E-waste refers to old electronics and should not be thrown into the regular MSW. Where should it go? Why is this important?
Can leach endocrine disrupting chemicals out of landfills if thrown away with regular MSW (should be disposed of at special facilities that recycle parts)
________________consumption is the most sustainable because it decreases natural resources harvesting and the energy inputs to creating, packaging, and shipping goods
Reducing
Describe primary and secondary treatment of sewage.
Primary: Physical removal of large debris (TP, leaves, plastic, sediment) with a screen or grate
Screens or grates filter out large solids (paper, plastic)
Grit chamber allows sediment (sand, gravel) to settle out & be removed
Secondary: Biological breakdown of organic matter (feces) by bacteria; aerobic process that requires O2
O2 is bubbled into aeration tank filled with bacteria that break down org. matter into CO2 and nutrients like N & P
Secondary treatment removes 70% of P and 50% of N
DOES NOT remove POPs such as medications or pesticides
LD 50 refers to __.
___the dose or concentration of the chemical that kills 50% of the population being studied (ex: arsenic LD50 in mice = 13 mg/kg)
Identify the routes of exposure to the following pollutants:
Lead
Mercury
CO
PM
Arsenic
•Lead → water pipes & paint chips
•Mercury → seafood (tuna)
•CO → indoor biomass comb.
•PM → pollen, dust, etc.
•Arsenic → rice, groundwater
Describe a vector. Give an example.
A living organism (rat, mosquito, flea, bat, etc.) that carry and transmit infectious pathogens to other organisms.
Waste incineration (burn) is an option for limited landfill space. Name one pro and one con that this practice provides.
•Can reduce volume by 90%, but also releases CO2 and air pollutants (PM, SOx, NOx)
•Bottom ash may contain toxic metals (lead, mercury, cadmium) & is stored in ash ponds, then taken to special landfills
•Toxic metals can leach out of storage ponds or be released into atmosphere
•Can be burned to generate electricity
Identify an example of reusing products to reduce waste.
Buying second hand clothes, using old wood pallets for furniture, washing plastic takeout food containers and reusing
___________________ inorganic, solid waste that collects at the bottom of tanks in primary and secondary treatment
Sludge
•Water is spun/pumped off to concentrate it further
•Dry, remaining physical waste is collected to be put in landfill, burned, or turned into fertilizer pellets
In a LD curve, describe threshold.
Lowest dose where an effect (death, paralysis, cancer) starts to occur
Bacterial infection caused by food or water being contaminated with feces (often from sewage release into rivers & streams used for drinking water)
dysentery -
•Causes intestinal swelling and can result in blood in feces
•Results in severe dehydration due to diarrhea (fluid loss)
The plague is a bacterial infection. Identify the vector(s) that transmit this pathogen.
Fleas, mice/rats
In a city, the total amount of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) generated per person is 2.5 kilograms per day. The population of the city is 1.2 million people.
Calculate the total amount of MSW generated by the city per day.
If the city recycles 30% of its total MSW, how much MSW is recycled per day?
If the MSW is sent to a landfill, and the landfill has a capacity of 500,000 cubic meters, how many days will it take for the landfill to fill up if the daily waste sent to the landfill is 60% of the total MSW generated?
Note: Assume that 1 cubic meter of MSW weighs 1.2 tons.
1.
= 2.5 kg/person/day × 1,200,000 people
= 3,000,000 kg/day or 3,000 tons/day (since 1 ton = 1,000 kg)
2.
= 0.30 × 3,000,000 kg/day
= 900,000 kg/day or 900 tons/day
3. Calculate how many days it will take for the landfill to fill up:
The landfill receives 60% of the total MSW generated.
MSW sent to the landfill per day = 60% × Total MSW generated
= 0.60 × 3,000,000 kg/day
= 1,800,000 kg/day or 1,800 tons/day
__Total tons the landfill can hold = Landfill capacity × Weight per cubic meter
= 500,000 cubic meters × 1.2 tons/cubic meter
= 600,000 tons
To find how many days it will take to fill the landfill:
Days to fill the landfill = Total landfill capacity / MSW sent to the landfill per day
= 600,000 tons / 1,800 tons/day
= 333.33 days
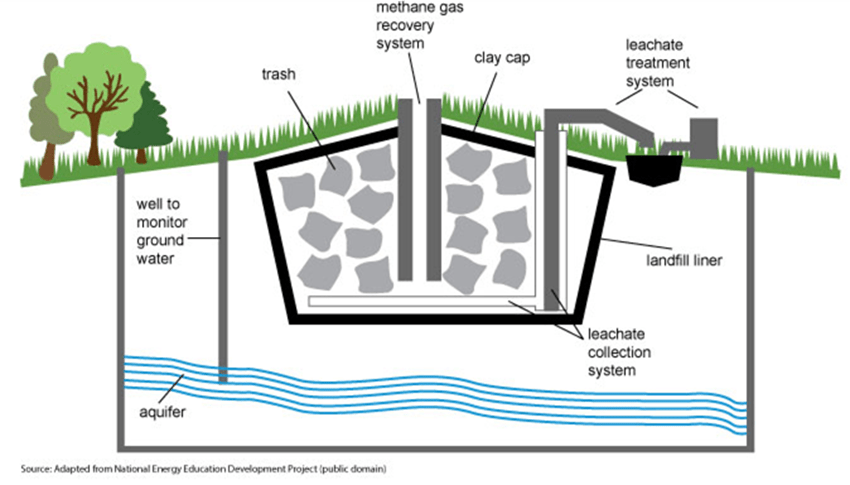
In the provided image, explain one key feature of the 'sanitary landfill' that is essential for its success.
•Clay/plastic bottom liner: layer of clay/plastic on the bottom of a hole in the ground; prevents pollutants from leaking out into soil/groundwater
•Leachate Collection System: System of tubes/pipes at bottom to collect leachate (water draining through waste & carrying pollutants) for treatment & disposal
•Methane Recovery System: System of tubes/pipes to collect that methane produced by anaerobic decomposition in the landfill
•Methane can be used to generate electricity or heat buildings
•Clay Cap: Clay-soil mixture used to cover the landfill once it’s full; keeps out animals, keeps in smell, and allows vegetation to regrow
Some areas do not go on to __________ treatment. _____________ uses chemical filters to remove more of the nitrates & phosphates from secondary treatment discharge
Tertiary - Ecological or chemical treatments to reduce pollutants left after primary & secondary (N, P, bacteria)
•Critical step because effluent that is discharged into surface waters with elevated nitrate/phosphate levels leads to eutrophication
•Expensive and not always used
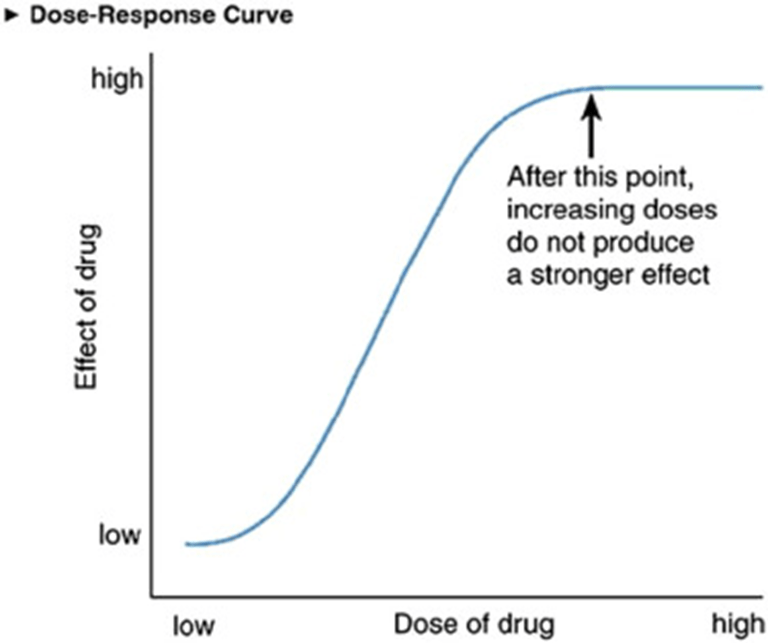
In this graph, what is the LD50? If it cannot be determined, why or why not?
A type of cancerous tumor caused by exposure to asbestos, primarily affecting the lining (epithelium) of the respiratory tract, heart, or abdominal cavity
Mesothelioma
Bacterial (pathogen) infection that targets the lungs
Causes night sweats, fever, coughing blood; treatable in developed nations with access to powerful antibiotics
Leading cause of death by disease in the developing world ~ 9 million cases per year and 2 million deaths (for comparison ~ 2.8 million global deaths from Covid-19)
Tuberculosis (TB)
Landfills generally have very low rates of decomposition, identify the 3 factors that are rarely present together that results in slow decomposition.
low oxygen, moisture, and organic material
Identify one pro and one con of recycling.
Pro:
●Reduces demand for new materials, especially metals and wood which cause habitat destruction & soil erosion when harvested
●Reduces energy required to ship raw materials and produce new products (fewer FF comb, less CC)
●Reduces landfill volume, conserving landfill space & reducing need for more landfills
Con:
●Recycling is costly and still requires significant energy
●Cities that offer recycling services need to process, sort, and sell collected materials; prices change rapidly, leading to “recycled” materials often being thrown away
●When citizens recycle items that shouldn’t be recycled (wrappers with food, styrofoam, etc.) it increases the cost for cities to sort & process
The final step in sewage treatment is to disinfect. Describe this process.
Identify one pollutant that is targeted during this process.
UV light, ozone, or chlorine is used to kill bacteria or other pathogens, such as e. Coli
E. Coli, Coliform bacteria, Giardia, Pathogens, Microorganisms/bacteria, Cholera, Viruses
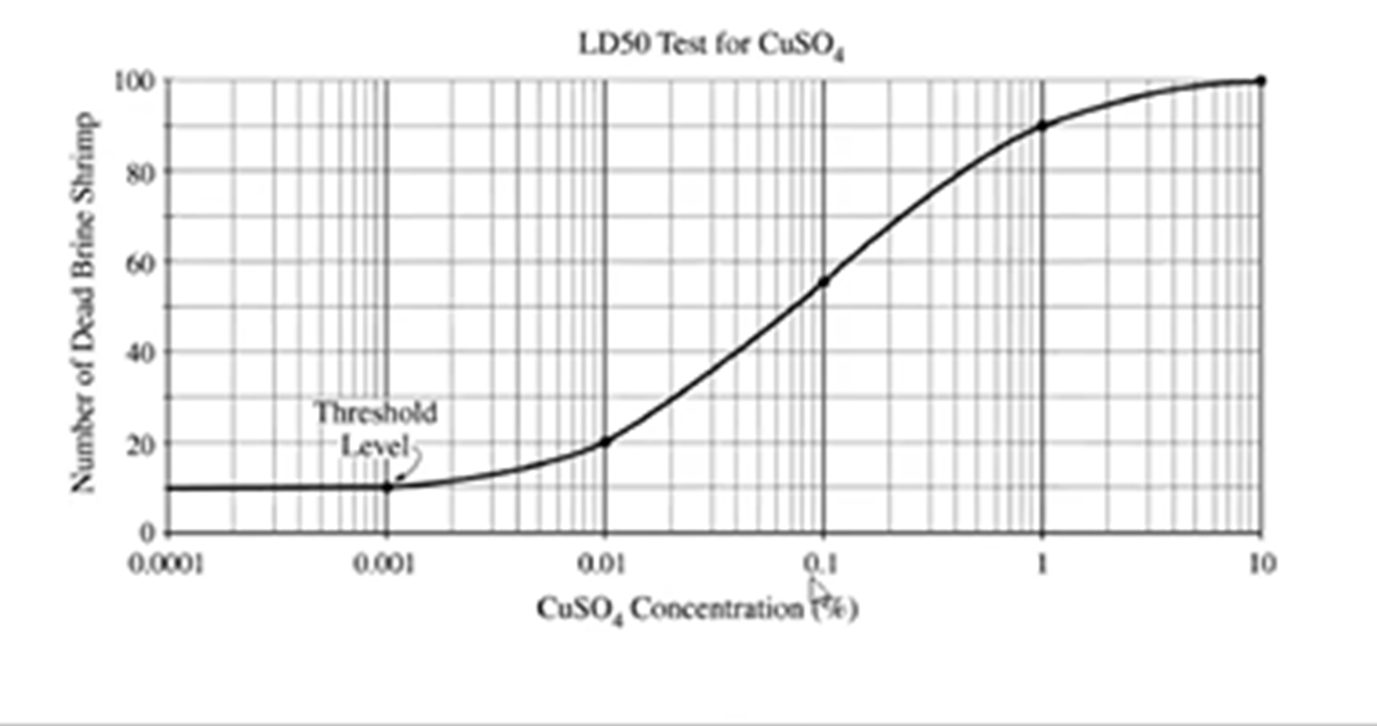
What is the LD50 concentration for brine shrimp?
0.07-0.09 %
Identify one human health concern human health exposure to Tropospheric Ozone (O3)
•Worsens respiratory conditions like asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, COPD
•Limits overall lung function
•Irritates muscles or resp. tract causing constriction of airways & shortness of breath
•Irritates eyes
West Nile
Zika
Malaria
Warmer Temperatures: Mosquitoes thrive in warmer climates. As global temperatures rise due to climate change, regions that were once too cold for mosquitoes to live in are becoming more hospitable. This increases the range of mosquitoes, allowing them to spread into new areas, including higher altitudes and regions previously unaffected by these diseases.
Changing Precipitation Patterns: Mosquitoes need stagnant water to breed. Climate change is altering rainfall patterns, leading to more frequent and intense flooding in some areas, which creates new breeding grounds. In other areas, droughts can lead to people storing water in containers, providing additional breeding sites.
Longer Seasons: Rising temperatures extend the breeding and feeding seasons of mosquitoes, meaning that they are active for longer periods throughout the year, increasing the likelihood of transmission of disease-causing pathogens.
Increased Human Movement: Climate change can also cause displacement, leading to human migration into areas where they may come into contact with mosquitoes carrying diseases they haven't been exposed to before. This increases the risk of disease spread.
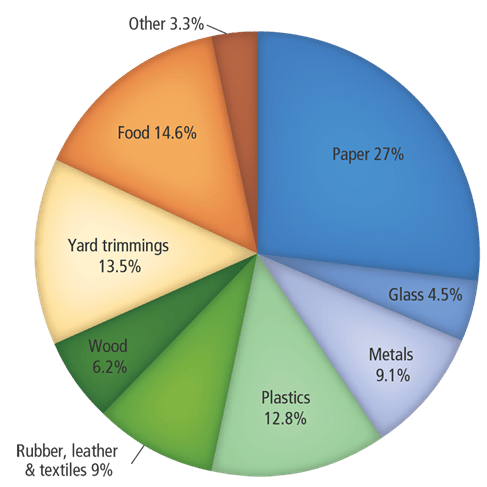
Above is the MSW stream composition of the United States. Propose a solution the federal government could enact that would reduce the volume of waste entering landfills in the US by at least 15%. Use evidence from the graph above to support your proposed solution.
Composting Initiatives (Targeting Yard Waste and Organics)
Plastic Waste Reduction Policies
Food Waste Reduction Initiatives
Expanded Recycling Programs (Targeting Paper, Plastics, Metals, Glass)
Approximately 30 million mobile devices were sold in 1998 in the US. The number sold increased to 180 million devices in 2007.
(a)Calculate the percent increase of mobile device sales from 1998 to 2007.
(a)Each mobile device sold in 2007 contained an average of 0.03 grams of gold. Calculate the number of grams of gold that were used in the production or the mobile devices sold in 2007.
Percent increase = [(1.8 X 10^8 - 3.0 X 10^7)/ 3.0 X 10^7] X 100 = 500%
Total Gold=180 million×0.03 grams Total Gold=5.4 million
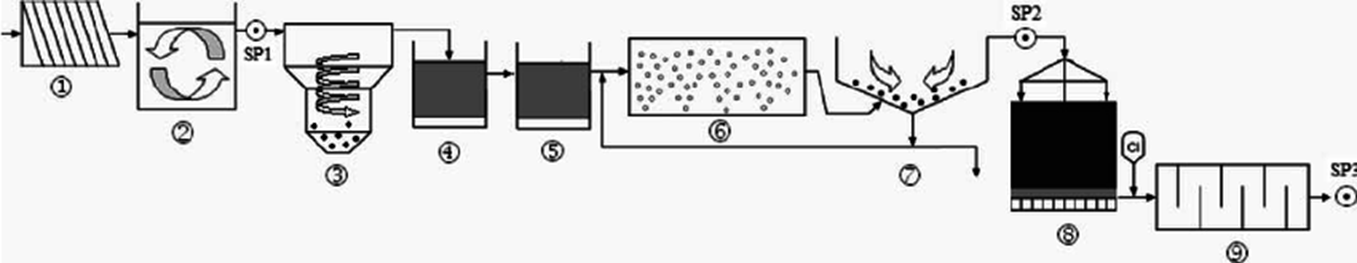
Identify a number on the wastewater treatment diagram below that represents a step of secondary treatment. Describe a pollutant removed by this process.
4, 5, 6 bacteria perform aerobic decomposition to break down of organic matter
Removes 70% phosphorus and 50% nitrogen (does not remove POPs)
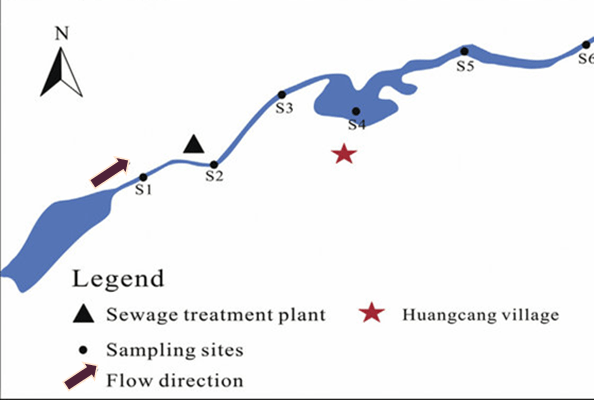
Below is a map of a river that is used as the main drinking water source for the Chinese village of Huangcang. Chinese scientists suspect that the sewage treatment plant is releasing untreated sewage into the river.
a)If scientists plan to measure fecal coliform bacterial counts at the six sampling sites below, make a claim about which site should serve as the control group in the experiment. Justify your answer with evidence.
b)Identify a disease that scientists could test for in the people of Huangcang and explain how the prevalence of this disease would help the researchers determine whether the sewage treatment plant is releasing untreated sewage into the river.
S3 as it is down stream far enough from the plant to determine a good sampling but before the village.
Dysentery is caused directly from untreated sewage released into drinking water.
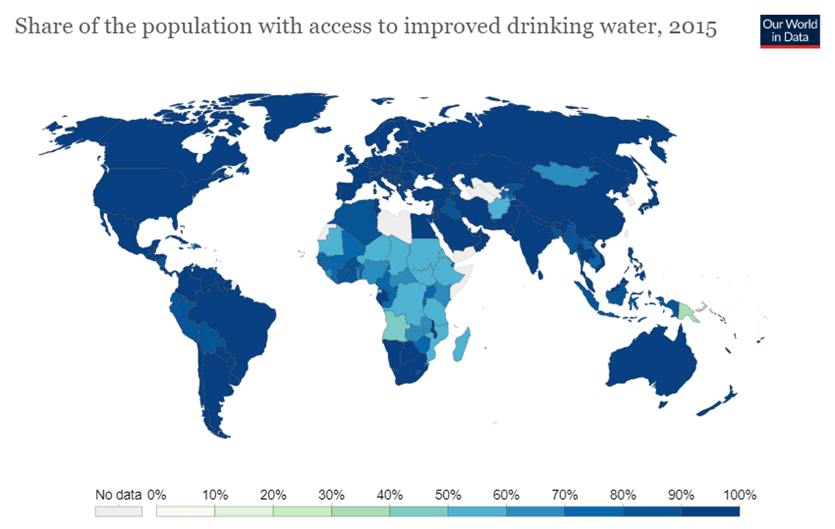
Based on this map, make a claim about a region of the world that likely has a high incidence of Cholera.
Since cholera is a bacterial infection transmitted through contaminated water, regions with limited access to clean water, such as Angola, which has one of the lowest percentages of clean water access in Africa, will be most affected.