What is a hypothesis and what must it include?
A hypothesis is a testable prediction. It must include the independent and dependent variable and a prediction of the outcome.
What instrument is used to measure the volume of a liquid?
Measuring cylinder (graduated cylinder).
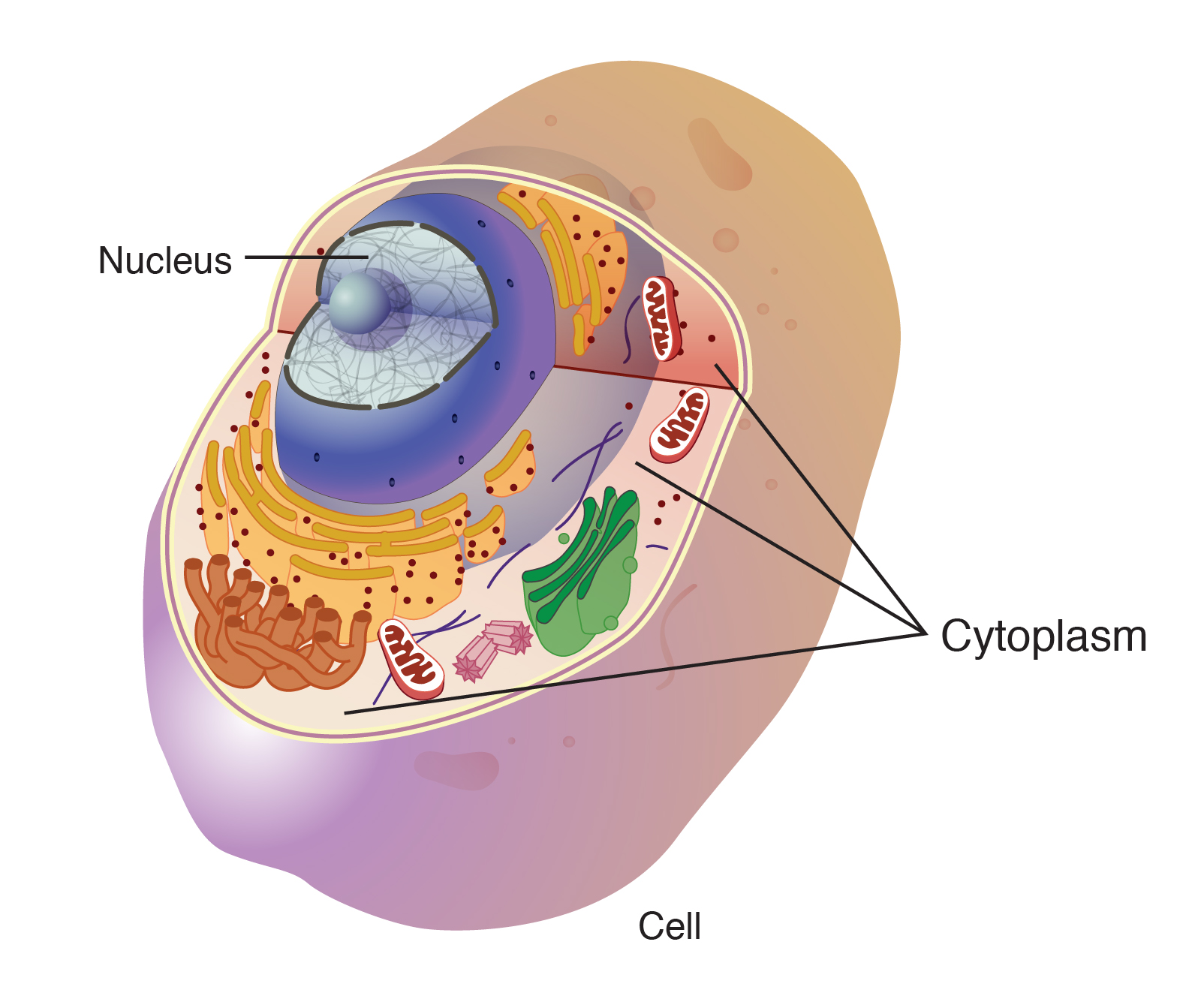
What part of the cell controls all of its activities?
The nucleus.
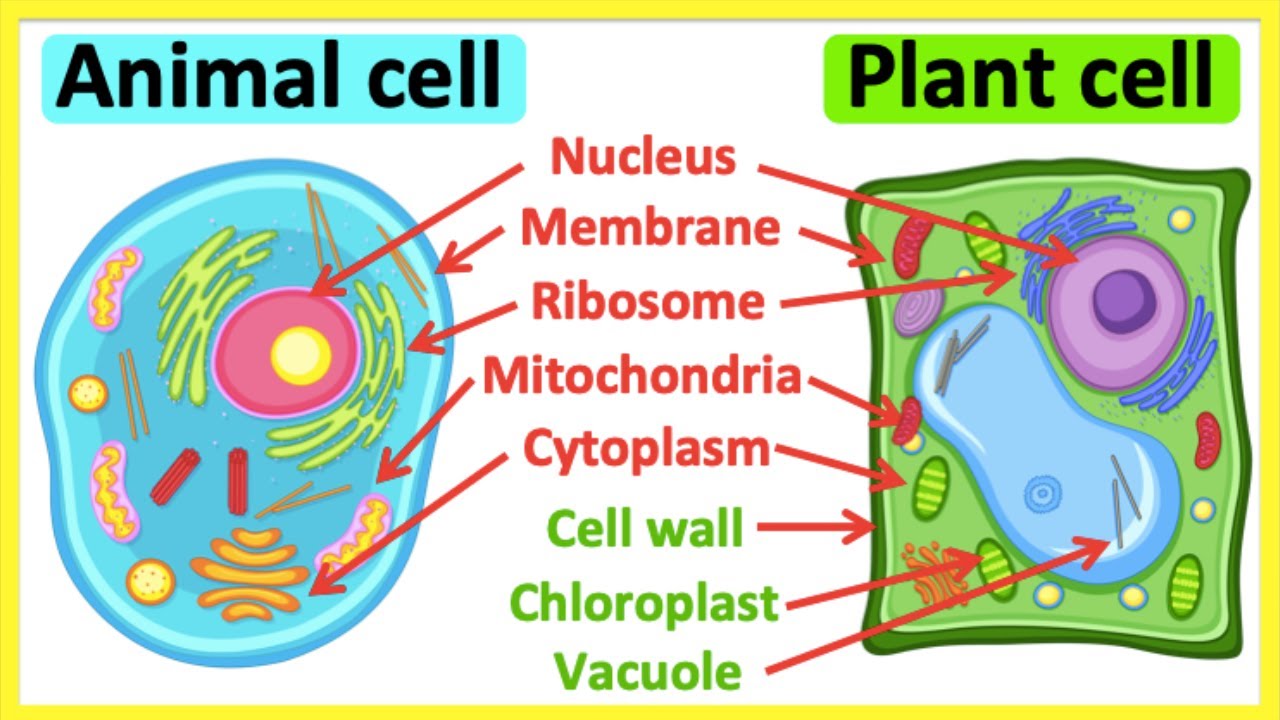
What is the difference between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells have chloroplasts, a large vacuole, and a cell wall; animal cells do not.
What does "unicellular" mean?
Made of only one cell.
Identify the independent variable in this investigation: "How does the amount of water affect the growth of yeast?"
The amount of water.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? Give an example of each.
Qualitative = observations using senses (e.g. colour, texture); Quantitative = numerical data (e.g. 5 cm).
What is the jelly-like substance that holds all the organelles in place?
The Cytoplasm

What are two organelles that are found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
Chloroplast and cell wall.

What type of organism is yeast: unicellular or multicellular?
Unicellular.

How can you increase the reliability of an experiment?
Repeat the experiment more times (multiple trials) and take the average
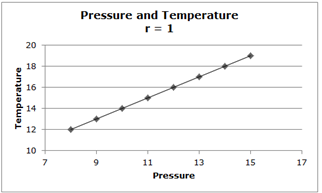
Describe this trend
A positive relationship - A graph shows that as pressure increases, the temperature increases.
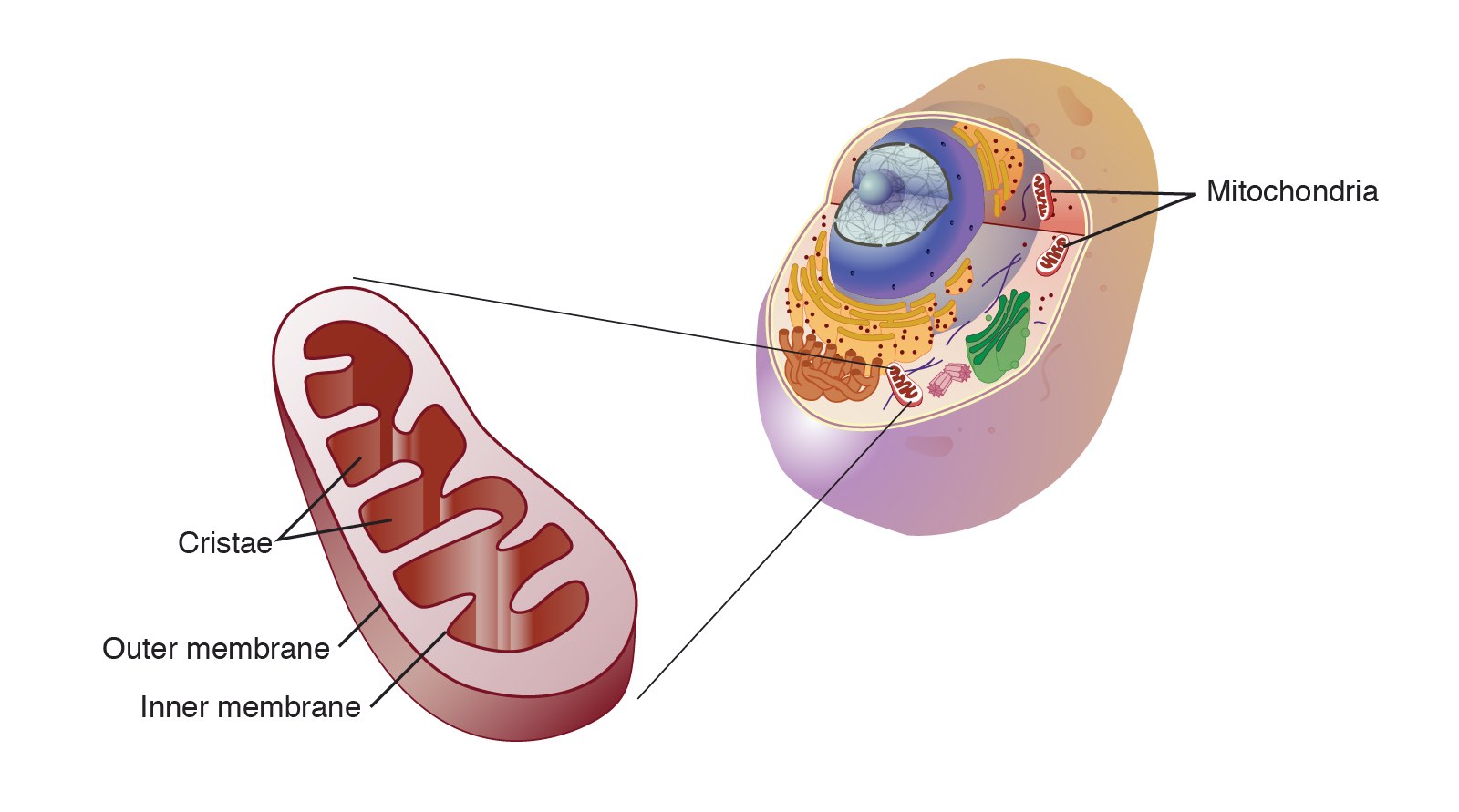
Which organelle is responsible for releasing energy from food?
Mitochondria
Identify this structure: A rigid layer that surrounds the plant cell and provides support.
Cell wall.
Arrange the following from simplest to most complex: tissue, cell, organ, body system.
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Body System.
What is the purpose of a control variable in a scientific investigation?
To provide a standard for comparison; it shows what happens when no variables are changed.
A student counts bubbles produced by a plant in sunlight. Name one error they might make and how to reduce it.
Human error in counting; reduce it by repeating trials and averaging results.
Explain the difference between the function of a chloroplast and a mitochondrion.
Chloroplasts do photosynthesis (make food); mitochondria release energy from food.
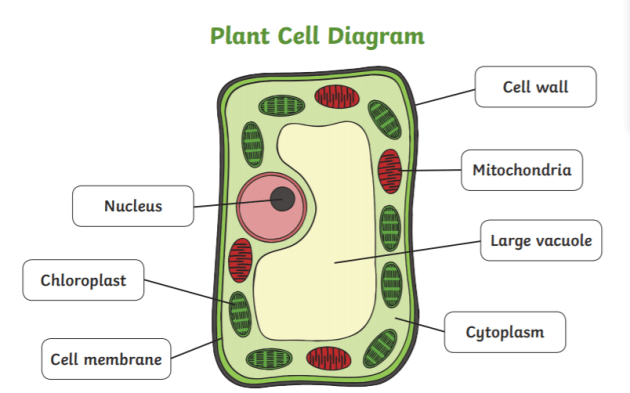
A student finds a new cell under a microscope. How could they determine if it’s a plant or animal cell? List at least two features.
Look for chloroplasts or a cell wall (plant); lack of these indicates an animal cell.
What is a specialised cell? Give one example and its function.
A cell that performs a specific function, e.g., red blood cells carry oxygen.
Design an experiment to test how temperature affects the growth of mould. Include aim, IV, DV, and one controlled variable.
Aim: To investigate how temperature affects mould growth.
IV: Temperature.
DV: Amount of mould growth.
Controlled: Type of food, amount of moisture, and time.
You are given three sets of results from an experiment. Explain how you would calculate the average and why this is important.
Add all values, divide by the number of trials. It improves reliability and reduces the impact of outliers.
Why do muscle cells have more mitochondria than skin cells?
Because they need more energy to contract and perform movement
What are the chemical equations for Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration.
What organelle is responsible for these processes?
Photosynthesis - Chloroplasts
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen

Cellular Respiration - Mitochondria
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy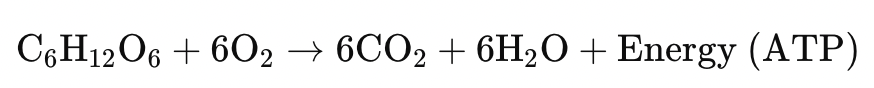
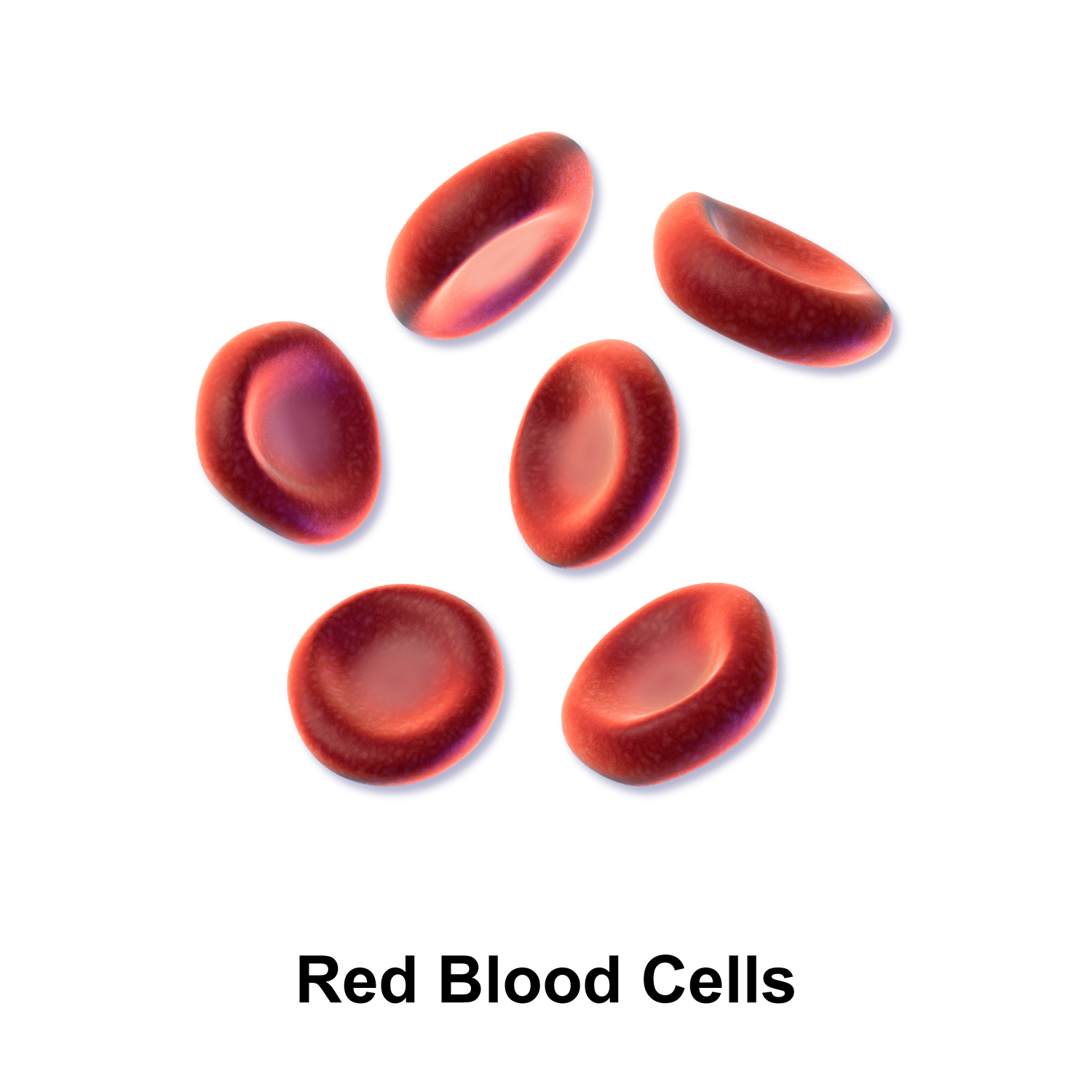
Explain how the structure of red blood cells helps them perform their function. Include two key features.
They are disc-shaped for smooth flow and have no nucleus for more space to carry oxygen.