what does the mitochondria do?
It is the powerhouse of the cell.
Osmosis involves the movement of what substance?
Water. Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
What are large lower chambers of the heart are called?
Ventricles
What is this?: C6H12O6
glucose
What is a hypothesis?
a testable statement that describes how experimenters expect the dependent variable to change as the independent variable changes
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate.
Describe the direction of movement of particles during diffusion.
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
List 4 of the 8 qualities that all living things have in common.
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity (respond), Growth, Reproduction, Equilibrium, Excretion, Nutrition
List the following in order of complexity: systems, tissues, cells, organs
Cells, tissues, organs, systems
Name 3 things missing from this line graph.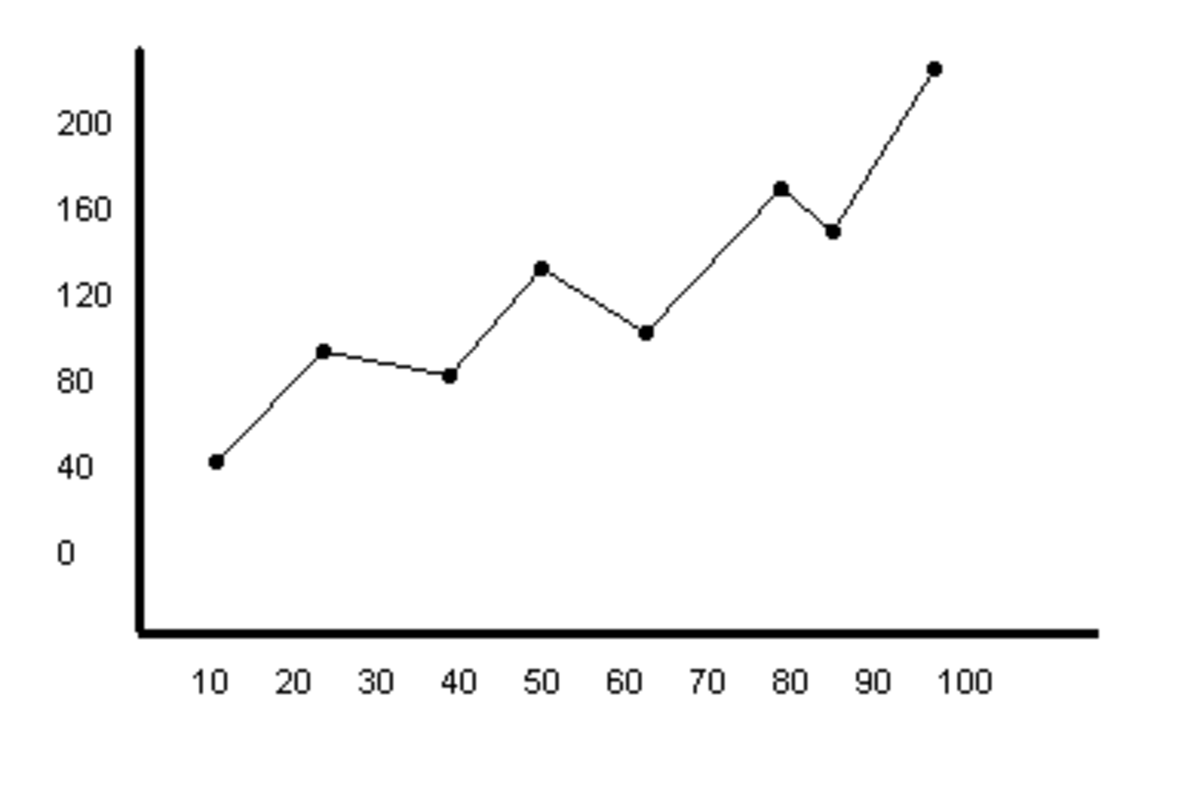
y-axis label
x-axis label
Title
What is the function of a nucleus?
Contains and protects the genetic information (DNA) of the cell.
What are 2 functions of the plasma membrane?
Protection
Barrier - separates the internal environment from the external
Allows substances in and out of the cell
Name 3 differences between a plant and animal cell.
Plants have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole and a cell wall.
What is the relationship between DNA and chromosomes?
DNA contains the instructions, genes, to make proteins that tell what genetic traits the person will have. The DNA along with the proteins make up the chromosomes.
What is one way scientists try to make their results more reliable or fair?
Why are cells so small?
To increase the surface area to volume ratio.
The important point is that the surface area to the volume ratio gets smaller as the cell gets larger. Thus, if the cell grows beyond a certain limit, not enough material will be able to cross the membrane fast enough to accommodate the increased cellular volume.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Passive transport is a movement of ions and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input. Active is movement into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy.
What is photosynthesis?
What are 2 of the inputs and 1 of the outputs of the process?
the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water (inputs). Photosynthesis in plants generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen (output) as a byproduct.
what is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic?
anaerobic - doesn't requires oxygen
aerobic - requires oxygen
An experiment that investigates the effect of light colour on plant growth. What are the independent variable and dependent variable?
IV - light colour
DV - amount of growth
what is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate, and then release waste products.
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis?
endo - the taking in of matter by a living cell by invagination of its membrane to form a vacuole.
exo - a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
What advantage does internal fertilization have compared to external fertilization?
Internal fertilization - more protection.
Even though fewer offspring are produced through this method, their survival rate is higher than that for external fertilization.
What is the difference between and a genotype and phenotype?
A genotype refers to the genetic characteristics of an organism. A phenotype refers to the physical characteristics.
What is the difference between causation and correlation?
correlation - when there is a relationship between two variables.
causation - when change in one variable leads to reliable change in another