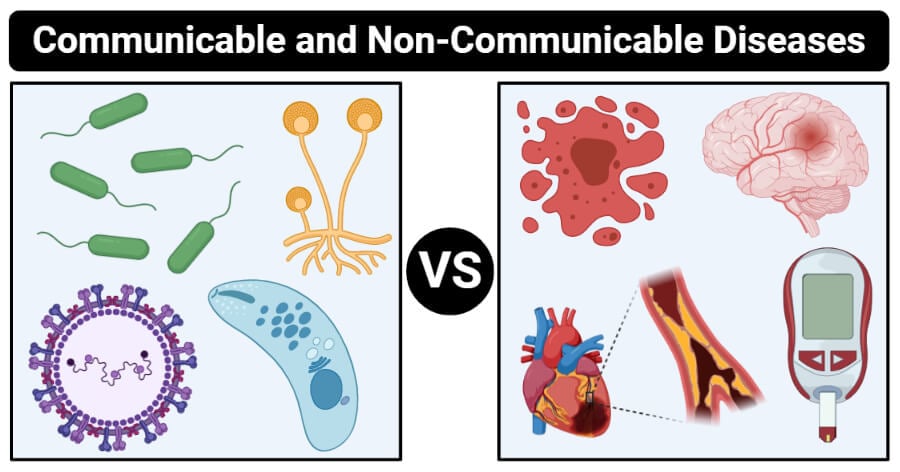
These 2 diseases cannot be spread.
Cancer, diabetes, coronary heart disease#
This element will explode when added to water.

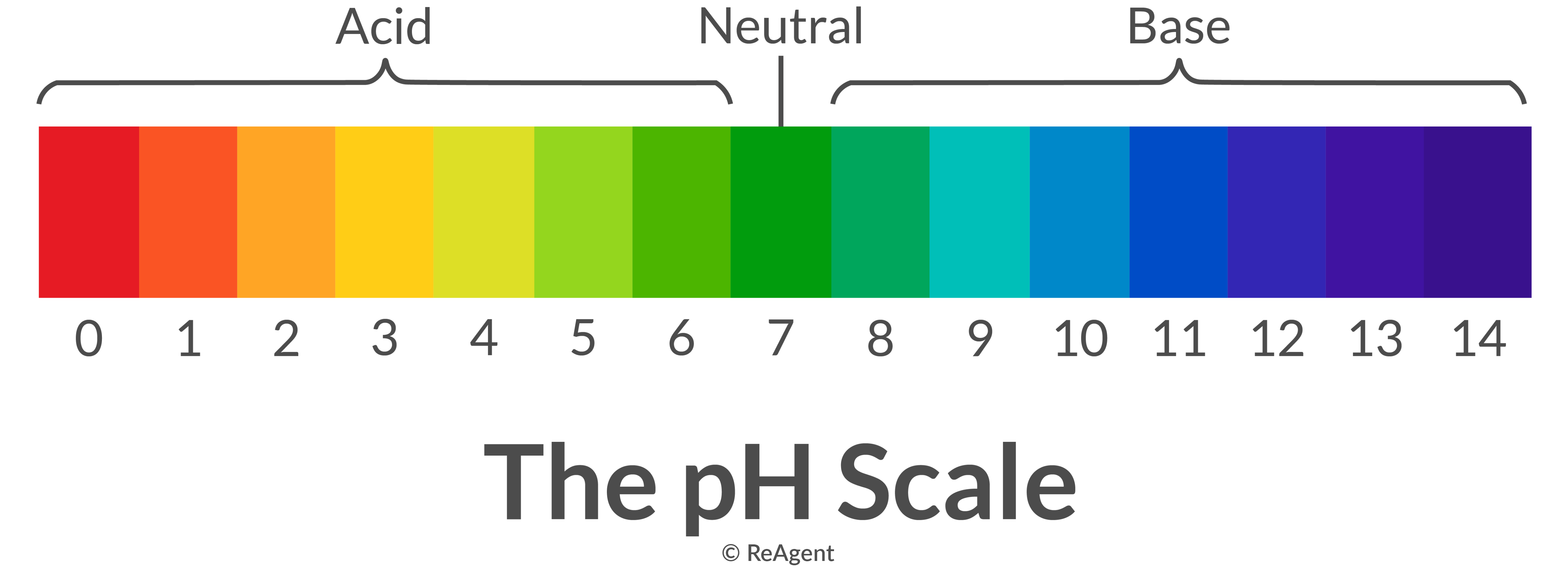
pH <7.
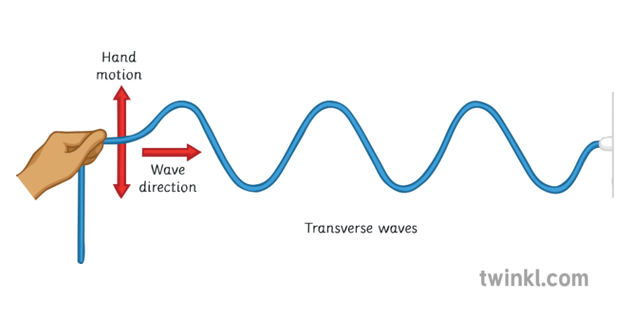
This is the way that transverse waves move compared to the energy transfer.
Perpendicular
Name a safety procedure in a lab WITHOUT mentioning goggles.
No running.
Standing up.
Tying hair.
This chemical makes cigarettes and vapes addictive.

Nicotine.
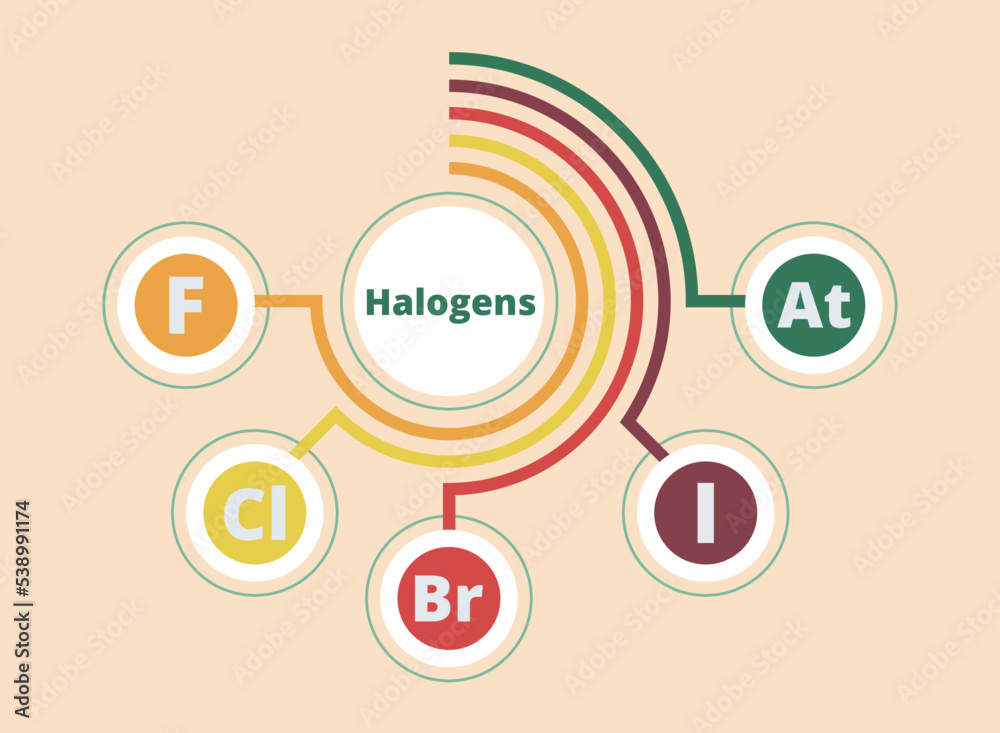
This group gets more reactive as you move UP the group.
Group 7.
This is how you need to extract pure zinc.
Reduction with carbon.

SONAR, medical imaging, non-imaging medicine.
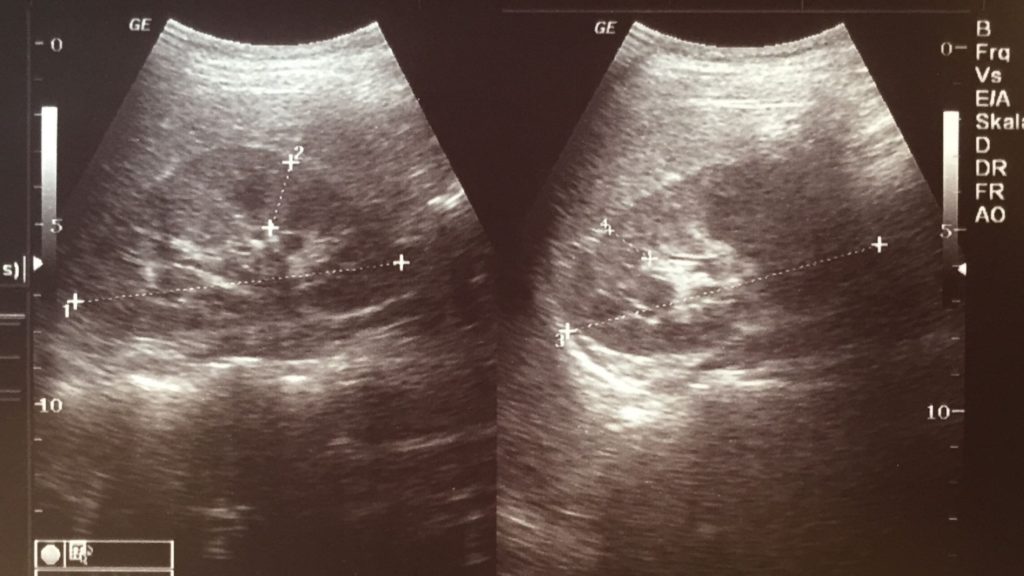
Who is this British man?

This type of protein is found on the outside of a pathogen.

Antigens.
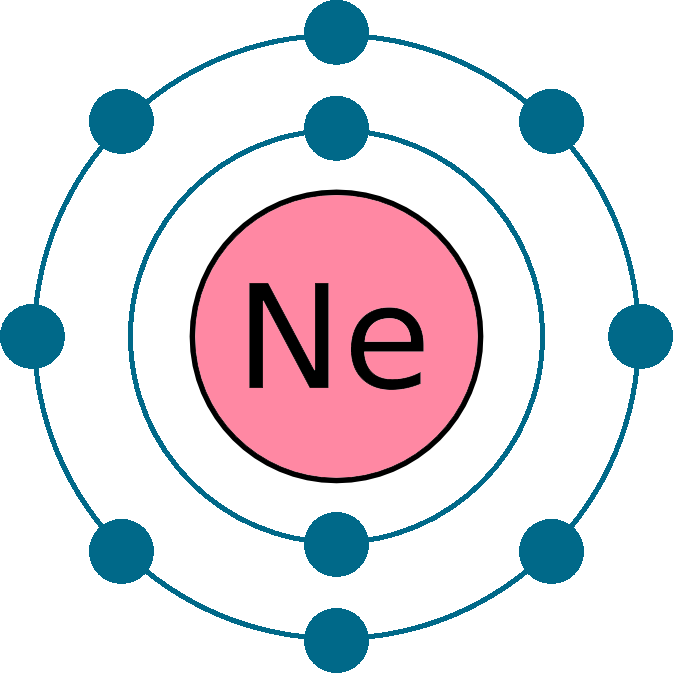
This is why Group 0 is not reactive.
Full outer shell of electrons.
What is formed at the cathode while doing the electrolysis of copper sulfate?

Copper.
Which colour gets refracted the most?
Violet


Name a food high in fiber.

After vaccination, your body produces these to fight off the pathogens.

Antibodies.
Conservation of mass =
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
Name the chemical reaction shown below

Thermal decomposition
What is the name of angle r?

Angle of reflection
Name a used for infrared waves.
Thermal images, remotes.
This is what a vaccine is made of.
(3 Key Words)
Small amount of dead or inactive pathogens.
Balance this equation:
CH4 + _O2 -> CO2 + _H2O
/methanecombustion-58e3e6005f9b58ef7e0daa10.jpg)
Complete the chemical equation.
magnesium carbonate + nitric acid -> _______ ______ + water + carbon dioxide
magnesium carbonate + nitric acid -> magnesium nitrate + water + carbon dioxide
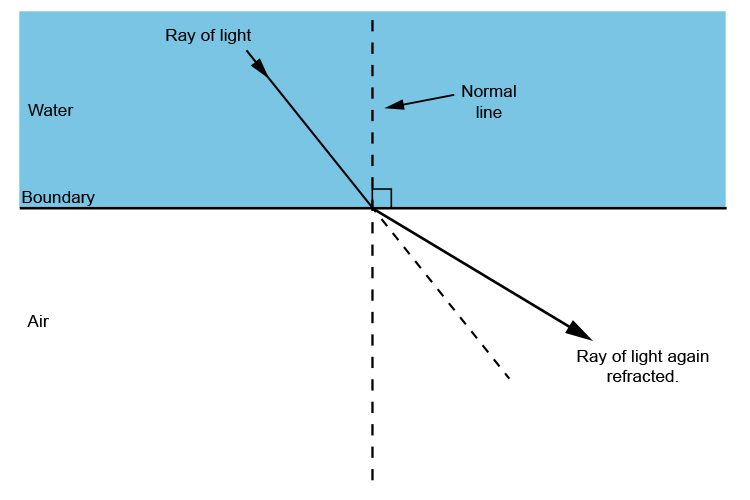
How will light bend against the normal when travelling from water to air?
Away from the normal.
Explain the difference between a group 1 metal and a transition metal.
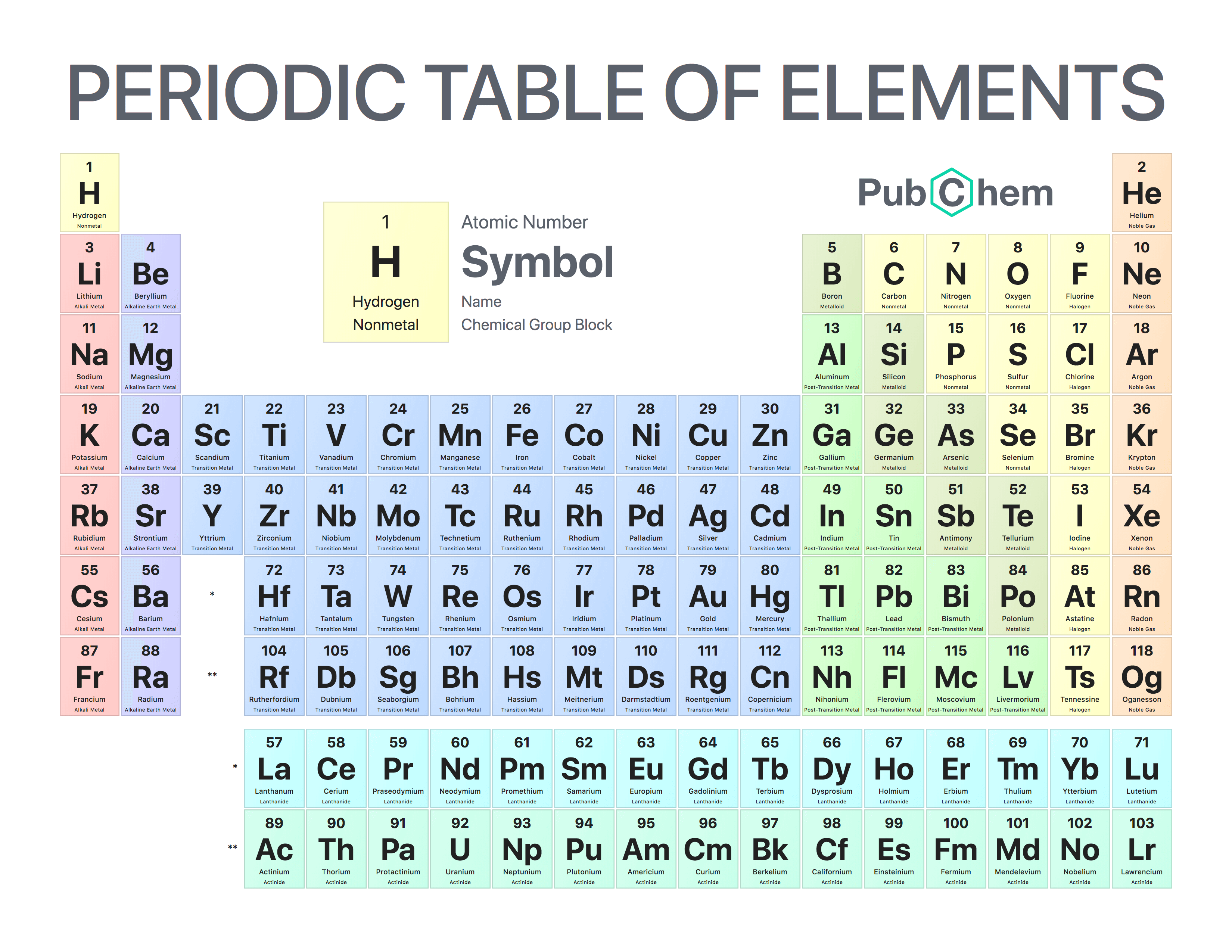
Group 1 metals are soft with low melting points. They also are very reactive.

Transition metals are hard with high melting points. They are not as reactive and form different coloured metals.
