What is the longest mountain range on the eastern side of Australia, running mostly through New South Wales and into Queensland? (Weekes)
Great Dividing Range
What does GDP stand for? (Cassandra)
Gross Domestic Product
What is spatial variation? (Archie)
the difference or change in a variable (such as population, soil quality, or water temperature) across different geographic locations
Why does housing closer to the city cost more? (Elias)
Convenient access to jobs shops and entertainment with limited land area. Demand
What natural process slowly wears down rocks and shapes the Earth’s surface using wind, water, and ice. (Carter)
Erosion
Define GDP (Jesse)
The value of goods and services a country produces
What does HDI stand for? (Shapcott)
Human Development Index
What percentage of Australia's mainland is Desert? (Weekes)
18%
Give one example of an MEDC and one example of an LEDC (Cassandra)
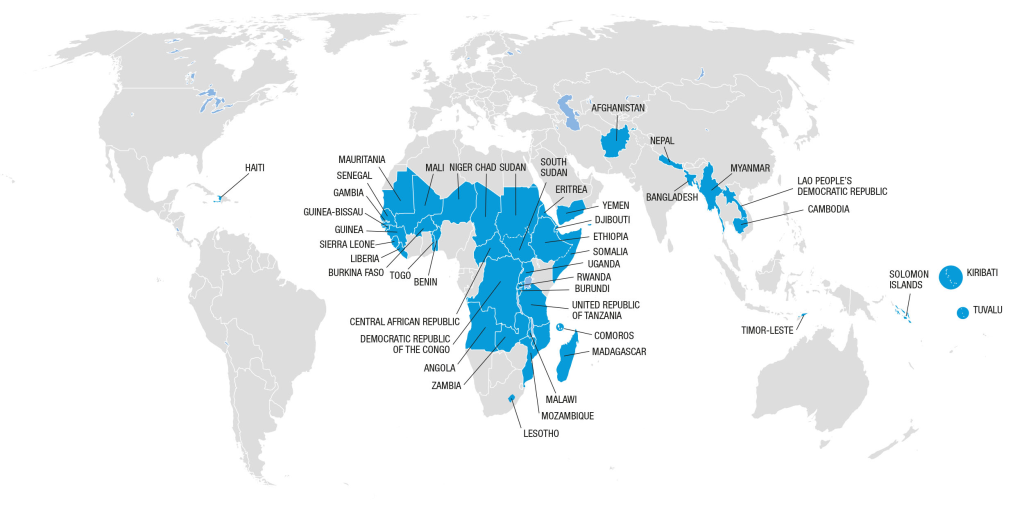
What are some of the main causes of spatial variations in human wellbeing between countries? (Carter)
Environmental factors include climate, soil quality, and natural resources.
Human factors include social structures, economic development, political stability
Differences in access to resources, healthcare, education, and opportunities, leading to differences in quality of life across different geographical areas.
What are the impacts of over fishing? (Archie)
disrupting food webs and decreasing biodiversity through species depletion. Threatens food security.Destroys people's livelihoods
List THREE ways humans change environments
Farming, Mining, Pollution, Deforestation, Urbanisation, Tourism
What is human wellbeing? (Munce)
the state of a person's physical, mental, emotional, and social health and their overall quality of life
How can cities be more sustainable? (Charlotte)
By using clean energy, recycling, and improving public transport.
Name Four features of the Water Cycle?
Name the 4 spheres (Beasley)
Biosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere
Why has the world become more urbanised? (Izabel)
More opportunities in cities and urbanised areas for work.Greater access to services (medical, education, social services)
photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion, sedimentation, burial, and extraction
How does urbanisation change environments and places? (Barry)
Urbanisation changes environments and places by replacing natural land with buildings and roads, increasing pollution and waste, and reducing green spaces, but it can also lead to improved infrastructure, transport, and services for people.
Average life expectancy of Australian citizens (Zac)[within 1]
83