What are three ways to determine the age of a fossil.
Carbon Dating
Index fossil dating
Relative ageing
What is the difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction?
Exothermic releases energy (heat), endothermic absorbs energy.
What is the main fuel for a star during most of its life?
Hydrogen (undergoing nuclear fusion)
Name the four spheres of the Earth.
Biosphere, Lithosphere (Geosphere), Atmosphere, Hydrosphere.
What is one feature of the exosphere?
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth’s atmosphere.
Air is extremely thin, and particles can escape into space.
It contains mostly hydrogen and helium.
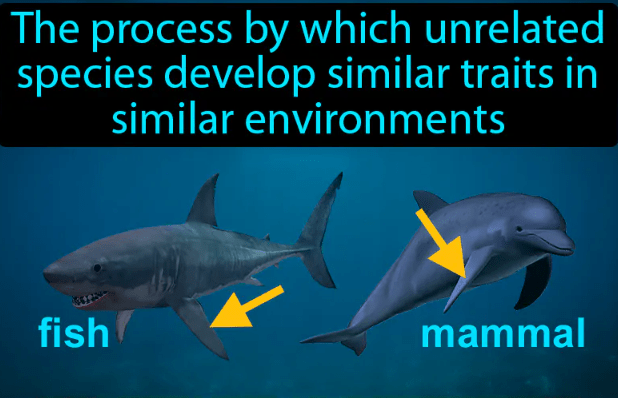
Convergent Evolution
Give an example of a neutralisation reaction.
Acid + base → salt + water
(e.g., HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O).
Name one type of telescope used to observe space.
Optical telescope, radio telescope, X-ray telescope
What is one layer of the atmosphere?
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Exosphere.
What type of graph would best show how temperature affects reaction rates?
Line graph
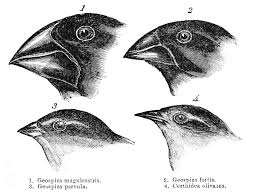
When a single species evolves different traits to help them survive, often due to environmental change or geographic isolations.
Divergent Evolution
What is the main difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds transfer electrons; covalent bonds share electrons.
What is an Astronomical Unit (AU) used to measure?
distances, primarily within our solar system
The average distance between Earth and the Sun (~150 million km)
Give an example of how a volcanic eruption impacts all four spheres.
Lithosphere – lava flow
Atmosphere – ash
Hydrosphere – acid rain
Biosphere – destroyed habitats.
Explain red-shift and what it tells us about the universe.
Light from distant galaxies is shifted to longer wavelengths, indicating they are moving away → the universe is expanding.
What is speciation?
Formation of new species from one original species, usually due to isolation and selection pressures.
What is particle theory and how does it explain reaction rates?
Matter is made of tiny particles that move; increasing temperature, concentration, or surface area increases collision frequency → faster reactions.
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where are main sequence stars located?
Diagonal band from top-left (hot, bright, more massive) to bottom-right (cool, dim, less massive).
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Extra warming caused by human-produced greenhouse gases trapping more heat in the atmosphere.
Describe how acid reacts with a metal and explain why bubbles appear.
Acid reacts with metal to form a salt and hydrogen gas; bubbles are hydrogen gas being released.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Homologous – same structure, different function; Analogous – different structure, same function.
What is the word equation for photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen (with sunlight and chlorophyll)
Explain hydrogen nuclear fusion in stars and the energy it produces.
Hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei, releasing energy as light and heat.
Which process in the nitrogen cycle converts atmospheric nitrogen into forms plants can use?
Nitrogen fixation
Explain how acid rain is linked to human activity and its impact on ecosystems.
Burning fossil fuels releases Sulfur dioxide and Nitrogen oxides → reacts with water → acid rain; damages plants, water quality, soil.