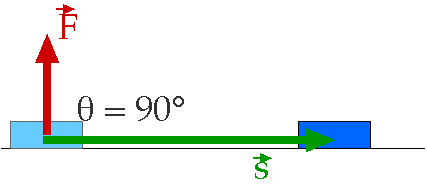 In the image above, the perpendicular Normal Force does this much work on the object shown.
In the image above, the perpendicular Normal Force does this much work on the object shown.
Zero!
 In the images of springs shown, the middle spring is compressed the most, so that box has the most of this type of energy.
In the images of springs shown, the middle spring is compressed the most, so that box has the most of this type of energy.
Potential Energy

In the image shown, the roller coaster cart is at the bottom of a big hill, at rest. A chain must pull the cart to get to the top of the first hill, doing ____ in the process.
Work
Friction is often a force that opposes motion, removing energy from the system and doing this kind of work.
Negative Work
On Earth, a certain object has 200 J of potential energy. On another planet, that same object, held at the same height, has only 150 J of potential energy, because there is less of this.
Gravity
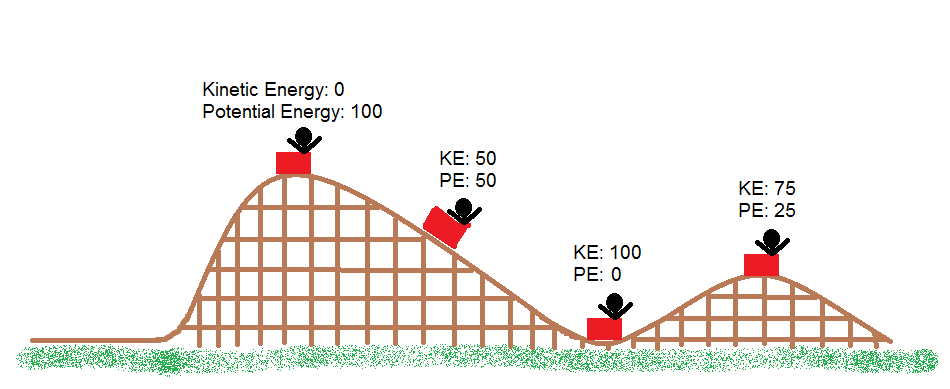
The roller coaster shown is a great example of this physics term, showing that the total energy remains constant in a closed system.
Conservation of Energy
A 5 kg box is sliding at 10 m/s until it reaches a bumpy patch that slows it to a stop over the course of 2 m. How much work is done by the friction of the bumpy patch?
-250 J
A 15 kg object on earth is held 25 m above the ground at rest, how much total energy does it have?
3675 J (or 3750 J)

At the top of the first hill, the cart is at rest with 2200 J of PE, at the bottom of the first hill, the cart has 300 J of PE, and _____ of KE.
1900 J
Jake pulls a large box with a rope to move it 15 meters across the room. If Jake pulls with 210 N and the rope is angled 60o above the ground, how much work does Jake do?
1575 J
At the top of a 52 m cliff, a 5 kg object sits at rest. When dropped off the cliff, the speed of the object will be this much.
31.9 m/s

In the four positions shown, this position is where the cart will have the highest velocity.
C