Where does the medical terminology, the languages for A & P (and other sciences) stem from?
Latin and Greek
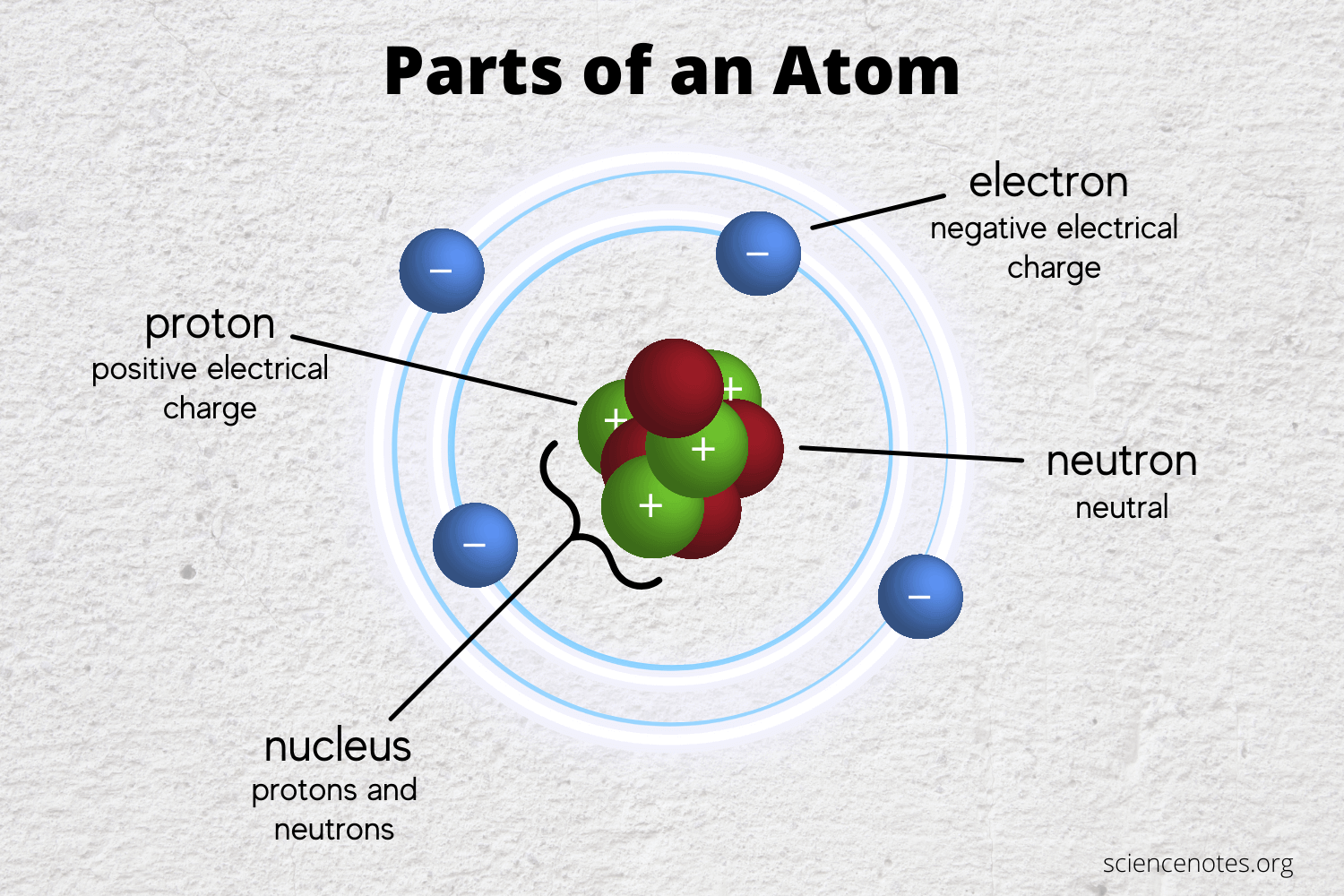
What is the electrical charge of a proton?
Positive
the liquid (semi- or half-liquid) filling the cell is called _________________________.
Cytosol
What is produced on ribosomes?
Proteins
What are the four passive transportation methods to transport particles into and out of the cell through the cytoplasmic membrane?
1. Simple Diffusion
2. Facilitated Diffusion
3. Filtration
4. Osmosis
In the levels of organization, what is the next increasing structure after the tissue?
atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue ....next ?
Organ
Atom structure:
Where are the negatively charged electrons located?
Shells or orbits surrounding the nucleus.
All the content of the cell, including the solid organelles (compartments), as well as the liquid cytosol is called the ________________.
Cytoplasm
What is produced inside (and a few outside) the mitochondria?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP); cell energy.
Which of the two main transportation processes (particles into and out of the cell), Active or Passive Transport requires ATP energy?
Active Transport
What is the largest structure in the levels of organization?
Organism
What two subatomic chemicals are located in the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and neutrons.
Which two organelles have the phospholipid bilayer membranes surround the structure TWICE?
Nucleus and mitochondria.

What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Transporting substances and messages.
Why does Active Transport through the cell membrane (also called cytoplasmic or plasma membrane) require ATP energy?
Because particles move AGAINST the concentration gradient, from a concentration of low to high particles, which in nature always goes the other way around.
Nature: particles automatically move from a higher to a lower concentration (WITH the concentration gradient) to "try" to even both sides out. Movement to the side of low particles is done until both sides have an equal number of particles.
What is the internal stability of the body called?
Homeostasis
If an atom loses or gains one or more electron/s, it becomes an _____________.
Ion
Where are most of the ribosomes located (other than a few disbursed throughout the cytosol)?
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rough_ER-4e539384788e43c498d45acaf500e5bf.jpg)
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus (also called Golgi complex).
Packing, sorting, compartmentalizing, transporting.
What are the four major macromolecules in the human body?
1. CARBOHYDRATES (sugars and starches)
2. LIPIDS (fats and oils)
3. PROTEINS
4. NUCLEIC ACIDS (DNA, RNA, ATP)
Extra information:
SUGARS: a lot of sugar terminology ends in -ose, such as in glucose, lactose/milk sugar, fructose/fruit sugar etc., also, reading labels, saccharide pertains to sugar, such as mono-, di- and polysaccharides
PROTEINS: made up of long chains of amino acids/always containing nitrogen; also, shorter amino acid chains are sometimes called peptides, as in dipeptide or polypeptide
True or False:
The structure of a body part is closely related to its function!
True
What is the charge of an ion that gained an electron?
Negative
What two main chemical structures (in addition to others) is the cell membrane (cytoplasmic membrane or plasma membrane) and the membrane surrounding all organelles, made up of?
Phosphate heads, lipid tails (TWICE); it is a phospholipid bilayer.
What are the two main transportation mechanisms (transporting particles into and out of the cell) called?
Active transport and Passive transport.
Where in an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy molecule are the HIGH ENERGY bonds located (between which chemical groups)?
Between the phosphate groups.
An ATP molecule is made up of an adenine, a ribose sugar and three phosphate groups. When the bond between the phosphate groups is broken, it releases HIGH energy, which can be used to build other large molecules (ANABOLISM)