Cellular respiration needs this gas exchanged in the lungs
Oxygen
The term for energy stored in food.
Chemical potential energy
Digestion begins in this part of your body
The mouth
A ball at the top of a hill has this type of energy
What is gravitational potential energy
This transports oxygen and nutrients in the body
What is the circulatory system
The name of the tiny sacs where gaseous exchange takes place
Alveoli
The heat transfer method seen in liquids and gases
Convection
Mechanical digestion occurs in two main places in the body
What is the stomach and mouth
A ball rolling down a hill is transforming one type of energy to another of energy.
What is the transformation of gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy
This vessel transports blood towards the lungs
What is the pulmonary artery
The role of the diaphragm.
The diaphragm is a muscle that moves up and down (involuntarily) to fill and then empty the lungs of air.
Types of energy associated with this activity

Elastic potential energy
Gravitational potential energy
Kinetic energy
Heat and sound energy
The relative sizes of glucose and starch molecules
Glucose molecules are smaller than starch molecules
The percentage of useful energy output from energy input is given this name.
What is energy efficiency.
This blood vessel has thick muscular walls
What is arteries
List the pathway air takes from the mouth to the alveoli
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles
What are solar cells used for?
Conversion of light to electrical energy
The enzyme found in the stomach that increases the rate of digestion of proteins
Protease
Three types of heat transfer
Conduction, convection and radiation
Two types of blood cells
Red blood cells and white blood cells
Breathing rate increases during exercise
Increased demand for energy increases the rate of cellular respiration which requires more oxygen. Increasing the rate of breathing enables more oxygen to enter the bloodstream. It also allows for the exchange of carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
Explain this diagram. Name an object this diagram could be associated with.

Sankey diagram
Useful (sound and light) and wasted energy (heat)
Television, iPad, laptop
The role of the villi in the small intestine
Increase surface area to increase rate of absorption of nutrients
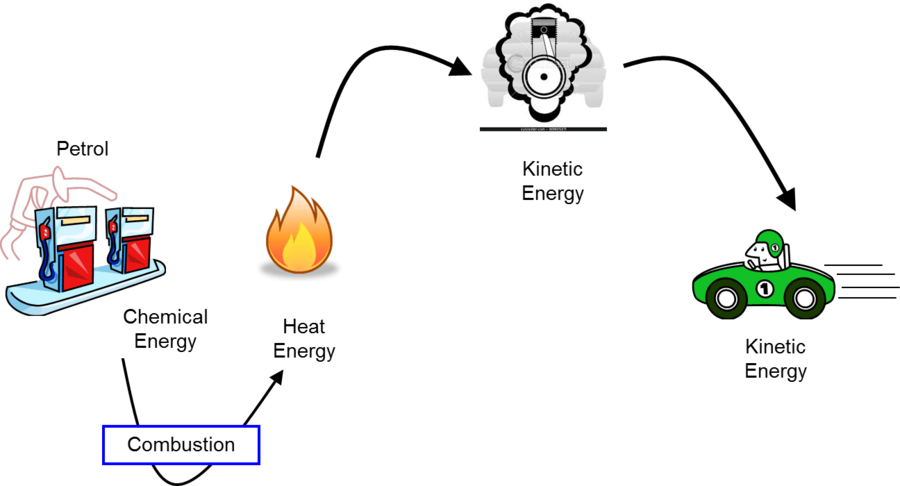
Name the energy transformations associated with a petrol fuelled car.
Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart via the vena cava. List the chambers of the heart and blood vessels - in order - that blood travels through before it is returned to the body via the aorta.

Right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, left atrium, left ventricle