What is the main source of energy that supports the majority of ecosystems on Earth?
Sunlight
What is the definition of populations?
Number of individuals in a given area
What is an abiotic and biotic factors? Give an example of each.
Abiotic = Non-living Thing; snow, rocks, clouds
Biotic = Living Thing; Ex. humans, your dog, plants
What is an omnivore? How is it different from a carnivore and a herbivore?
Omnivores eat both plants and animals; herbivores eat only plants; carnivores eat only animals
What are threatened species and endangered species?
Threatened = Species that has low numbers, but not low enough to be classified as endangered; Endangered = very low numbers; extinction is possible
What happens to energy as it moves up through the trophic levels of a food chain? Write out the Rule of 10.
Energy decreases as it moves up; follow the Rule of 10-only 10% is passed to the next level
How is population density calculated? What does it help scientists understand?
- dividing the total number of individuals within a population by the total land area that they occupy
- can indicate resource availability, overcrowding stress, the spread of disease, and the competitive
What does HIPCO stand for?
Habitat Loss, Invasive species, Population growth, Pollution, Climate Change, Overexploitation
What is carrying capacity?
Max number of individuals an ecosystem can support
What is an ecosystem service? List some examples.
Direct and indirect benefits that ecosystems provide humans (clean air/water, food, pollination, flood control, etc)
Why do higher-level consumers receive less energy than organisms at the bottom?
A significant amount of energy is lost as heat at each trophic level transfer (90%)
What is carrying capacity? Give an example.
Max number of individuals an ecosystem can support
Deer in a forest
Fish on a coral Reef
What is the Endangered Species Act?
Law passed in 1973 that aims at protecting and conserving organisms at risk of extinction
What are invasive species? Give an example.
An organism that outcompetes native species, lowering biodiversity
Zebra mussels, Asian carp, lionfish
What is ecotourism? How can it support biodiversity conservation?
Using the natural landscape as a tourist attraction; this provides money for the government and protects the environment
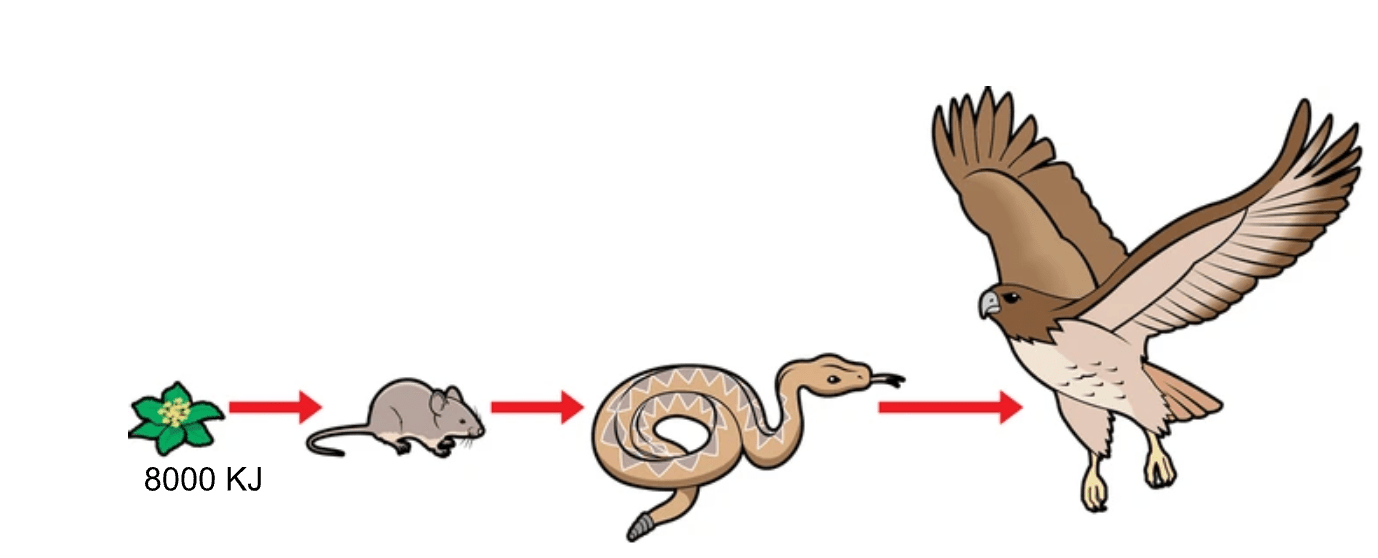
How much energy will the mouse receive?
800 KJ
Name the population distribution patterns. 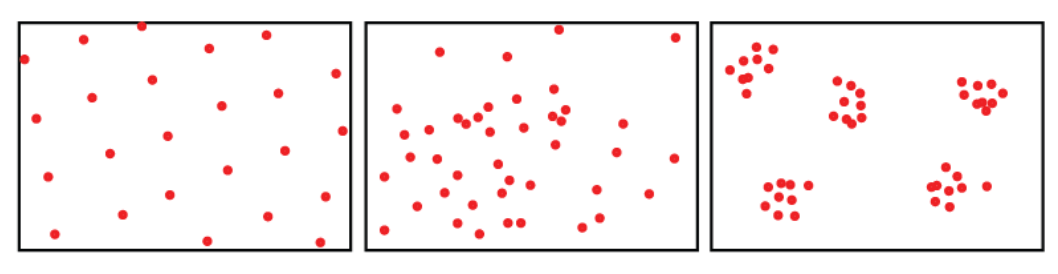
Uniform (left), Random (middle), Clumped (right)
What is the difference between exponential growth and logistic growth? What conditions allow exponential growth to occur?
Exponential growth (J-curve) occurs under ideal conditions with unlimited resources; Logistic growth (S-curve) occurs as populations reach carrying capacity (limiting factors take effect)
What are density-dependent limiting factors? What are examples?
Factors that limit population growth that requires large population size; Competition, disease, predation
What is habitat fragmentation?
Dividing/fragmenting an ecosystem overtime decreasing biodiversity
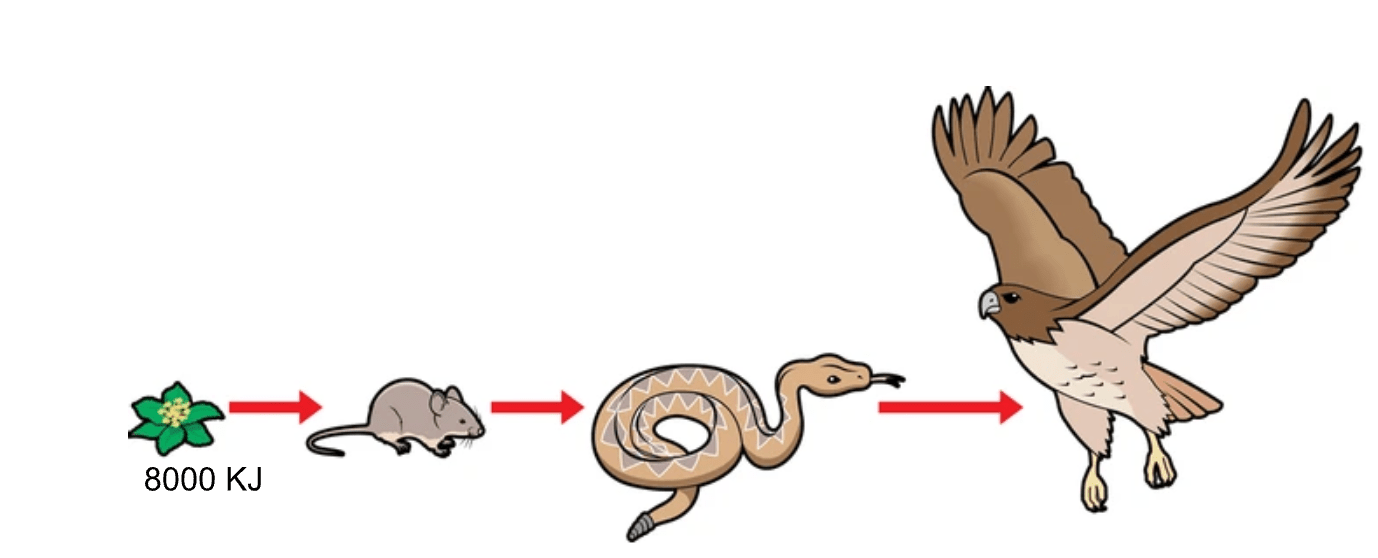
How much energy will the eagle receive?
8 KJ
What is a keystone species? What happens if we remove them? Give an example.
A species that has a huge impact on its ecosystem; if removed, the ecosystem can collapse
examples: wolves, sea otter, beavers, honey bees
What is mutualism, commensalism, or parasitism? How are both organisms affected? Give an example of each.
Mutualism (+/+)- bee and flower
Commensalism (+/0)- remora and shark
Parasitism (+/-)- flea and dog
What is primary succession? How is it different from secondary succession?
Starts from bare rock (no soil); Secondary starts from soil after a disturbance (like a fire).
What makes a tropical rainforest unique? What makes a desert biome unique?
Tropical Rainforests- Hot, wet and very high biodiversity typically near the equator
Desert- extremely dry environment, less than 25 cm of rain a year. Typically hot during the day and cold at night