The 3 Basic Components of the Cell Theory are:
•1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. (Schleiden & Schwann, 1838-39)
•2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. (Schleiden & Schwann, 1838-39)
•3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. (Virchow, 1858)
The organelle that is the control centre of the cell, identify all the features of this organelle.
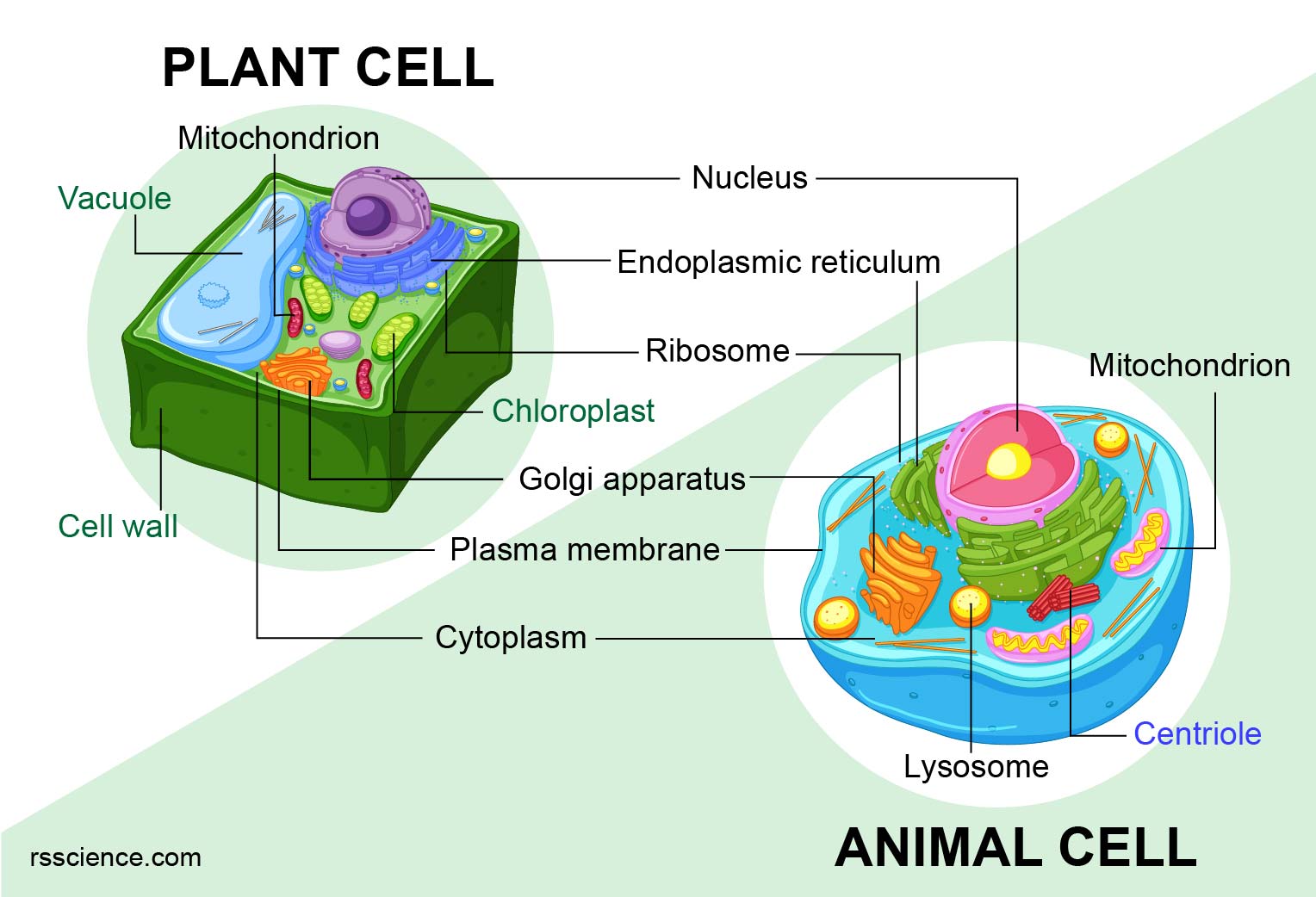
Nucleus
•Contains DNA
•Surrounded by a double membrane
•The easiest organelle to see under a microscope
Usually one per cell
Internal respiration is defined as:
The cells use the oxygen and glucose sugar to obtain energy, and produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
Define what microscopes are, and determine their uses.
A microscope is a tool that allows us to view things that are too small to see with the naked eye. The most common microscope is the compound light microscope.
It uses a system of two or more lens to collect and focus the transmitted visible light through the specimen to the eye.
Name and describe the characteristics of RBCs, including function and adaptations.
Red blood cells
•RBCs lose their nucleus at maturity.
•Make up about 99% of the blood’s cellular component.
•Red color is due to hemoglobin.
Cells are define as:
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
Name and describe the features of 2 organelles found in only in plants.
Cell Wall
•Found in plant and bacterial cells
•Rigid, protective barrier
•Located outside of the cell membrane
Made of cellulose (fiber)
Chloroplast
•Little solar panel
•Found only in plant cells
•Contains the green pigment chlorophyll
•Site of photosynthesis
•Reason why plants are green
Write the word equation for Cellular respiration and explain its importance, identifying where it takes place in the cell.
Cellular respiration
Glucose + oxygen = water + carbon dioxide + ENERGY
Mitochondria
In describing cells, units of measurement are in:
micrometre (µm, also called micron) and nanometre (nm)
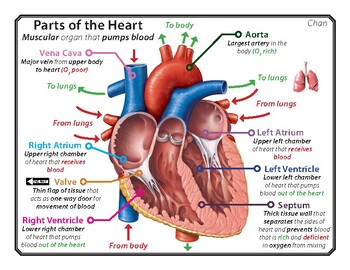
Why is the left ventricle of the heart thicker than the right?
The left ventricle of your heart is larger and thicker than the right ventricle. This is because it has to pump the blood further around the body, and against higher pressure, compared with the right ventricle.
In 1655, Robert Hooke looked at cells of what_____________. He thought they looked like_________________
•Looked at cells of cork and saw tiny circular holes.
•He thought they looked like cells of honeycomb, so he called them ‘cells’.
Describe why Ribosomes and Lysosomes are important for maintaining life.
Ribosome
•A builder of all parts human
•Site of protein synthesis
•Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol
Lysosomes
•Garbage disposal of the cell
•Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes
Name parts of the heart and the roles of each of the 4 sections.
A typical compound light microscope will have____________ to objectives of what magnification?
They generally have a scanning (4X), low (10X), high (40X), and oil immersion (100X) objectives.
Blood vessels fall into three major classes, define the role of these vessels.
•Arteries and arterioles carry blood away from the heart.
•Veins and venules carry blood to the heart.
•Capillaries allow exchange of nutrients, wastes and gases.
Name and describe the 2 different types of cells, providing examples for each.
Prokaryotic Cells
•First cell type on earth
•Cell type of Bacteria and Archaea
•No membrane bound nucleus
•Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration
•Organelles not bound by membranes
Eukaryotic Cells
•Nucleus bound by membrane
•Include fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells
Possess many organelles
Create a Venn diagram of eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

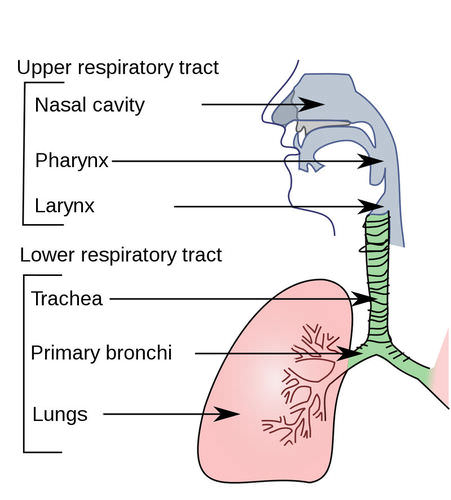
Draw and explain what is happening in the gas exchange section of the lungs.
Calculate the total magnification for the compound light microscopes we used. Show your working out.
Name the components of blood and what they do.
Plasma: the liquid portion.
Red blood cells.
White cells.
Platelets.
Draw, name and describe the function of 4 different specialised cells.
Draw: Create a diagram of a animal cell and plant cell highlighting all organelles covered in class.
Draw the pathway of oxygen through the respiratory system.
Draw a labelled diagram of a microscope.

Draw a labelled diagram of the circulatory system.