The concept focussing on the relationships, interactions, and connections between people, places, and systems. It explores how various elements and processes are interrelated and impact each other.
Interconnection
The two processes that form coastal landforms from the movement of water and wind.
Erosion and deposition
The type of map that displays both natural and cultural features along with elevation to display the shape of the Earth’s surface.
Topographic map
The term for the movement of water in a wave as it breaks onto a beach.
Swash

A naturally formed feature on the Earth’s surface, having a characteristic shape or form.
Landform
The internal forces that help to shape the Earth's surface.
Tectonic movements
The term for the movement of water from a broken wave as it runs down a beach returning to the ocean.
Backwash

The concept relating to the unique characteristics and qualities that distinguish one location from another. It encompasses the physical, cultural, and human aspects that give a specific area its identity.
Place
The large, powerful storm waves that have a strong backwash and weaker swash. They are involved in erosive processes.
Destructive waves

The mapping feature that displays the origin of the map, so the reader knows where the information comes from.
Source
The accumulation of sediments on the coast.
Beach
A landscape characterised by dry, desert-like conditions with very limited rainfall.
Arid landscape
The deepest trench on Earth is:
*Double points if you can identify the deepest point within this trench at almost 11,000m deep!
The Mariana Trench
*Challenger Deep is the deepest place on Earth
The less powerful, gentle rolling waves with a strong swash and very weak backwash. These are involved in deposition processes.
Constructive waves
This concept encompasses the natural and built surroundings in which humans and other organisms interact. It involves understanding the interplay between the physical environment, ecosystems, and human activities.
Environment
Identify this feature:
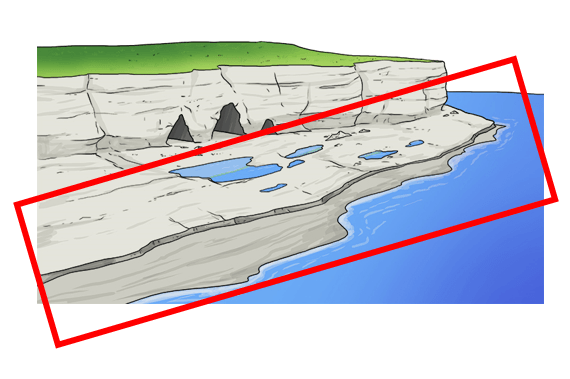
*Double points: is it formed by erosion or deposition?
Wave cut platform (or shore platform)
Formed by EROSION.
Displays all the symbols and colours that are used to represent features on a map.
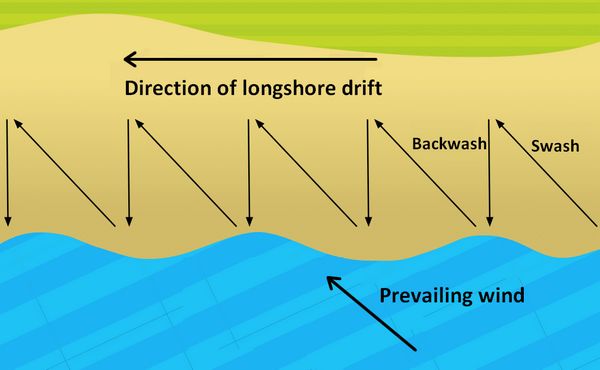
The process by which material like sand and shells is moved along a beach in the same direction as the prevailing wind.
Longshore drift
The landscape represented by areas consisting of human-made structures and infrastructure.
Urban (or human) landscape
Sea-floor spreading occurs at which type of tectonic boundary?
Divergent plate boundary

The formation made up of a long, narrow ridge of sand with one end connected to the land and the other extending out to sea.
*Double points if you can identify the process that makes this occur.
Spit
The concept addressing the balance between meeting the needs of the present generation while ensuring the well-being of future generations and the health of the planet. It involves considering environmental, social, and economic factors to promote responsible resource use and conservation.
Sustainability
A formation referring to a long, narrow ridge of sand linking the mainland to an island.
Tombolo
The Prime Meridian passes through this part of London.
Greenwich, United Kingdom
The landform that has a high, steep-faced rockface that protrudes into the sea.
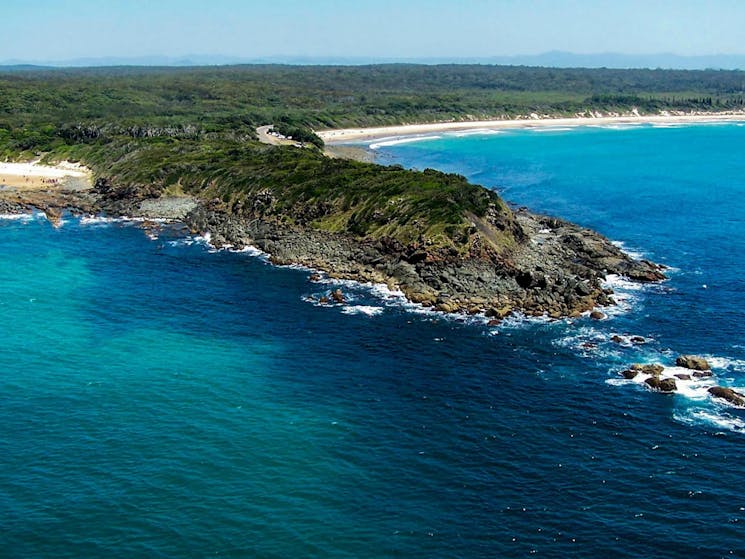

Headland
What scientific instrument is used to record seismic activity?
Seismograph
Basaltic rock
Which formation is the result of two back-to-back caves eroding to form a tunnel through a headland?
Arch
The concept referring to the physical dimensions, locations, and arrangements of objects, places, and phenomena. It involves understanding how areas are organised and the relationships between them.
Space
The shaping process that results in a stack formation.
Erosion.
What type of slope does an area with widely spaced contour lines result in?
A gentle slope
The coastal management technique involving planting natural grasses and shrubs that help bind the sand and reduce erosion.

Dune revegetation
Name the pipe that carries magma from the volcanic chamber to the vent.
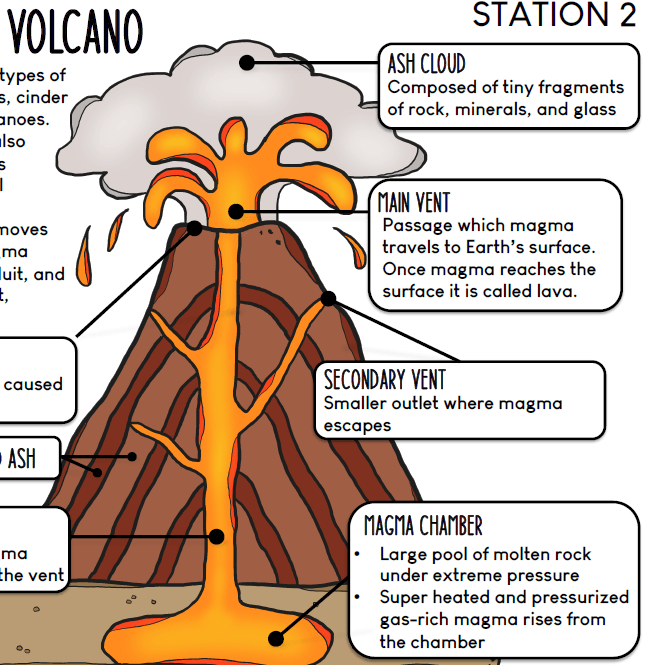
Conduit
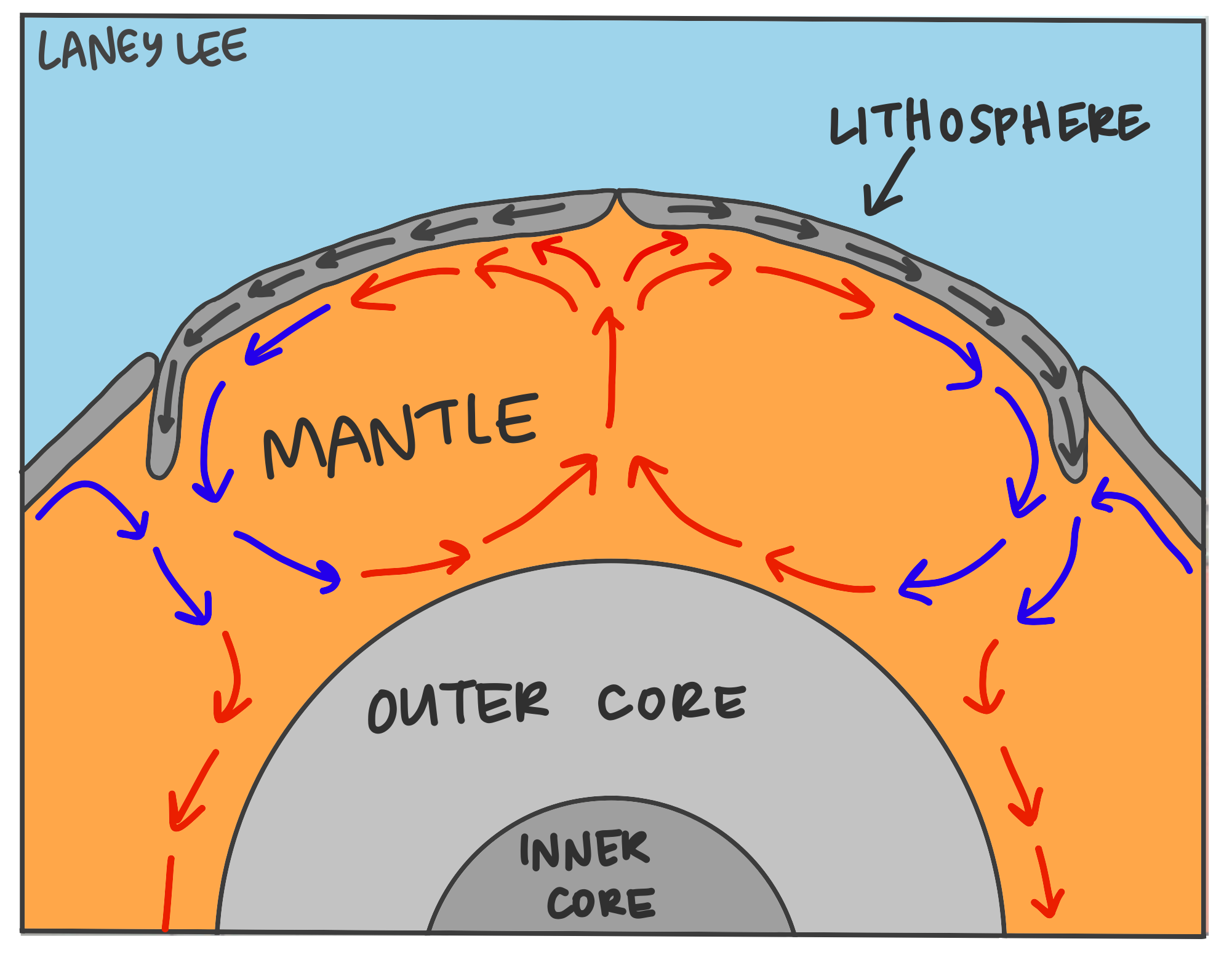
What churns the molten rock material within the mantle which moves the tectonic plates?
Convection currents
The coastal management technique which involves working with nature to rejuvenate coastal areas, using low technology and spending minimal money.
Soft engineering
The concept examining the dynamic nature of the Earth and the transformations that occur over time. It involves studying the processes, patterns, and causes of changes in physical and human landscapes.
Change
The coastal management technique which involves building physical structures to protect the coast.
Hard engineering.
Tropic of Capricorn
A shore perpendicular structure typically constructed using rocks, which is aimed at trapping sand that is moving along the beach.
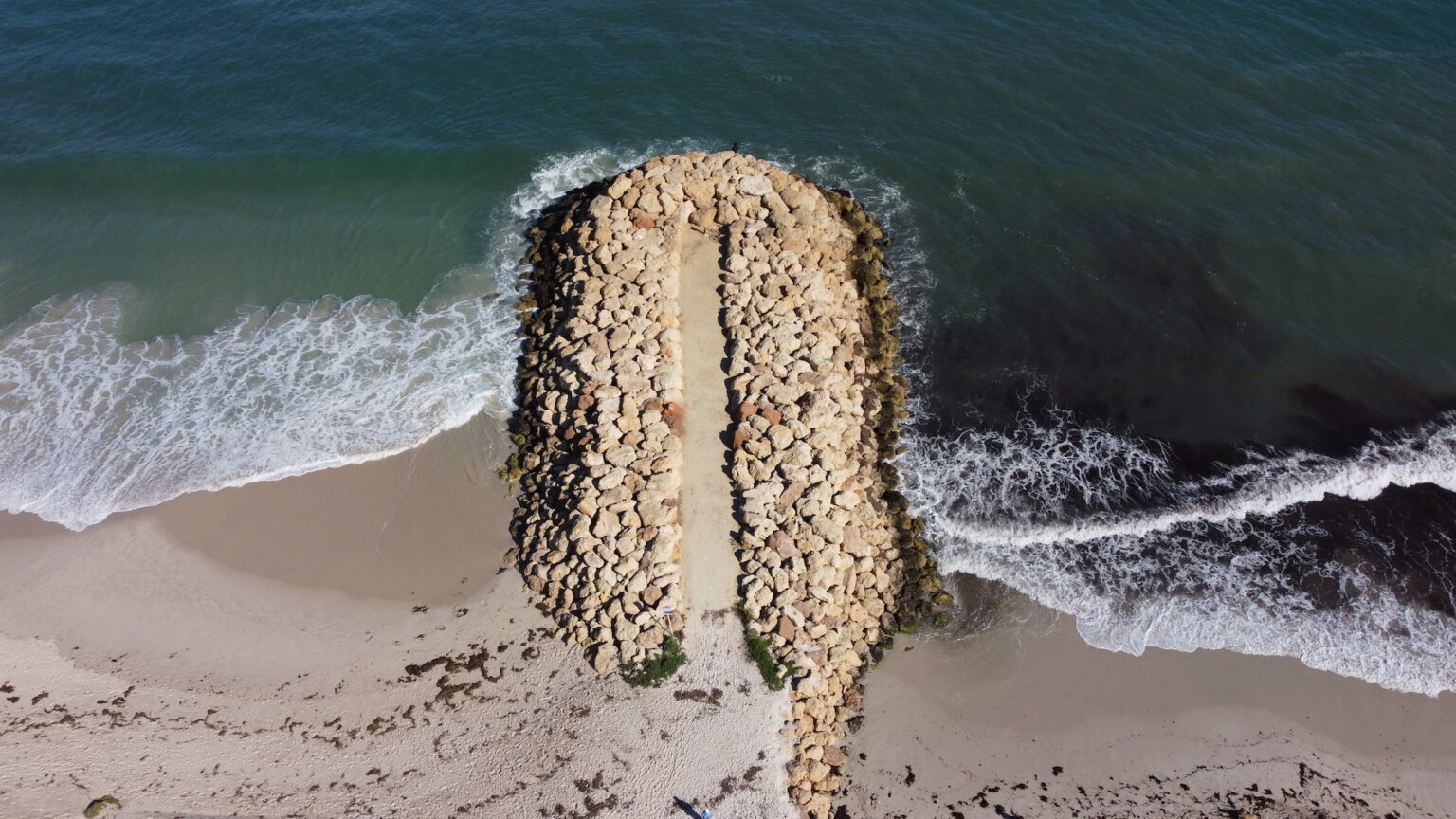

Groyne
The landscape characterised by distinctive landforms that are the result of the dissolution of soluble rock.
Karst landscape
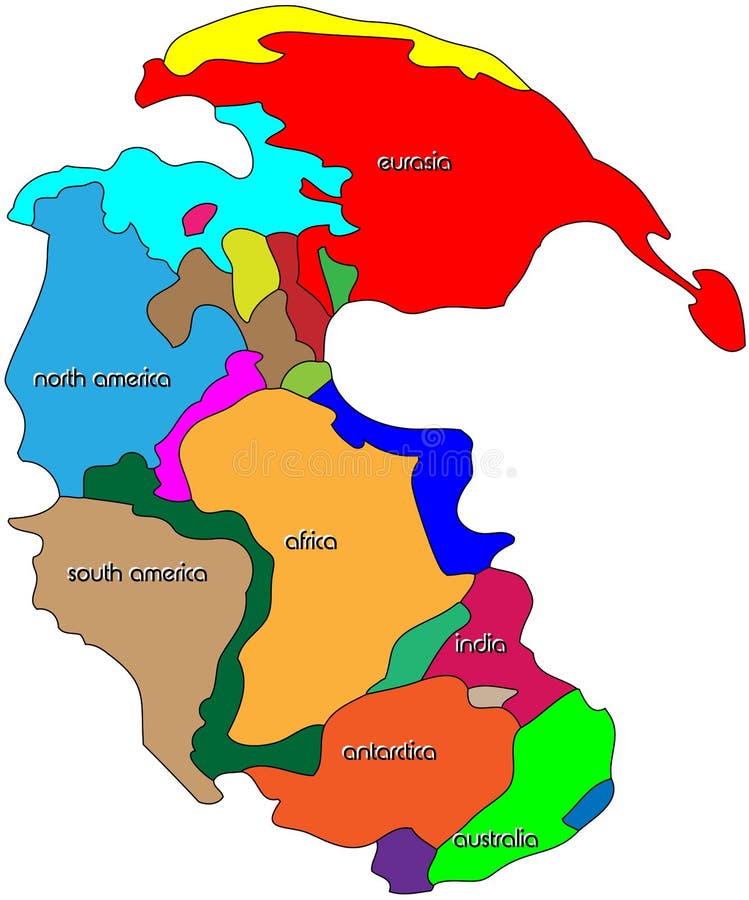
The supercontinent that began breaking up into smaller continents and drifted apart about 200 million years ago.
Pangea
What would the predominant wind direction be?
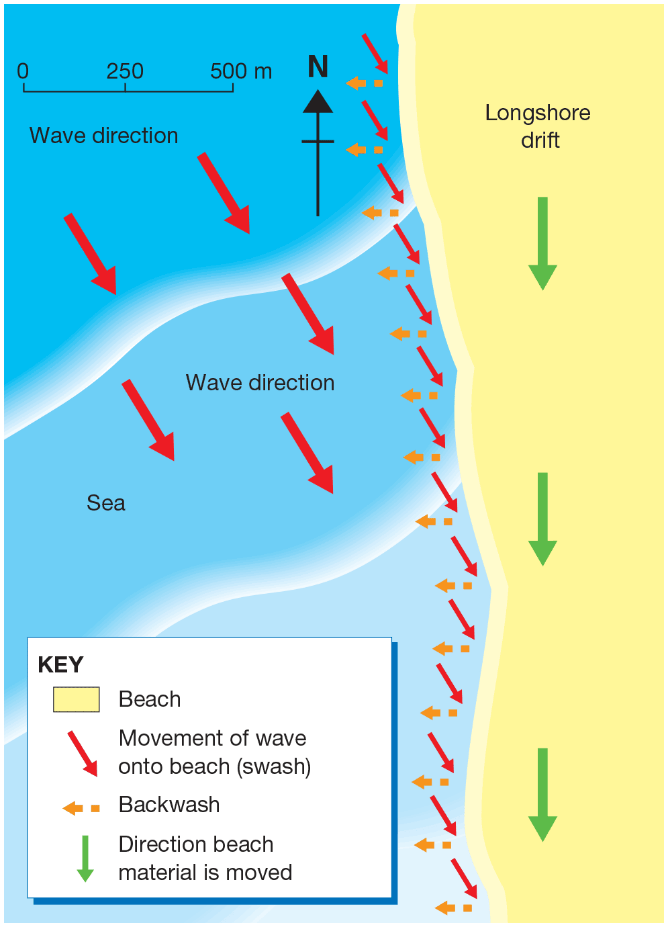
North-west
The predominant wind direction is the main direction from which the wind blows (shown by the direction of the waves).