Name 'e'
Reflected ray
 What is the angle of reflection?
What is the angle of reflection?
45o
Describe the image seen in a plane mirror
Upright and the same size as the object
A flat mirror is also known as a
plane mirror
Name 3 natural sources of light
examples include: the sun, stars, lightning, auroras, bioluminescence etc
Name 'a'
Incident ray
What is the angle of incidence?
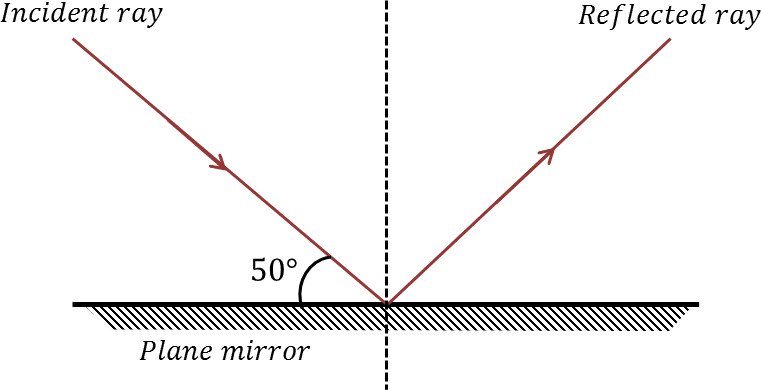
40o
Describe the image seen in a concave mirror
Can be upside down or upright; generally larger than the object
A mirror that curves inwards is called a
concave mirror
Name 3 artificial sources of light
examples include: torch, lightbulb, phone screen, fireworks etc
Name 'd'
Angle of reflection
The law of reflection states that
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Describe the image seen in a convex mirror
Upright and smaller than the object
A mirror that curves outwards is called a
convex mirror
The moon is not a light source, but it appears to be - why is this?
It is reflecting light from the sun
Name 'b'
Angle of incidence
What is the angle of reflection?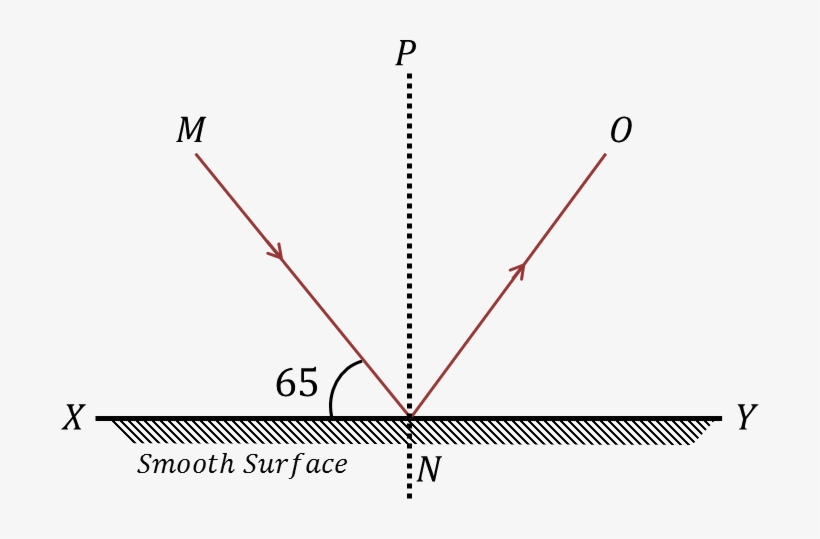
25o
Where is the focal point of a convex mirror?
Behind the mirror
Which slide is best to use when drawing simple ray diagrams?
thin single slit slide
How do we see objects that aren't light sources?
They reflect light from a light source into our eyes
Name 'c'
The normal
What is the value of q?
56o
Where is the focal point of a concave mirror?
In front of the mirror
When using the 3-slit slide, which side of the lightbox should you use?
The side furthest from the lightbulb
How does light travel? (where does it start, what path does it take, and does it stay on that path forever?)
Light travels from a light source in a straight line in all directions until it hits an object