What does the mass number tell you about the atom of each element?
How is the modern periodic table arranged?
protons + neutrons
by increasing atomic number (protons)

The elements all react with water to produce a gas. Name the gas!
hydrogen
Identify if the following are ionic or covalent:
A. Metal joins with a Nonmetal to form a compound
B. Two non-metals join together.
A. Ionic
B. Covalent
Identify if the following are ionic or covalent:
A. When two atoms share electrons
B. When atoms gain or lose electrons
C. When a compound that is dissolved in water conducts electricity.
A. Covalent
B. Ionic
C. (generally) ionic
Identify the following giant covalent structures AND give one application for each.
a. Diamond - drill tips or jewelry
b. Graphite - pencils or lubricants
Sodium has the electronic structure 2.8.1
Draw a bohr model to show it's atomic structure. Include the number of protons and neutrons in the center.


Using the table above...
a. predict the melting point for sodium [1]
b. predict the boiling point for potassium. [1]
a Below 180 °C and above 63 °C (any number between 63-180)
b Below 883 °C and above 688 °C (any number between 688-883)
What is the definition of an ION?
Include how an atom becomes an Anion or Cation.
Ion is an atom (or group of atoms) which has an electrical charge.
Anions have gained electrons to become negative.
Cations have lost electrons to become positive.
What is the chemical formula for this molecule of methane shown?
CH4
A. What holds the lattice together for NaCl?
B. What does this lattice structure tell you about the melting and boiling point of NaCl?
A. The strong electrostatic forces between the positive sodium ions and the negative chlorine ions.
B. The melting- and boiling points of sodium chloride will be high because the electrostatic forces are strong.

Draw the electronic structure of a fluoride ion. Include all electrons, you do not need to show the nucleus.
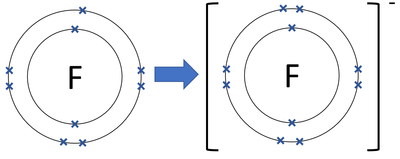
Diagram should be the same as in the question, but with one additional cross in the outer shell.

Predict sodium's reaction with water using the table. Refer to lithium and potassium in your answer.
[1] More bubbles of gas and more heat will be generated than with lithium,
[2] but less than with potassium.
What is an ionic bond? Include the term electrostatic force of attraction in your answer.
An ionic bond is a compound that is formed between oppositely charged ions that are attracted through the electrostatic force.
Write one example for these covalent compounds...
A. Molecule but not a compound
B. Compound AND molecule
C. Macromolecule (Giant Covalent Structure)
A. Any diatomic molecule --> H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
B. ANY covalent compound that has more than one different element (H2O, CH4, CO2, etc)
C. Any giant structure we've covered...DIAMOND, GRAPHITE, DNA, Chromosomes.., proteins etc
Sort the following in terms of their melting points.
Diamond, Water (simple covalent), Graphite
HIGHEST - Diamond - Graphite - Water - LOWEST
Explain why a fluoride ion is more stable than a fluorine ion. [2]
Write the symbol for a fluoride ion. [1]
A fluorine ion is more stable than a fluorine atom because the outer (highest energy level) shell of electrons is full. [2]
F- [1]

What are the mass numbers for the following elements in the table? (23,7,39,85)
What is the trend for reactivity and atomic size for the alkali metals?
[1] Li-7 ,Na-23, K-39, Rb-87
[2] Reactivity AND size increases as you go down the group.
Write the chemical NAME and FORMULA for the bonding between sodium and oxygen.
Name: sodium oxide
Formula: Na2O
What are intermolecular forces?
forces between molecules (that determine physical properties for simple covalent molecules)
Explain the difference between simple covalent structures and giant covalent structures (in terms of atoms).
Simple covalent structures have discrete/fixed numbers of atoms
Giant covalent structures have continuous network of atoms extensively linked by covalent bonds.
Which electrons have the highest energy in a chlorine atom?
The 7 valence electrons have the highest energy because they are the furthest away from the nucleus's electrostatic attraction.
Explain why Potassium is more reactive than sodium. [3]
Include size, electrostatic attraction and what's happening to the valence electron in your answer.
[1] Potassium has more energy levels/shells/size is bigger
[1] so it's valence electron has the weakest electrostatic attraction to the nucleus
[1] making it easier to be loss (transferred to another atom)
Write the electronic structures for the bonding between aluminium chloride. Include how many chloride ions there will be.
Al3+ = [2,8]
Cl- = [2,8,8], Cl- = [2,8,8], Cl- = [2,8,8]
Draw the dot-cross diagram for a molecule of ammonia NH3

Explain why ionic compounds dissolved in water and graphite conduct electricity while most simple covalent compounds and diamond do not.
Ionic compounds have free moving ions when placed in water
Graphite has delocalized electrons (free moving electrons)
Simple covalent and diamond has neither of these for charge to flow.