Define: Opportunity cost
Opportunity cost is where there is a lack of resources for more than one option, the opportunity cost is what you have lost by choosing the other option
Provide an example of a Capital (Factor of production) for a Pizza Shop
Pizza Ovens
Cutters
etc
Natural resources that come from the earth e.g. timber, water
What factor or production is this?
Land
Fill in the blanks:
Markets are places (______ and digital) where consumers and producers _______ things of value (goods/_____).
physical
exchange
Services
What does supply mean?
Goods or services a producer is able and willing to supply
What are the two sectors of a circular flow chart?
Households
Businesses
Define: Labour (Factor of production)
The human effort and 'work' that goes into the creating goods and services
Provide an example of Labour (factor of production) for a Pizza shop
Chef, waiter
etc
Provide an example of a Land item from Boost Juice
Strawberries
Bananas
Milk
etc
where houses are bought and sold:
What type of market is this
Housing
What does demand mean?
Explain (without examples) how businesses and consumers are interdependent on one another
Both rely on each other to survive
Define: Scarcity
Unlimited wants, Limited resources
Opportunity Cost
The idea that combines the capital, land and labour is the definition of what factor of production
enterprise
workers sell their skills, knowledge and effort to employers:
What market is this?
Labour
According to the law of supply, if prices go up, supply goes _____.
If prices go down, supply goes ____.
up
down
Provide two ways Households are dependant on businesses
- to buy goods and services
- to earn wages
Define: Enterprise (Factor of production)
the idea that combines capital, labour, land to create a specific product/service
A tractor is an example of what factor or production
Capital
Name the four Factors of Production
Capital
Enterprise
Land
Labour
where shares in Australian companies are bought and sold:
What market is this?
stock exchange
According to the law of demand:
As the price goes down, the demand goes ____
As the price goes up, the demand goes _____
down
Provide to ways businesses are dependant on households
To work
To buy goods and services
Define: Interdependence
The dependance between businesses and households for both to survive
Labour and Stock are examples of what?
Markets
produce an example for each factor or production for a chocolate bar
capital: mixing machine
entreprise: Cadbury
Land: cocoa beans
labour: factory workers
for example
House market
Stock Exchange
Foreign exchange
Labour Market
Define:
Equilibrium
and
Disequilibrium
Equilibrium is the point where the supply and the demand line crossover
When the amount tha tproducers supply is not equal to the amount the consumers want to buy
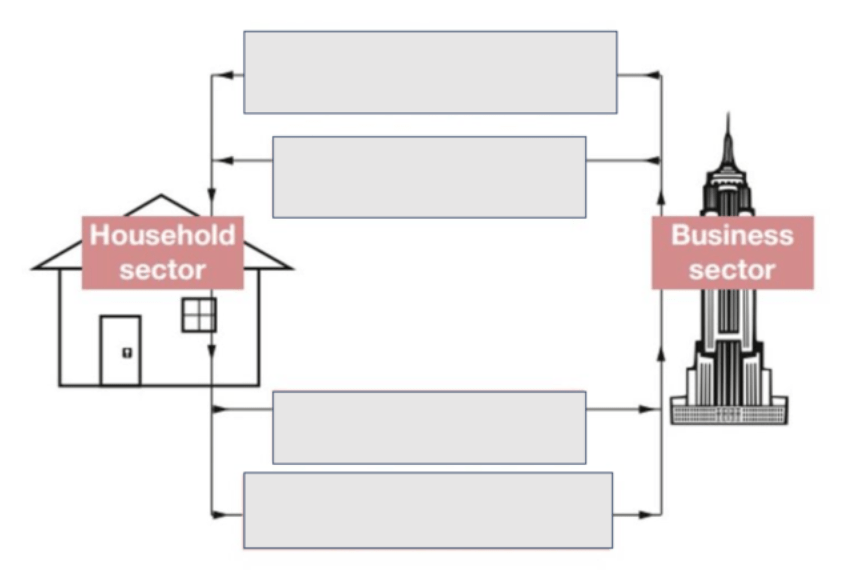 Fill in the blanks
Fill in the blanks
top: business provide goods and services to consumers
Second:Business pay wages to workers
Third:Workers provide labour to businesses
Bottom: Consumers pay for goods and services