DNA stands for?
deoxyribonucleic acid
Transcribe means to?
Copy
Translation occurs before or after transcription?
After
Name the 3 steps of speciation
1. Variation
2. Isolation
3. Selection
What is the shape / structure of DNA?
Double helix
DNA base pairs?
A/T
C/G
Describe the basic process of translation.
mRNA sequence is translated (converted) into amino acids. Amino acids build a chain, which codes for a protein. This protein codes for a trait.
Define natural selection.
Process by which an environmental factor acts on a population and results in some organisms having a greater chance of survival and producing more offspring than others.
The sugar in DNA is?
Deoxyribose sugar
RNA base pairs?
A/U
C/G
Give the name of the type of chain that is build by amino acids during translation.
Polypeptide chain (protein)
Species survive through what suiting their environment
Adaptations, traits
DNA is made of?
Sugar, phosphate and nucleotide base
Transcribe the following DNA template strand into mRNA...
ATG CGT CAT TTA
UAC GCA GUA AAU
Use the codon chart to find the amino acid.
GUA

Val
Identify the sources of evidence for evolution.
- fossil record
- comparitive anatomy
- DNA sequencing
- Geographic distribution
This is called a?
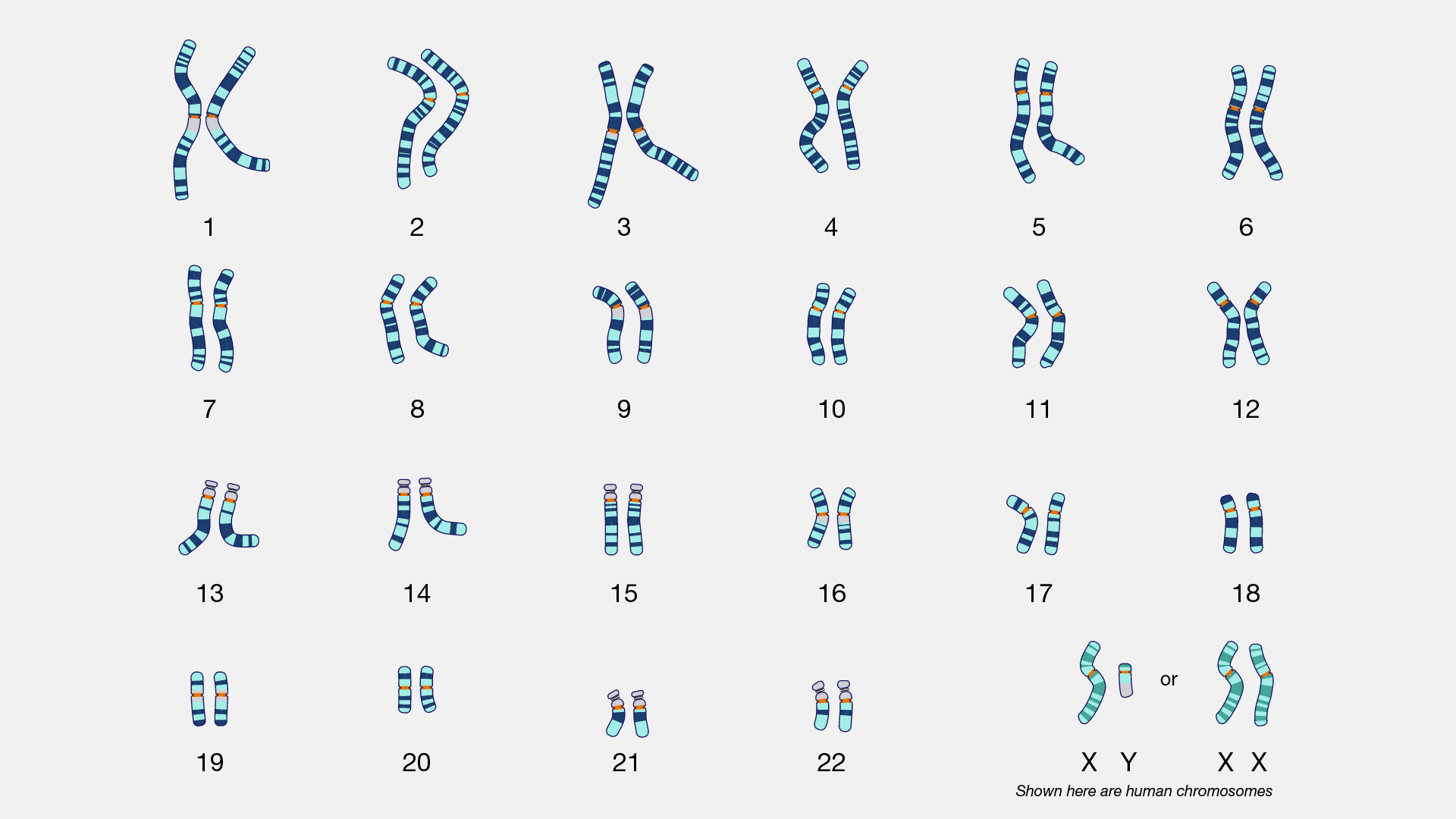
Karyotype
How can DNA mutations arise?
Spontaneously or by damage to a strand of DNA.
Translate the following using the codon chart.
ACG GGG CGC AUG GUU

Thr, Gly, Arg, Met, Val
Describe how Darwin's finches provide evidence for evolution through natural selection.
- Darwin observed the Galapagos finches had a graded series of beak sizes and shapes and predicted these species were modified from one original mainland species.
- Darwin called differences among species natural selection, which is caused by the inheritance of traits, competition between individuals, and the variation of traits.
- Offspring with inherited characteristics that allow them to best compete will survive and have more offspring than those individuals with variations that are less able to compete.
- Large-billed finches feed more efficiently on large, hard seeds, whereas smaller billed finches feed more efficiently on small, soft seeds.
- When small, soft seeds become rare, large-billed finches will survive better, and there will be more larger-billed birds in the following generation; when large, hard seeds become rare, the opposite will occur.