What is the greenhouse effect?
A) Natural process that traps heat in Earth’s atmosphere
B) When pollution from cars, factories, etc weather changes
C) The destruction of forests leading to climate change
D) The warming caused by ocean current changes
A) Natural process that traps heat in Earth’s atmosphere
Question: What is physical water scarcity?
A) When water is polluted
B) When there is not enough water due to climate and/or geography
C) When water is expensive
D) When people don’t want to use water
B) When there is not enough water due to climate and/or geography
Question: What is fieldwork in geography?
A) Writing reports on maps and using data
B) Using satellite images and maps to learn about the world
C) Collecting information about the world through direct observation
D) Reading previous geographers work to collect data
Answer: C) Collecting information about the world through direct observation
Question: What is the difference between an immigrant and an emigrant?
A) Immigrants leave; emigrants arrive
B) Emigrants are always refugees
C) Immigrants arrive; emigrants leave
D) There is no difference
C) Immigrants arrive; emigrants leave
Identify two human activities that increase greenhouse gas emissions.
Burning fossil fuels for energy releases carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Cattle farming releases methane (CH₄) through digestion and waste of animals.
Deforestation which leads to less CO2 being absorbed by trees from the atmosphere
Factories can release different byproducts such as N2o and CFCs which capture and keep heat
Other options can be accepted if they release GHGs
What is a watershed?
A watershed is an area of land where all the rain and rivers drain into a common outlet, like a lake, river, or ocean 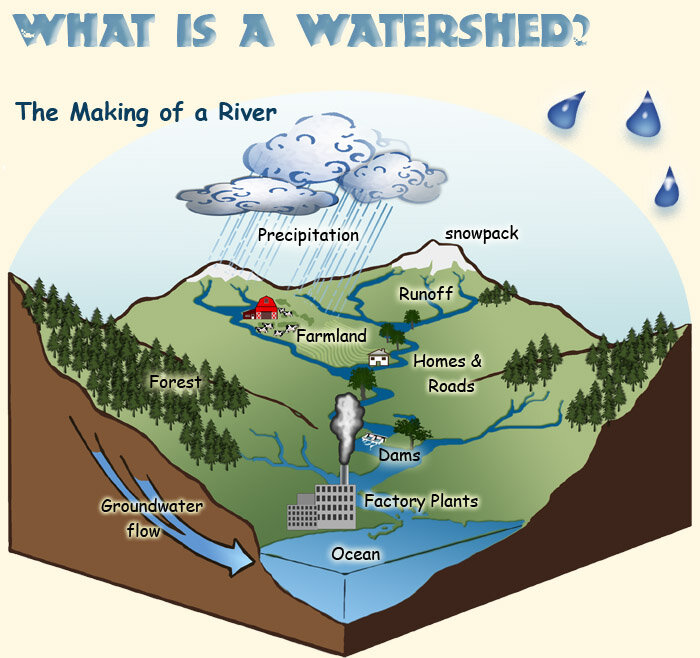
Define qualitative data and give one example.
(100 marks for each correct identification)
Qualitative data is descriptive and based on observations or opinions.
Example: Open-ended questionnaires to collecting opinions or pictures
Define voluntary migration and give one example.(100 pts for correct definition and 100pts for relevant example)
Voluntary migration is when someone chooses to move, for example, moving to another country for a better job or education opportunity or to be united with family.
What are the three Milankovitch cycles? Name and describe each one briefly.
(50 points for naming, 50 points for correct explanation)
Possible Answers:
Answer:
Eccentricity: Changes in Earth's orbit shape (from circular to elliptical) over ~100,000 years.
Obliquity: Changes in Earth's tilt (~41,000 years), affecting seasons.
Precession: Wobble in Earth's rotation (~26,000 years), changing timing of seasons.
Define economic water scarcity and briefly explain how it can increase the risk of water-borne diseases?
(150 points for definition, 150 points for explanation)
Economic Water Scarcity: happens when people don't have access to water due to lack of money, infrastructure, or government support, even though water may be available in the environment.
Spread of Illness: In areas with economic water scarcity, people may rely on unsafe water sources. Lack of sanitation and clean infrastructure leads to contamination, spreading diseases like cholera and dysentery.
Question: Put these steps of the fieldwork process in the correct order:
A) Data Presentation
B) Evaluation
C) Data Collection
D) Enquiry Question
E) Analysis
F) Planning
(Must get all in correct order for full marks)
Enquiry Question
Planning
Data Collection
Data Presentation
Analysis
Evaluation
List one economic, one social, and one environmental challenge a host country might face when hosting many refugees.
Possible answers:
Economic: Pressure on housing and jobs, supply services to refugees
Social: Tension between groups or cultural misunderstandings
Environmental: Overcrowding in cities or pressure on natural resources
Identify two pieces of evidence for climate change and briefly explain what they show.
(100 points for correction identification, 100 points for each explanation)
Possible Answers:
Tree rings: Wider rings show warm/wet years, narrower rings show cold/dry years—shows long-term climate patterns.
Sea level records: Rising levels indicate melting ice caps and warming oceans—evidence of global warming.
- Ice cores: Show the amounts and types of gases in the atmosphere absorbed and then frozen in ice layers
- Temperature (atmosphere or ocean) records: Records from 1800s onwards show record of temperatures from different locations
Define the terms point source and non-point source pollution and give one example of each.
(100 points per correct definition, 100 points per correct example)
Answer:
Point source pollution comes from a single, identifiable source (e.g., a factory pipe, oil spill, sewage drains).
Non-point source pollution comes from many scattered sources that are not directly identifiable (e.g., runoff from farms, street runoff, waste leaking from landfills).
In our fieldwork, explain one method we used to collect qualitative data and one method we used to collect quantitative data.
(200 marks for each correct explanation)
For qualitative data we took different measurements of water quality, including PH, bacterial test, TDS (total dissolved solvents), and had some close-ended questions in our questionnaire.
For quantitative data we used a questionnaire with open-ended questions to collect local residents opinions or experiences with access to water and safety
(100pts per correct definition, 100 pts per relevant example)
Push factor: A reason that forces someone to leave their home country.
Example: War or conflict, economic deprivation, climate change or natural disasters, lack of education or job opportunitiesPull factor: A reason that attracts someone to move to a new country.
Example: Better job opportunities, education opportunities, safety, higher quality of life (ie better salary, better living conditions)
For the waste and agriculture sectors, suggest one solution each sector to reduce emissions and explain how they work.
(250 points for each correct solution that is relevant to reducing GHG emissions)
Possible answers
Waste: Increase composting to reduce landfill methane. Increase recycling of plastics to reduce energy needed for new raw materials.
Agriculture: Use precision fertiliser techniques to reduce nitrous oxide emissions. Change diets of animals to reduce their methane emissions.
List five sources of water pollution and a potential pollutant from each source.
(50 points for each correct identification, sources and pollutants)
Possible answers:
Farms (agriculture) – Fertilisers (nitrates and phosphates)
Factories (industry) – Toxic chemicals or heavy metals (like mercury or lead)Urban areas (roads and cities) – Oil and petrol
Landfills (rubbish dumps) – Microplastics
Construction sites – Sediment (soil, sand, or mud)
Evaluate our fieldwork. Describe one way our fieldwork could be improved in the future and explain how this would make your results more reliable or useful.
Possible answers:
Collect water testing samples from more locations.
Include more types of water testing, for example for specific pollutants to help identifying potential sources
Collect opinions from more persons, or from more locations to collect wider variety of opinions to make it easier to identify patterns
- Collect information or data from local experts, ie NWSC, to better understand possible challenges or causes of pollution
Explain how migration can affect both the origin and host country in terms of development.
(250 marks per explanation, one for host and origin country impacts)
In the origin country, migration can cause “brain drain” if educated people leave, which slows down development.
In the host country, migration can help the economy grow by filling job shortages, especially in construction or healthcare.
Remittances improve local income for the country of origin
Returning immigrants may bring new skills or ideas to country of origin
Host country will have influx of new ideas, perspectives, adding diversity to workplaces and can help productivity
Immigrants may start businesses, adding income and jobs to the host countries economy
Host countries, especially cities, can become overpopulated and strain services reducing quality of life
