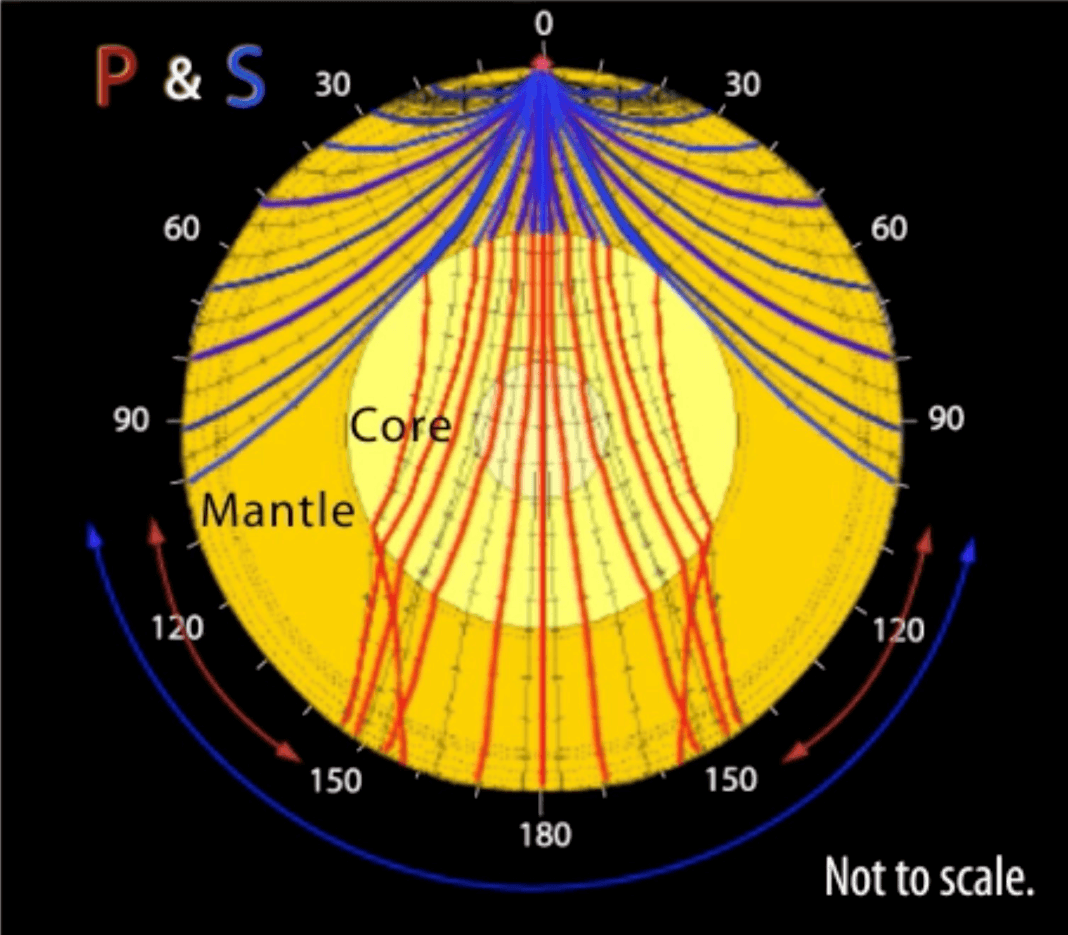
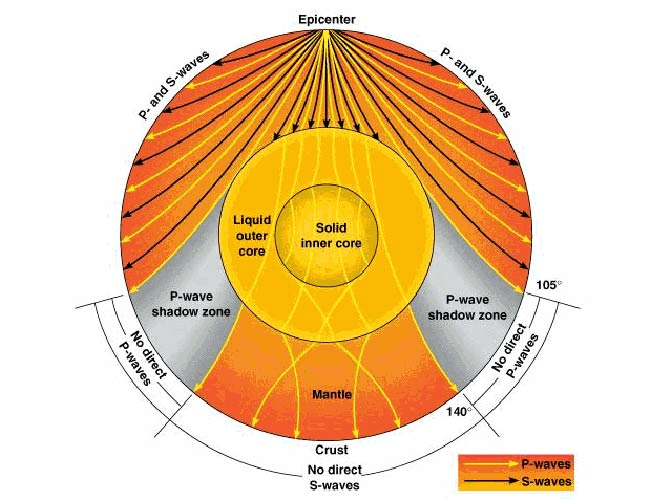
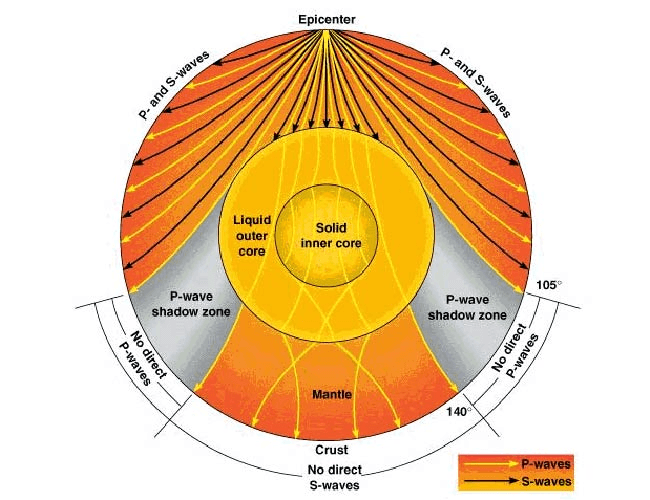
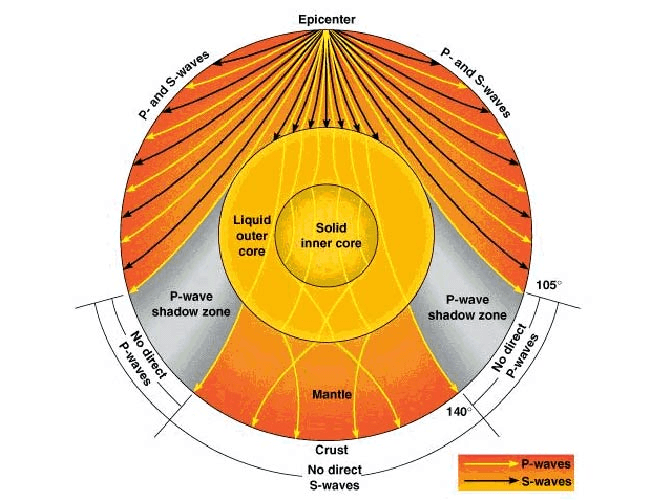
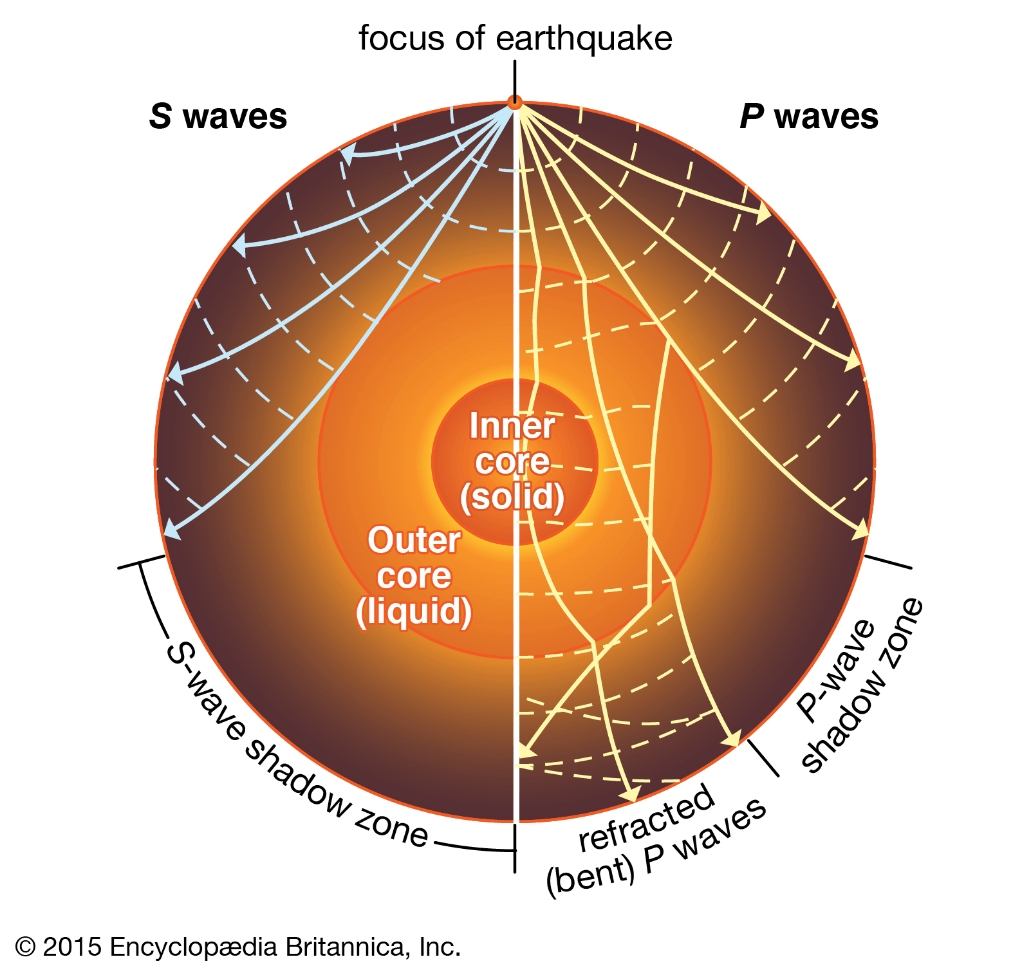
Which type of wave cannot travel through the liquid outer core?
'S' waves
What does this tell us about the center of Earth?

A compass tell us that the Earth is magnetic. So its interior is probably iron.

What do we call, 'a movement of the ground that happens when rocks break and move?' 516
an earthquake

What do 'P' and 'S' waves mean?
'P' waves are Primary [they get there first.]
'S' waves are Secondary.
What happens when S waves hit the liquid outer core of Earth?
A. They reflect back to the surface.
B. They are refracted as they pass through.
C. They are absorbed and do not pass through.
D. They move in all directions with no pattern.
C. They are absorbed and do not pass through the outer core.
Which wave is faster?
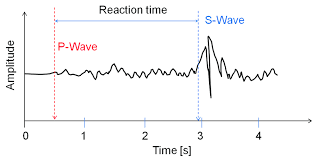
P waves [They arrived first.]
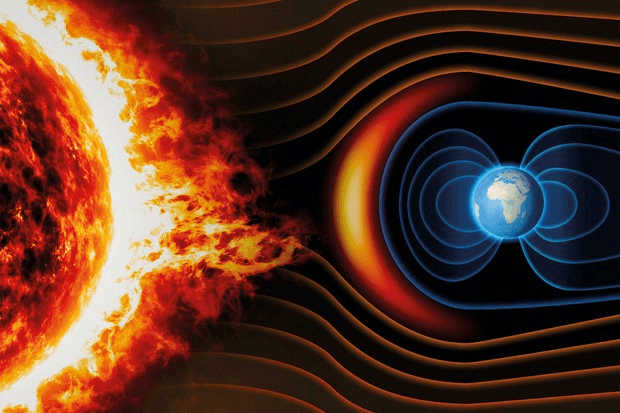
Scientists thinks that Earth's magnetic field may be produced by ___. 519
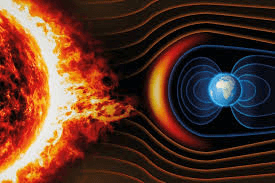
A. the relative motion between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core.
B. the interaction between meteors and Earth's atmosphere
C. gases released from volcanoes interacting with the ozone layer
D. EM waves from the sun entering Earth's atmosphere
A. the relative motion between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core.
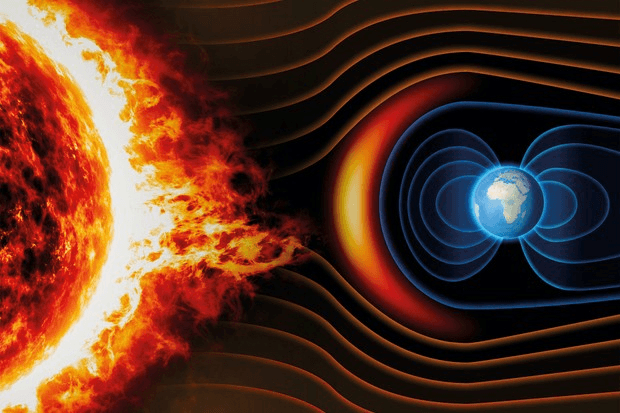
A. the relative motion between the liquid outer core and the solid inner core.
What devices collect and record seismic-wave data? 516
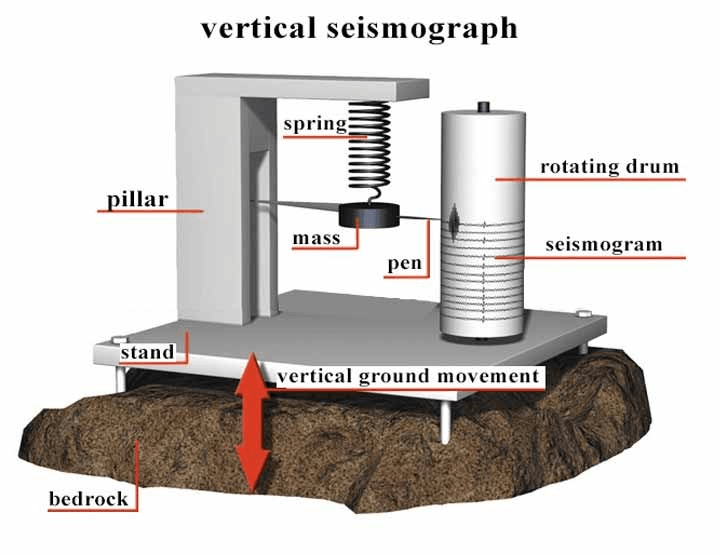
seismographs

What measurements are shown by the red lines?
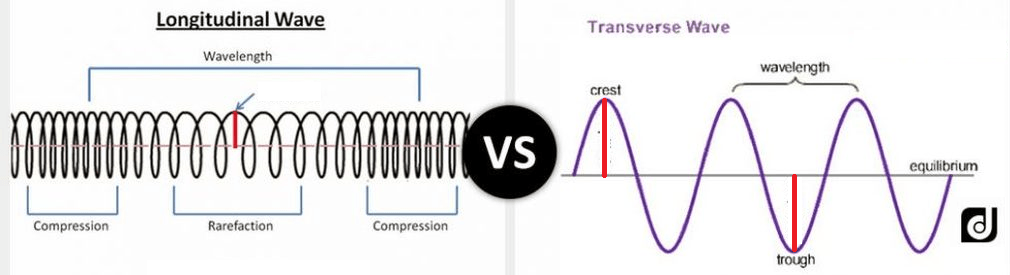
amplitude (how strong the wave is; its intensity)
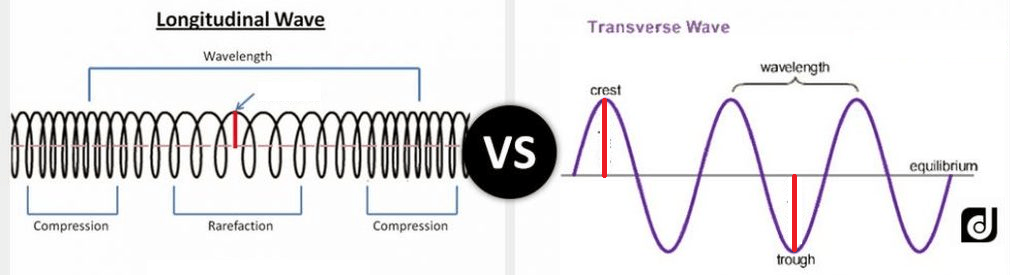
What happens when P waves hit Earth's core?
P waves are refracted each time they go through a different medium.
Which seismic waves are like sound waves because they travel through any medium?
'P' waves
What does the density of rocks tell us about the Earth? 519
A. Rocks from Earth's crust are more dense than the Earth as a whole. It is thought that the mantle and core are made of cheese; Swiss cheese. I love Swiss cheese.
B. Rocks that we find from Earth's crust are the same density as the entire planet. So it is believed that Earth has the same density throughout.
C. It is impossible to determine the density of Earth or of rocks in the mantle or core.
D. Because crust rocks are less dense than the overall density of Earth, the mantle and core must be more dense.
D. Because crust rocks are less dense than the overall density of Earth, the mantle and core must be more dense.
How do seismic waves travel from an earthquake?
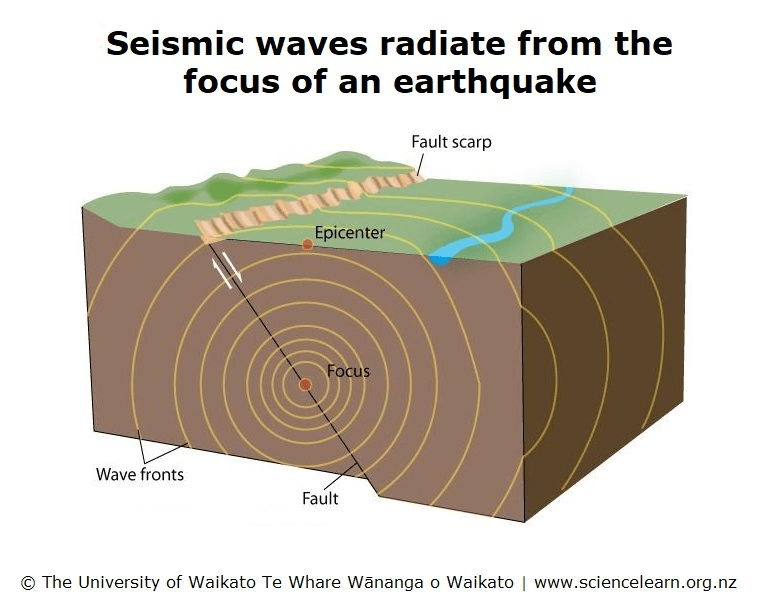
in all directions.
Why do we say that an 'S' wave is transverse?
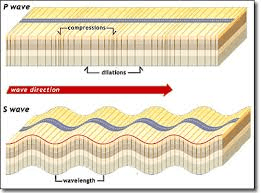
'S' waves vibrate at right angles to the direction that they travel. [This S wave is traveling from left to right, but vibrating up and down.]

Because S waves do not reach seismometers on the opposite side of Earth from an earthquake, they create a _______. 518
P-wave shadow zone
Which of these waves has the greatest amplitude?
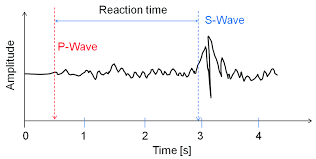
S waves [They often do.]
Why are meteors thought to have similar composition to Earth's crust, mantle and core? 519

A. Meteorites are materials from the interior of other planets.
B. Meteorites are actual material from Earth's interior.
C. Meteorites are thought to be made of matter that became the planets.
D. Meteors are material that erupted from volcanoes.
C. Meteorites are thought to be made of matter that became the planets.

What waves are released during an earthquake, allowing us to study Earth's interior?
P and S waves [Later we'll study Surface waves.]
Look at the comparison of the two types of waves that we have studied below. Which type are P waves?
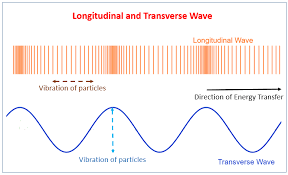
P waves are longitudinal.
How do scientists know what is inside Earth? 516
A. Scientists are able to drill into the mantle and core and view the outer mantle in deep mines.
B. Scientists use tools and types of technology to gather information about Earth's interior.
C. Scientists do laboratory experiments, such as testing how rock behaves under extreme pressure.
D. Answers B and C are correct.
E. Answers A, B, and C are all correct.
D. Answers B and C are correct.
Scientists use tools and types of technology to gather information about Earth's interior.
Scientists do laboratory experiments, such as testing how rock behaves under extreme pressure.
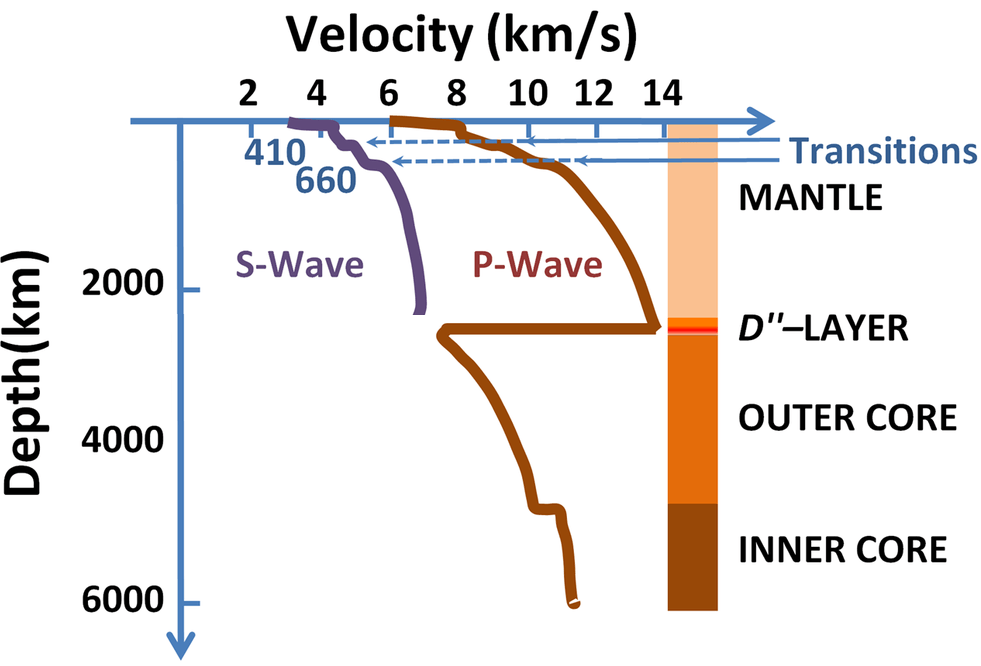
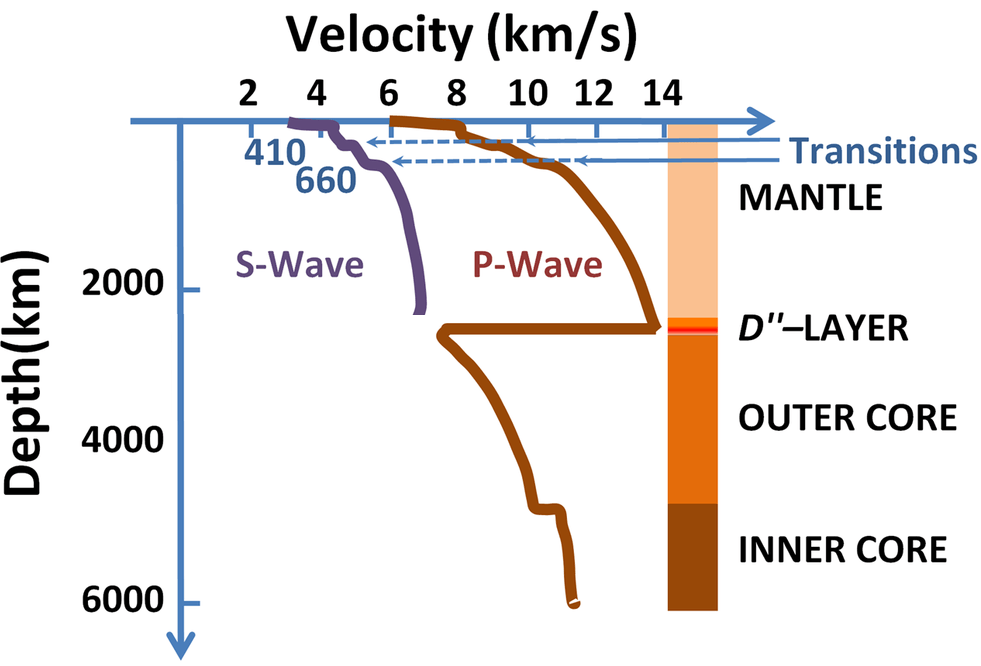
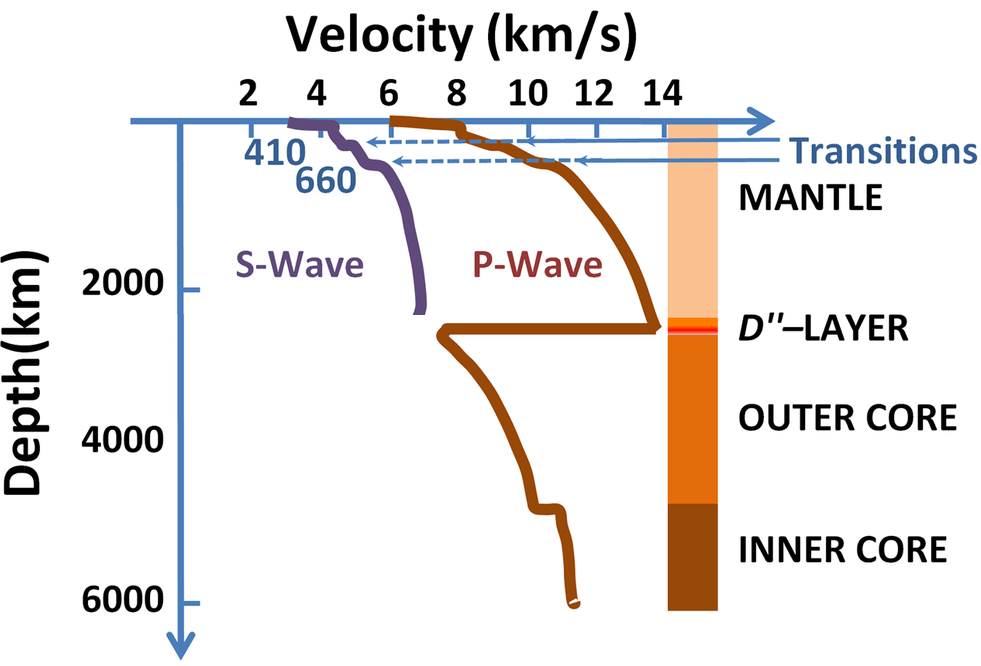
What can you tell about the speed of P waves from the graph below? Similar data is available on p. 518 at the bottom of the page.
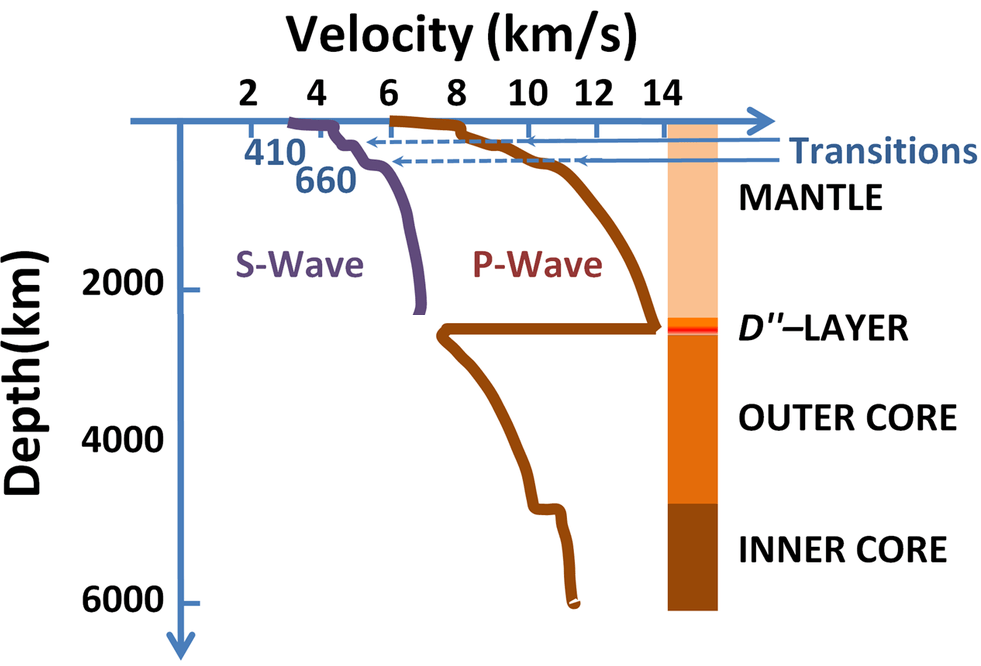
P waves have positive acceleration as they pass through the mantle. They slow down when they hit the outer core then accelerate. They accelerate again when they hit the inner core.
A xenolith is a piece of rock trapped in another type of rock. Most of the time, a xenolith is a rock embedded in magma while the magma was cooling. These bits and pieces, trapped in the magma but not melting into it, become xenoliths. earthsci. org

Mantle xenoliths give scientists: 519
A. an idea about what Earth's past was like.
B. samples of the inner and outer core, as well as the inner and outer mantle.
C. samples of rocks similar to those that are in Earth's mantle.
D. actual samples of some of Earth's upper mantle.
D. actual samples of some of Earth's upper mantle.

According to data on the graph, how long after P waves arrived did S waves arrive?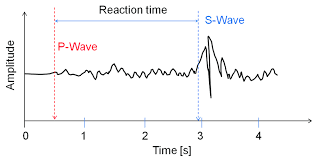
about 2.5 seconds
How do we determine the frequency of a wave?
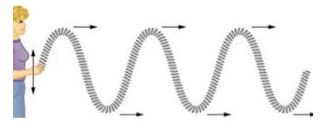
Wave frequency is the number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time.