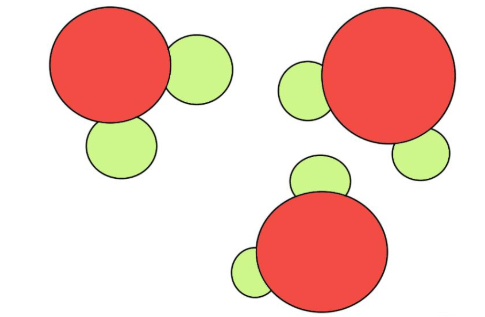
What is the difference between solid sphere model and the plum pudding model?
Solid Sphere (Dalton -1803): recognised that atoms for one element are different to other elements
Plum Pudding (Thomson - 1904): recognised electrons are a part of atoms
What state has particles sliding past each other, by tumbling and rolling, does not have a fixed shape but DOES have a fixed volume?
Liquid
Which state of matter has the fastest moving particles?
Gas
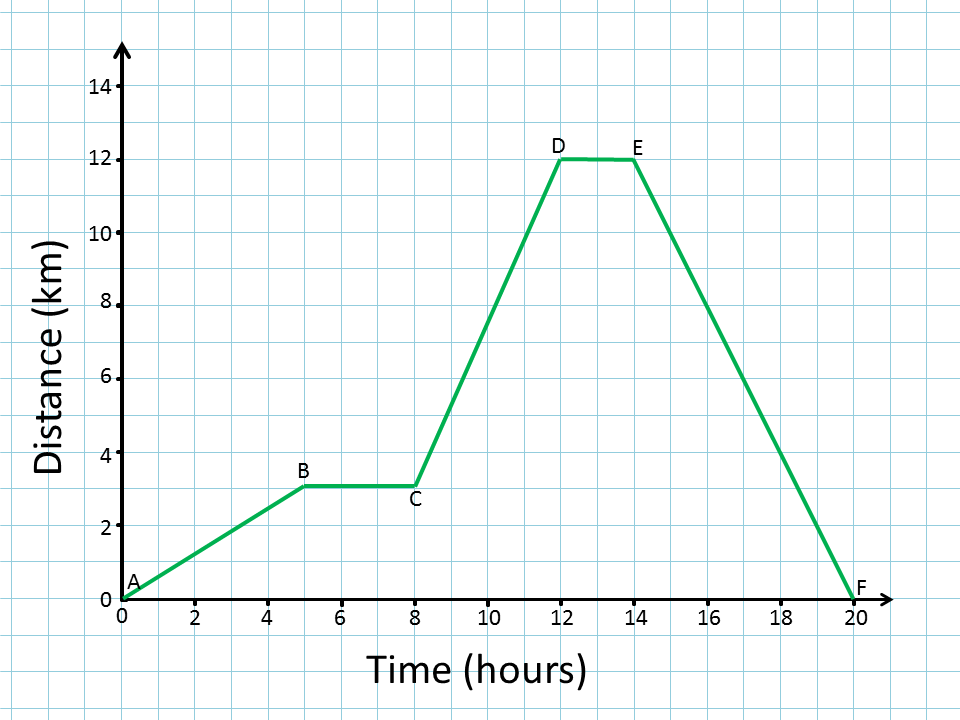
What is the Independent Variable on this graph?
Time (hours)
Physical or chemical change? Why?
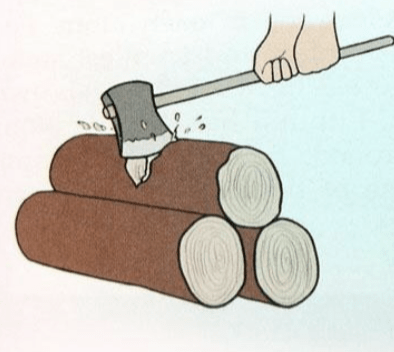
Physical:
- same state, no new substance, change in shape and size
A scientist who works at a university writes an article. Is this usually credible?
Yes – experts with qualifications are more reliable.
What is the smallest particle of an element?
Atom
What is the difference between the plum pudding model and the nuclear model?
Plum Pudding (Thomson - 1904): recognised electrons are a part of atoms
Nuclear Model (Rutherford - 1911): realised that there is a positive charge in the nucleus of an atom
What state has rapidly moving particles that are far apart, and does not have a fixed shape or volume?
Gas
How are the particles arranged in a solid, liquid, and gas?
Solid - close together and packed
Liquid - Slide past each other - still close
Gas - Far apart - moving rapidly
What is the dependent variable on this graph?
Distance (km)
What demonstrates that a physical change is occurring?
Change in:
- size
- shape
- state
- no new substance formed
- can be reversed
Which is more credible: an article by a high school student who did one experiment, or an article from a scientific journal? Why?
Scientific Journal – repeated testing, reviewed by experts.
What do we call two or more atoms bonded together?
Molecule
What is the difference between the Nuclear Model and the Planetary Model?
Nuclear Model (Rutherford - 1911): realised that there is a positive charge in the nucleus of an atom
Planetary Model (Bohr - 1913): proposed stable electron orbit, explained the emission spectra of some elements
What state vibrates in place, has strong forces, and has a definite shape and volume?
Solid
What are the key components of the particle model?
- Matter is Made Up of Tiny Particles
- Particles are Always in Motion
- Particles Have Spaces Between Them
- Particles Interact with Each Other
- Energy Affects Particle Motion
Describe the trends of this graph from point to point:
A-B: as time increases from 0-5 hours, the distance increases by 3km.
B-C: Time is increasing from 5-8 hours, but the distance is staying the same (3km)
C-D: Time and distance increase rapidly from 8 to 12 hours and 3 to 12 km.
D-E: The graph plateaus, thus time increase (by 2 hours), but distance stays the same (12km)
E-F: The slope of the line rapidly decreases from 16 hours to 20 hours, over 12 kms
What is an indicator of a chemical change?
- Colour
- Temperature
- A solid (precipitate) is formed
- Gas is produced (bubbles)
True or False: Personal stories (“I tried this and it worked for me”) are strong scientific evidence.
True
Water (H₂O) is an example of what?
A compound
What is the difference between the Planetary Model and the Quantum Model?
Planetary Model (Bohr - 1913): proposed stable electron orbit, explained the emission spectra of some elements
Quantum Model (Schrodinger - 1926):
- Shows electrons don’t move around the nucleus in orbits, but in clouds with no foxed positions
- Still wildly accepted as most accurate model
Explain why gases can be compressed but solids and liquids cannot.
The particles in a gas are very far apart, with large spaces between them. When pressure is applied, the particles can be pushed closer together, reducing the volume.
How does the particle model explain why gases spread out to fill a container?
Their particles are far apart and move quickly in all directions. Since they aren’t stuck together, they keep moving until they spread evenly through the whole space.
How far did the person/object travel in segment C to D?
9km
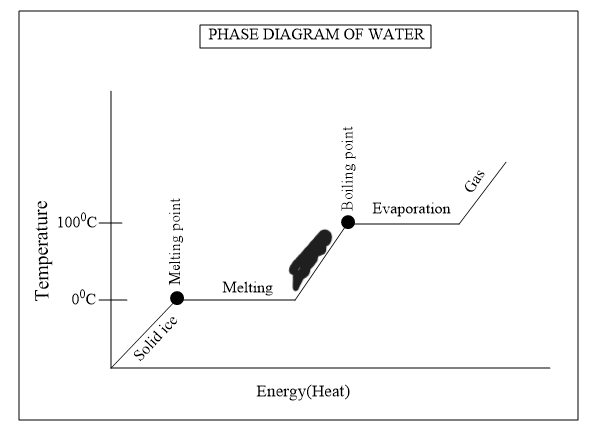
Is boiling water considered a physical change?
Yes - going form a liquid to a gas (state change)
An article uses lots of emotional words like “This is the ONLY solution!” Does this increase or decrease reliability?
Decrease – it shows bias.
What does this picture show?
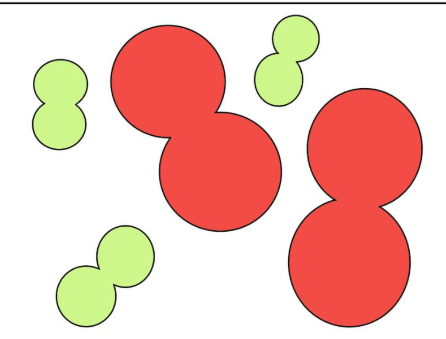
Elements, molecules, mixture
What is the difference between the Solid Sphere Model and the Quantum Model?
Solid Sphere Model (Dalton - 1803):
- recognised that atoms for one element are different to other elements
Quantum Model (Schrodinger - 1926):
- Shows electrons don’t move around the nucleus in orbits, but in clouds with no foxed positions
- Still wildly accepted as most accurate model
Compare particle movement in a liquid and a gas.
Liquid: Particles are close together but can slide past each other. They move more slowly than gas particles. This lets liquids flow and take the shape of their container, but they keep the same volume.
Gas: Particles are far apart and move very fast in all directions. They spread out to fill the whole container and can be compressed.
How is section A-B different from section D-E?
A-B: The two variables of time and distance are BOTH increasing.
D-E: Only time is increasing, distance is staying the same.
Is this a chemical or physical change? Why?

Chemical change:
- colour change: nail goes from grey to orange; solution goes from blue to yellow
- new substance has formed: the nail has rusted
Why is it important that health advice comes from doctors or medical organisations instead of random blogs?
Experts know evidence-based science.
What does this image show?