What is the electron domain geometry of NO2-.
Trigonal planar
1. If a molecule has a lone pair on its central atom, is it likely polar or nonpolar?
2. If a molecule has symmetric arrangement of terminal atoms, is it likely polar or nonpolar?
1. polar
2. nonpolar
What is the molecular geometry of this molecule:
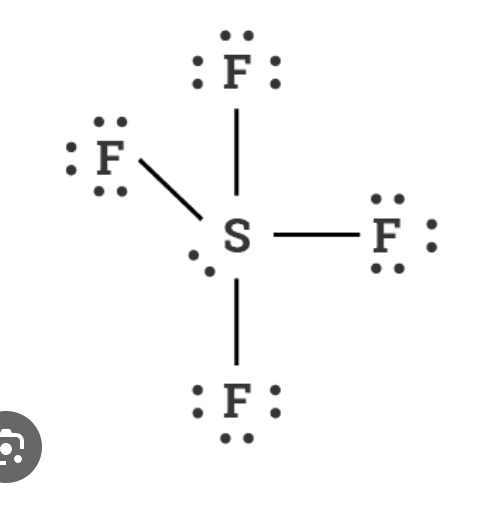
Seesaw
What molecular shapes are ALWAYS polar from the following options, even when bonds are equivalent (select all that apply):
a. bent
b. tetrahedral
c. seesaw
d. square planar
a and c
- square planar is the weird one that you just need to remember is nonpolar if all bonds are equivalent
Select all of the following that are properties of water due to hydrogen bonding:
A. Ice Floats
B. Low Boiling Point
C. High Surface Tension
D. Cohesion and Adhesion
A, C, D
(water has high boiling point due to h bonding)
1. What is the electron domain geometry of SF4?
2. What is the electron domain geometry of BrF5?
1. Trigonal Bipyramidal
2. Octahedral
1. CO2 -- polar or nonpolar? why? Is the BOND between C and O polar or nonpolar?
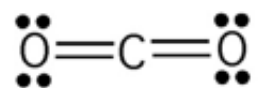
- CO2 as a molecule is nonpolar because it has no lone pairs on central atom and has symmetric arrangement of terminal atoms
- Bond between C and O is polar, C and O have different electronegativities
What are the molecular geometry of these molecules:
1. SF4
2. BrF5
1. Seesaw
2. Square Pyramidal
If a molecule is polar, does it have a higher or lower boiling point than a molecule that is nonpolar?
Polar --> polar molecules attract each other through partial charges (dipoles)
Rank the following types of bonds in terms of INCREASING strength:
Hydrogen Bond
Ionic Bond
London Dispersion Force
Dipole-Dipole
Dispersion Force < Dipole - Dipole < Hydrogen Bond < Ionic Bond
What is the Electron Domain geometry of these molecules?
1. H2S
2. SnCl2
1. Tetrahedral
2. Trigonal planar
Is the molecule BF3 polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar! No lone pairs on central atom, symmetry (X and Y forces cancel)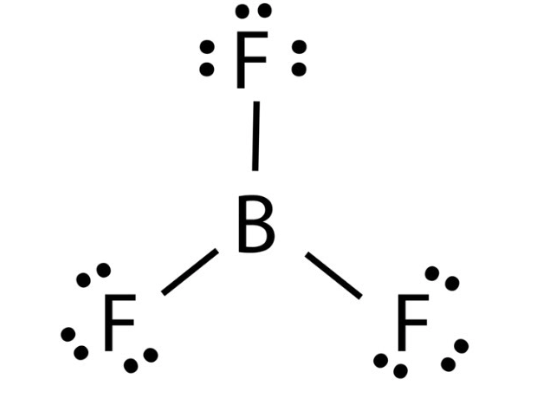
What is the molecular geometry of the following compounds:
1. H2S
2. SnCl2
1. Bent
2. Bent
Rank the following in order of increasing repulsivity:
A. single bond
B. triple bond
C. double bond
D. lone pair
A, C, B, D
Rank the following bonds in terms of low to high boiling point:
A. Hydrogen Bond
B. Dispersion Force
C. Dipole-Dipole
B < C < D
What is the electron domain geometry of the following molecules?
1. BF3
2. PCl5
3. O3
1. Trigonal Planar
2. Trigonal Bipyamidal
3. Trigonal Planar
1. SO2
2. SF6
1. Polar
2. Nonpolar
What is the molecular geometry of the following molecules:
1. BF3
2. PCl5
3. O3
1. Trigonal Planar
2. Trigonal Bipyramidal
3. Bent
Pictured below are structural isomers of a molecule. Which isomer is polar and which is nonpolar? Why?
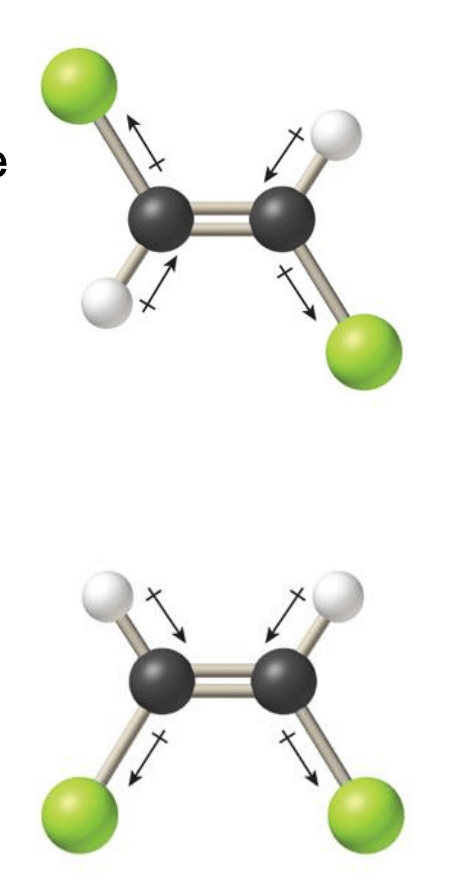
Top = Non-polar because dipoles cancel out
Bottom = Polar because the dipoles do not cancel out.
Rank the following molecules in terms of increasing boiling point:
CH4OH, NaCl, C3H6, CH4Cl
C3H6, CH4Cl, CH4OH, NaCl
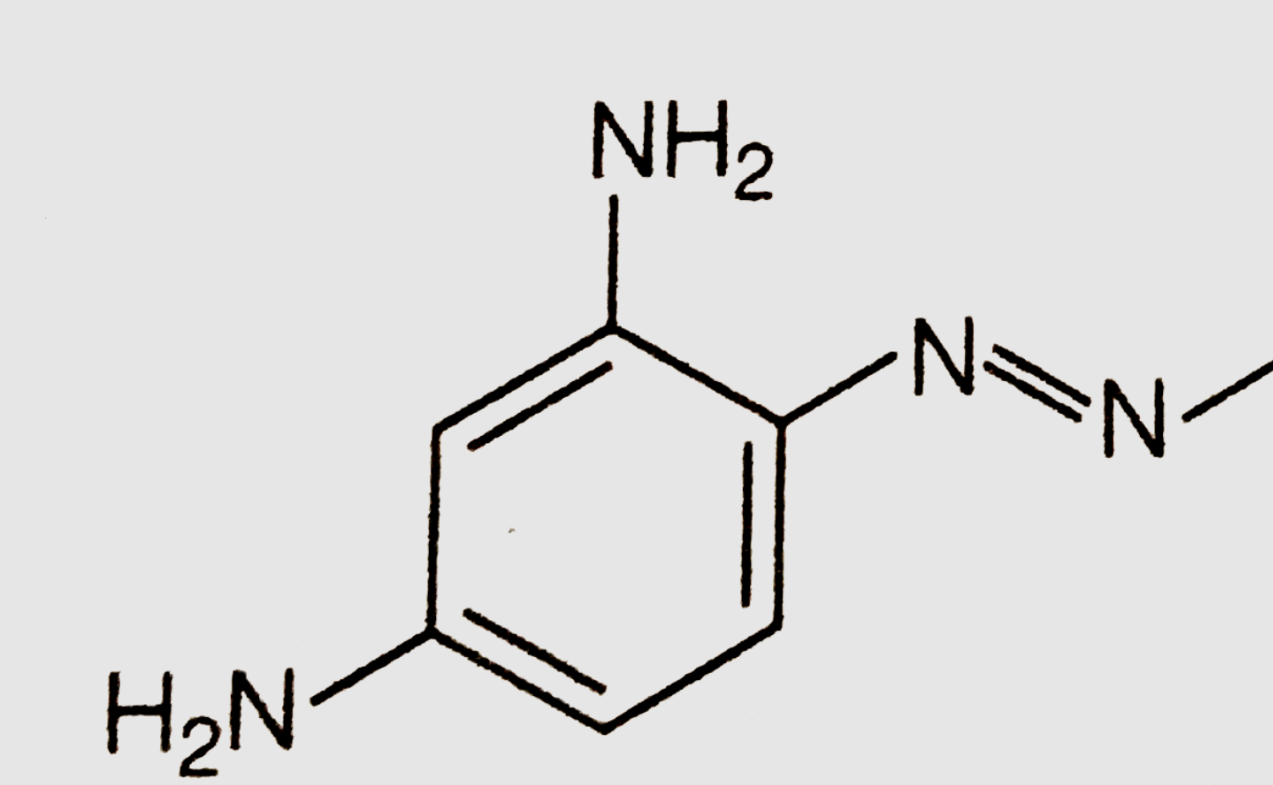 What is the ideal bond angle on the two nitrogens in this structure?
What is the ideal bond angle on the two nitrogens in this structure?
Answer: 120 degrees
Remember: Atoms need to have a full octet unless they are explicitly stated to have a + or - charge. This image can be confusing because it does not draw in lone pairs. On both nitrogen atoms there is a lone pair, meaning there are three electron domains.
Ideal bond angle = Electron Domain Geometry angle
1. CCl4
2. H2
3. XeF4
1. Nonpolar
2. Nonpolar
3. Polar
FREE SPACE!! Team that picks gets a bonus 500 points :)
YAY!
Rank the following in order of decreasing bond angle deviation assuming that each molecule has the same number of single, double, and triple bonds:
1. Seesaw
2. Trigonal Bipyramidal
3. T-shaped
T-shaped > Seesaw > Trigonal Bipyramidal
- more lone pairs = more repulsion = greater bond angle deviation
What types of molecules form the following bonds:
A. Dipole-Dipole
B. Hydrogen Bonds
C. Ionic Bonds
D. London Dispersion Forces
A. Polar molecules only
B. H with F,O,N
C. Metal and Nonmetal
D. ALL MOLECULES