Most human cases of rabies are now due to viruses associated with this animal.
What are bats.
===
Prior to 1950s, most cases of human rabies in the United States were related to dog bites. Proper use of rabies vaccines in animals has led to a major impact upon the dimunition of human cases in developing and developed countries.
Bonus question:
There are two major epidemiological rabies forms, urban and wildlife. What other animals are categorized under wildlife?
Family and genus of bacteria frequently attributed to exposure to parrots and parakeets.
What is Chlamydia psittaci.
This infection is a zoonotic disease transmitted from birds to humans.
Rabbit fever is caused by this bacterial zoonosis.
What is Francisella tularensis. (Tularemia)
====
Transmission to humans occurs through arthropod bites, ingestion of contaminated food or water, inhalation of contaminated aerosols, and handling of infected animal tissues.
This bacillus was grown in a sterile medium outside of an animal host and infected mice with resulting spores by Robert Koch in 1877 to demonstrate what has become known as Koch's postulates.
What is anthrax.
==
Anthrax, is derived from the Greek word anthrakos, meaning charcoal or carbuncle, and referring to the black skin lesions commonly seen with cutaneous anthrax infection.
This disease was known as Malta fever in 1880s due to consumption of goat milk by British soldiers on Malta island.
What is brucellosis.
===
Most common route for acquisition of brucellosis is through the consumption of unpasteurized infected milk or dairy products, including soft cheeses. Bacteria localize in animal reproductive organs, and are shed in large numbers in milk, products of conception, and other reproductive tract discharges. The organism is killed by pasteurization or boiling of milk, or fermentation and aging of cheeses, which increases acidity.
This disease is spread by the urine of infected animals caused by a spirochete bacteria.
What is leptospirosis.
===
The bacteria can survive for weeks to months in urine-contaminated soil or water. Transmission occurs through mucous membranes, conjunctiva, and skin cuts or abrasions.
Rabies virus exists on every continent except here.
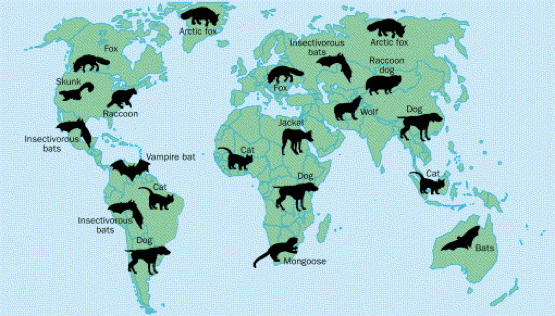
What is Antarctica
Predominant clinical presentation with illness that may range from a mild, flu-like illness to severe illness with multi-organ system involvement.
What is pneumonia.
===
Hisotry of exposure to a sick bird is the most useful information for making a presumptive diagnosis of psittacosis.
F. tularensis is classified as this category bioterrorism agent.
What is Category A.
===
BONUS: What are other Category A bioterrorism agents?
Natural reservoir of B. anthracis in the environment.
What is the soil.
====
Spores may remain viable in the soil for many decades. Spores in the environment are resistant to desiccation, extremes in temperature and pressure, and ultraviolet and ionizing radiation, however chemical disinfection can eliminate spore contamination of the environment.
True or False. Bucellosis can manifest in almost any organ or system and may cause abortion in pregnant women, most commonly in the third trimester.
What is False.
==
May cause abortion most commonly in the first and second trimester.
True or False. Great majority of infections with leptospires are icteric, and usually subclinical or mildly symptomatic and self-limited.
What is False.
==
Majority of infections are anicteric.
If a healthy domestic dog, cat, or ferret bites a person, the animal should be under veterinarian observation and supervision for at least this many days.
What is at least 10 days.
====
If clinical signs of rabies develop, the animal should be euthanized and its brain examined for diagnostic evidence of viral infection.
BONUS Question: What is standard test of choice for rabies?
Diagnosis confirmed for a positive human case is represented in this much of an increase in IgG antibodies against C. psittaci detected by MIF or CF in paired acute and convalescent phase serum specimens.
What is a four fold increase in IgG antibodies.
===
MIF = microimmunofluorescence
CF = complement fixation
True or False. Most commonly, the disease presents in humans as an indolent ulcer at the site of cutaneous inoculation accompanied by regional lymphadenitis.
What is True.
====
The major clinical forms of tularemia are: ulceroglandular (45–85% of cases); glandular (10–25%); oculoglandular (<5%); septic (<5%); oropharyngeal (<5%); and, pneumonic (<5%). All forms are accompanied by similar nonspecific symptoms of fever (38–40oC), chills, headache, cough, and generalized body aches.
Huam anthrax has three major clinical forms: inhalational, cutaneous, and gastrointestinal; with inhalatoinal as the most common form. True or False.
What is False.
==
Cutaneous is most common form. Lesion begins as a small, painless, but often pruritic papule, which quickly enlarges and develops a central vesicle or bulla. The vesicle ruptures or erodes, leaving an underlying necrotic ulcer. A characteristic black eschar develops over the surface of the ulcer; case fatality high as 20% without appropriate tx; but <1% with abx.
True or False. Brucellosis in domestic livestock in the United States is now extremely rare.
What is True.
====
Vaccines made from attenuated strains of Brucella are used to prevent brucellosis in livestock.
The organism is killed by pasteurization or boiling of milk, or fermentation and aging of cheeses, which increases acidity.
Severe icteric leptospirosis associated with renal failure and liver failure is known as this disease.
What is Weil's disease.
===
10% of leptospirosis can progress to severe illness where symptoms can include jaundice, renal failure, hemorrhage (especially pulmonary), aseptic meningitis, cardiac arrhythmias, pulmonary insufficiency, and hemodynamic collapse.
Most important method of modern rabies control.
What is prophylactic vaccination of dogs.
===
In the U.S., vaccines for domestic species contain inactivated or recombinant viruses. Some of these vaccines are administered annually and other vaccines produce immunity lasting at least three years.
Treatment consists of this specific class(es) of antibiotic therapy.
What is tetracyclines or macrolides.
===
With appropriate treatment, the disease is rarely fatal.
Diagnosis confirmed by isolation of F. tularensis by culture with this type of medium.
What is cysteine heart agar blood culture medium supplemented with antibiotics (CHAB-A).
===
Diagnosis is made by clinical findings combined with information on potentially infective exposures.
Treatment includes streptomycin (DOC), gentamicin, aminoglycosides, or tetracyclines.
Antibiotic treatment for anthrax post-exposure prophylaxis.
What is doxycycline and ciprofloxacin.
===
There is also antitoxin used to target anthrax toxins in the body to treat anthrax.
Anthrax vaccine adsorbed is the only licensed human anthrax vaccine in the U.S. recommended for those at high risk.
Pathogenic Brucella species are considered this U.S. category of bioterrorism agents.
What is Category B.
===
Category B agents are expected to cause moderate morbidity and low mortality rates, and are moderately easy to disseminate.
While waiting for confirmatory diagnostic test with Microscopic Agglutination Testing (MAT), this antibiotic treatment should be initiated in highly suspected cases.
What is doxycycline (mild) or penicillin (severe).
===
Early treatment may decrease the severity and duration of disease.
Current recommended postexposure treatment.
Human Rabies Immune Globulin in naive exposed persons and rabies vaccine on days 0, 3, 7, and 14.
====
Indicated treatment for wounds inflicted by animals are antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis.
Persons in occupations that involve contact with birds, such as poultry workers, pet shop employees, or veterinarians are at higher risk for infection by this mode of transmission.
What is direct inhalation of contaminated feces or respiratory secretions or aerosolization of fecal or respiratory dust.
====
Personal protective equipment, including an N-95 mask and gown, should be worn while in contact with ill birds or while cleaning their cages.
True or False. Type A F. tularensis is often associated with aquatic environments and rodents such as beaver, msukrats, and voles. Transmission among these animals may occur through ingestion of contaminated water, soil, or food.
What is False.
===
Type A F. tularensis occurs primarily in rabbits with transmission by ticks and tabanid or deer flies.
True or False. Prevention of human anthrax infection is primarily dependent on receiving the anthrax vaccine.
What is False.
==
Prevention is primarily dependent on the control of disease in animals, especially livestock. Annual immunization of livestock in areas of endemic anthrax is recommended.
True or False. Currently there is no livestock vaccine for brucellosis available.
What is False.
==
There is no human vaccine available for brucellosis in the U.S.
Prevention with PPE for those with occupational and laboratory exposure; pasteurize milk and dairy products to prevent foodborne infections.
PEP with doxycycline and rifampin for 3-6 weeks.
What is flooding or hurricanes.
===
Large leptospirosis outbreaks have occurred following flooding or exposure of large numbers of persons to contaminated surface water sources.