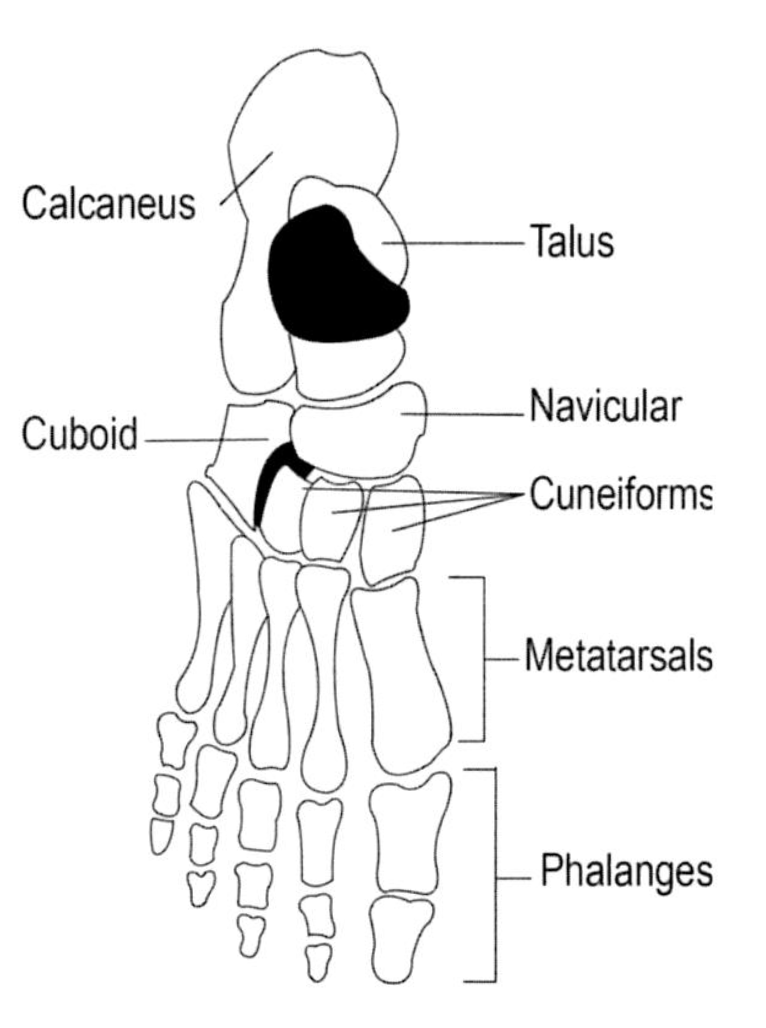
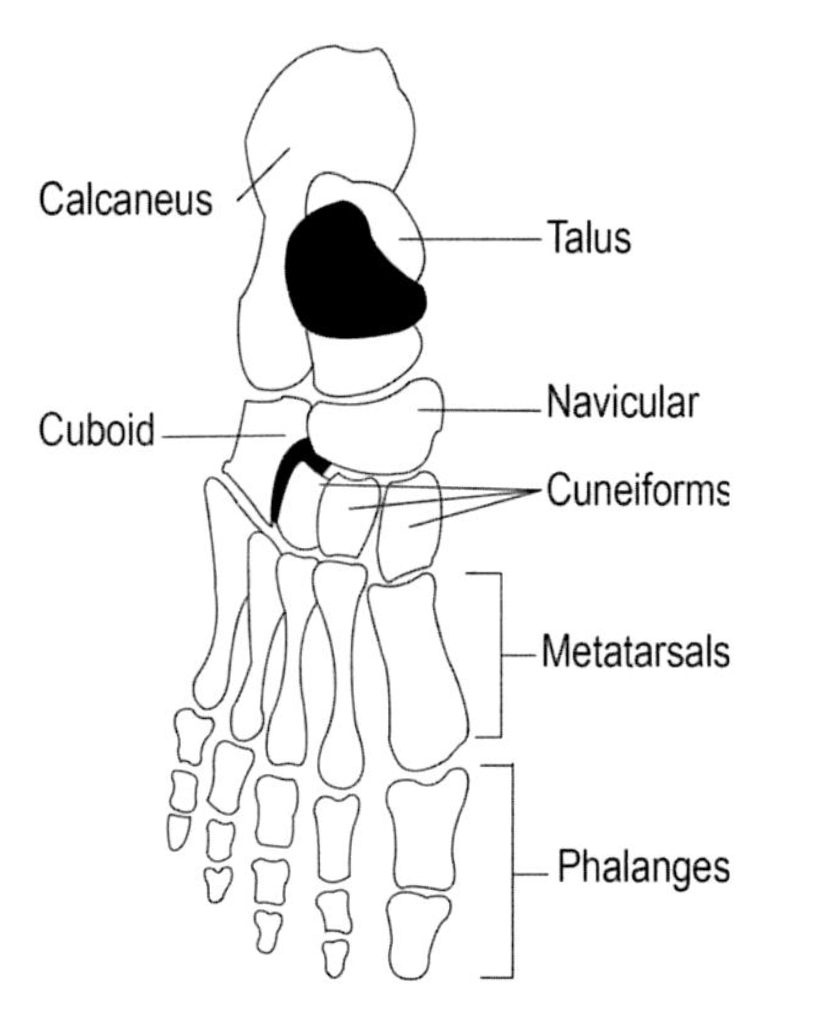
Name the bones covered
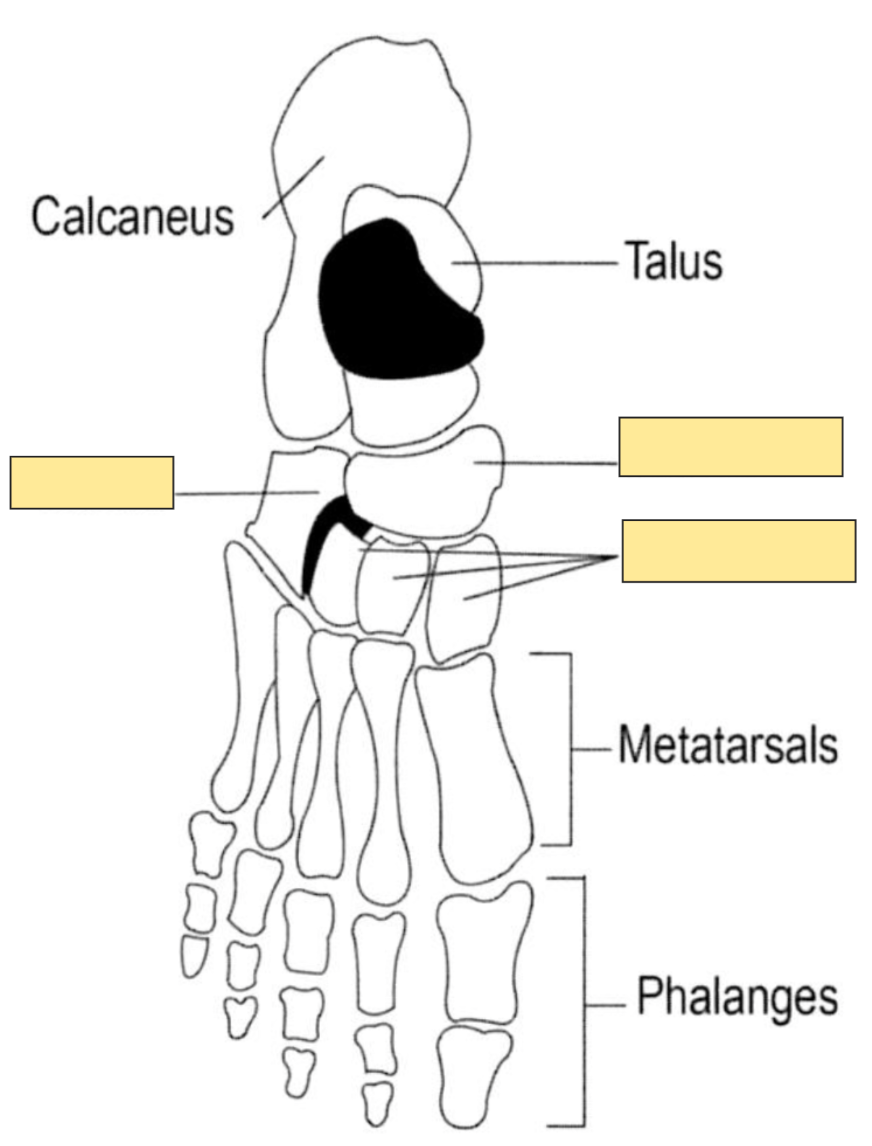
"Tiger Cubs Need MILC" = Talus, Calcaneous, Navicular, Medial Cuneiform, Intermediate Cuneiform, Lateral Cuneiform and the Cuboid bones.
What is a fluid-filled cyst arising from the synovial joint or tendon sheath
What is Ganglion Cyst?

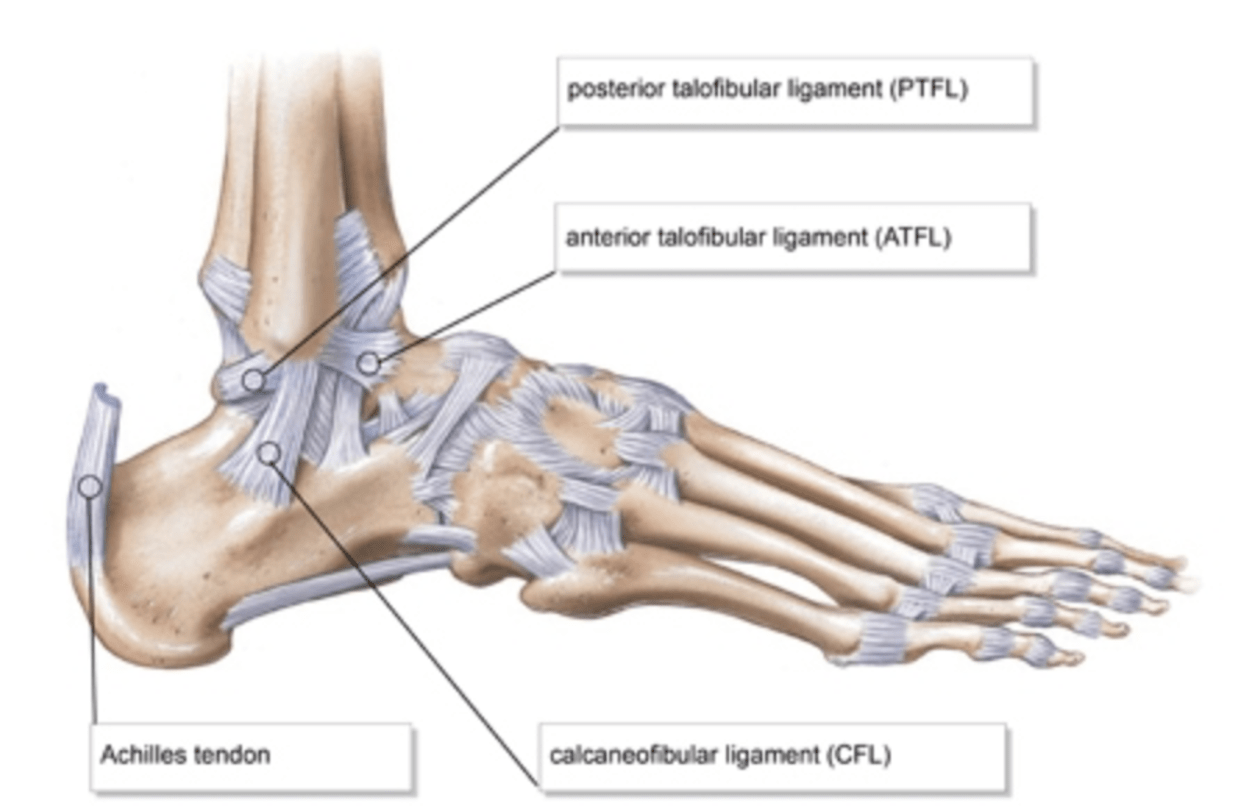
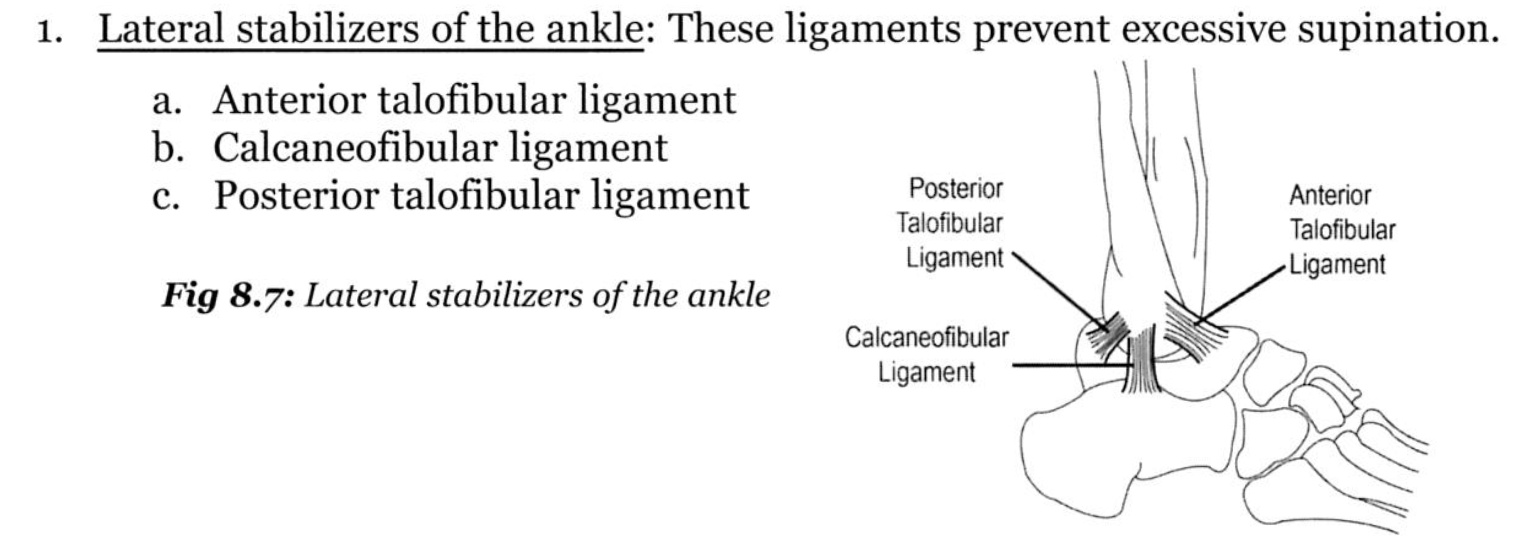
What are the lateral stabilizers of the ankle
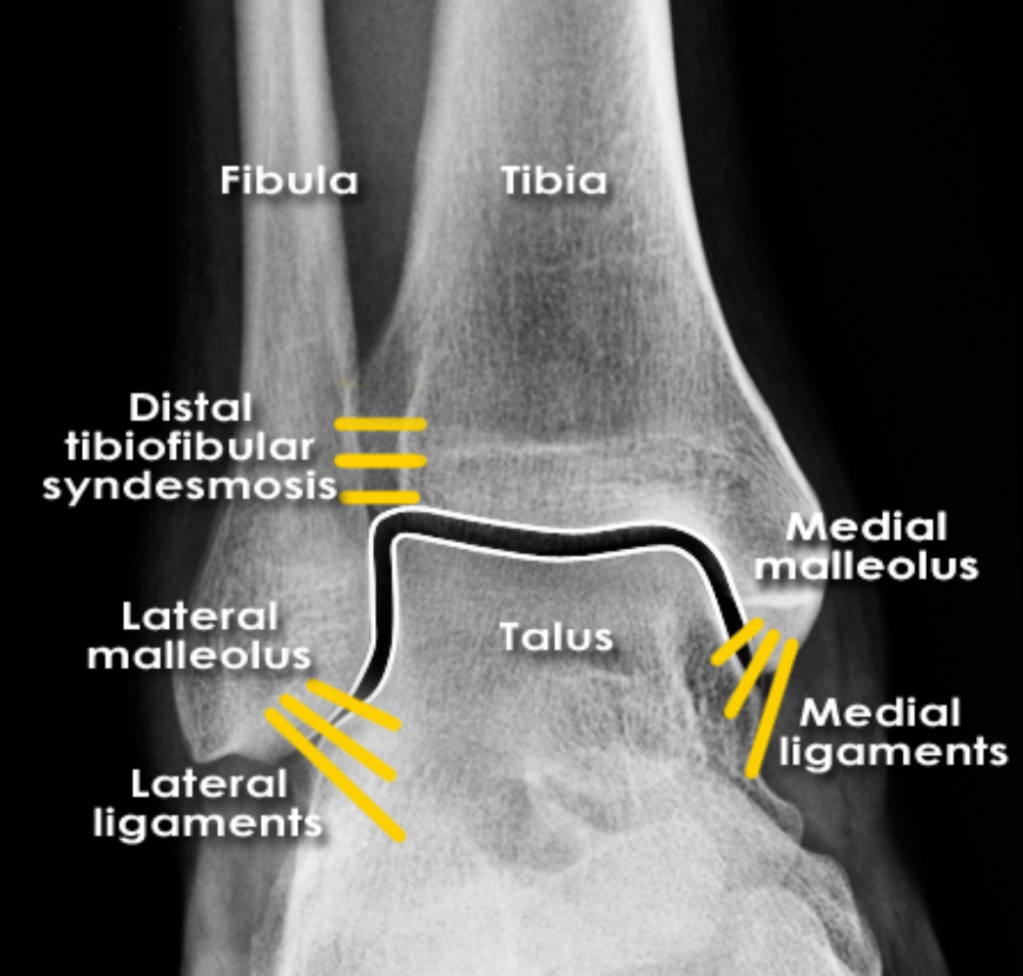
Name any abnormalities in the below imaging of ankle mortise
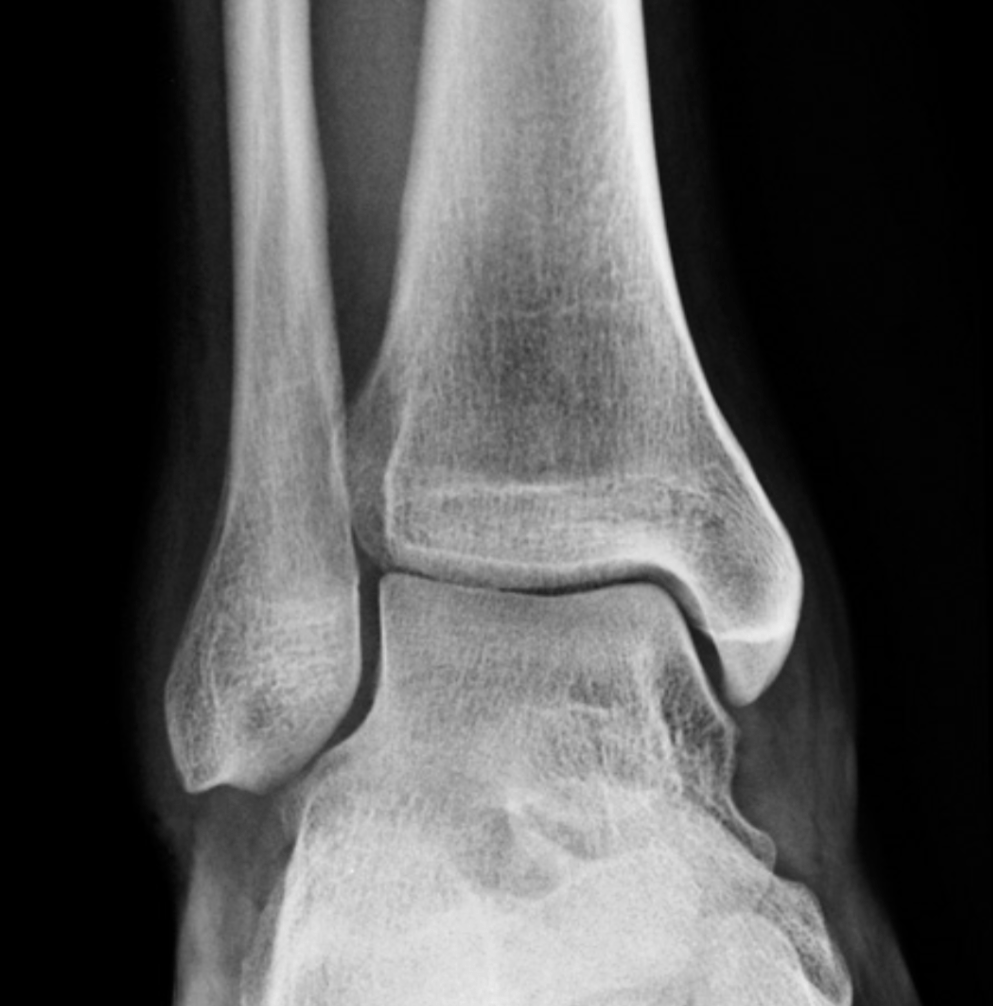
What is Normal?
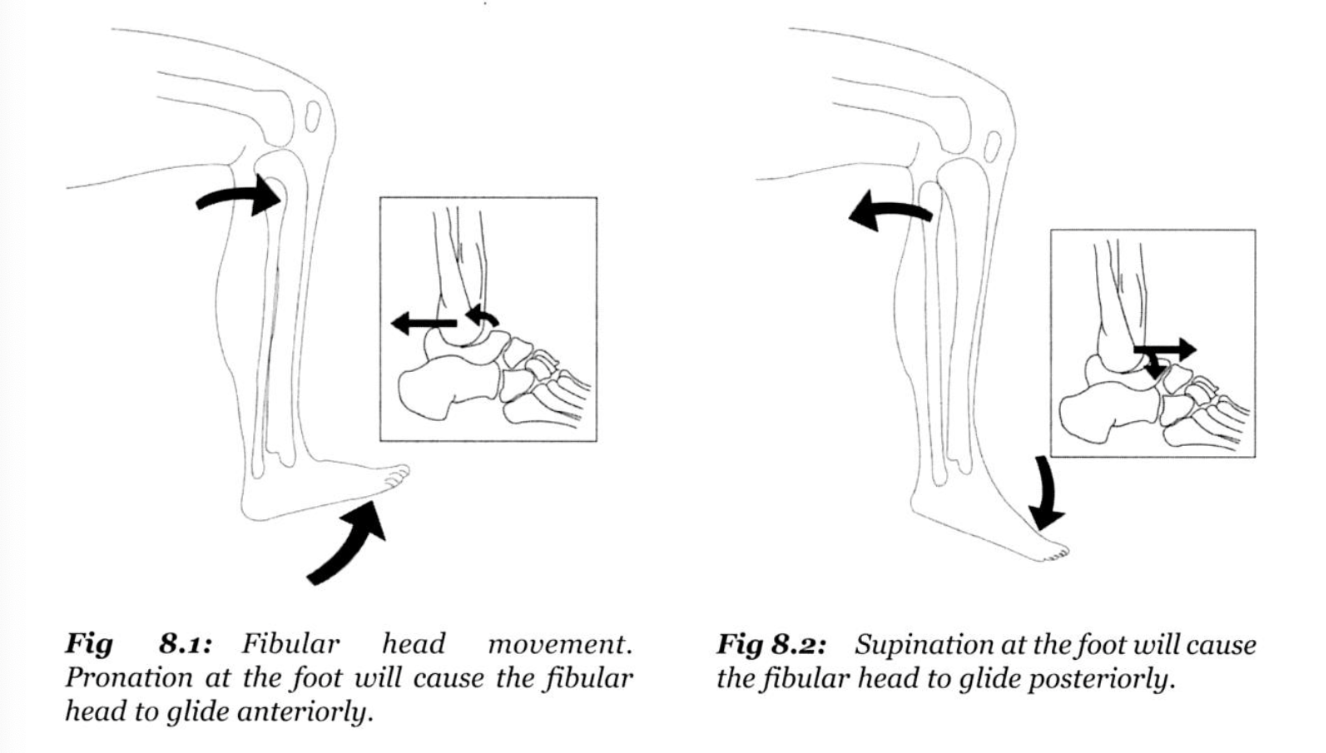
In a more common supination sprain, in which direction does the proximal fibular head move
What is Posterior?
Radial Head: Posterior with Pronation
Fibular Head: Anterior with Pronation
Your hands are parallel with your arm, so think P with P, whereas your feet are perpendicular to your leg, so think they are opposite (A/P).
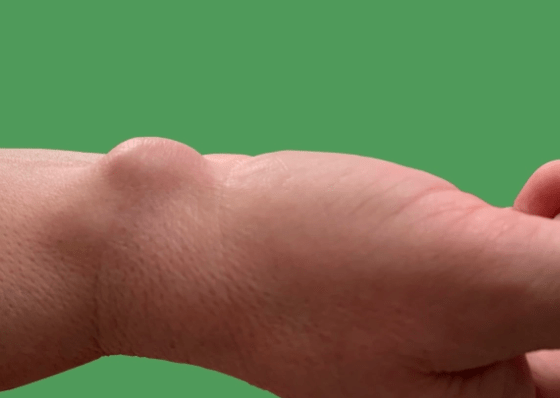
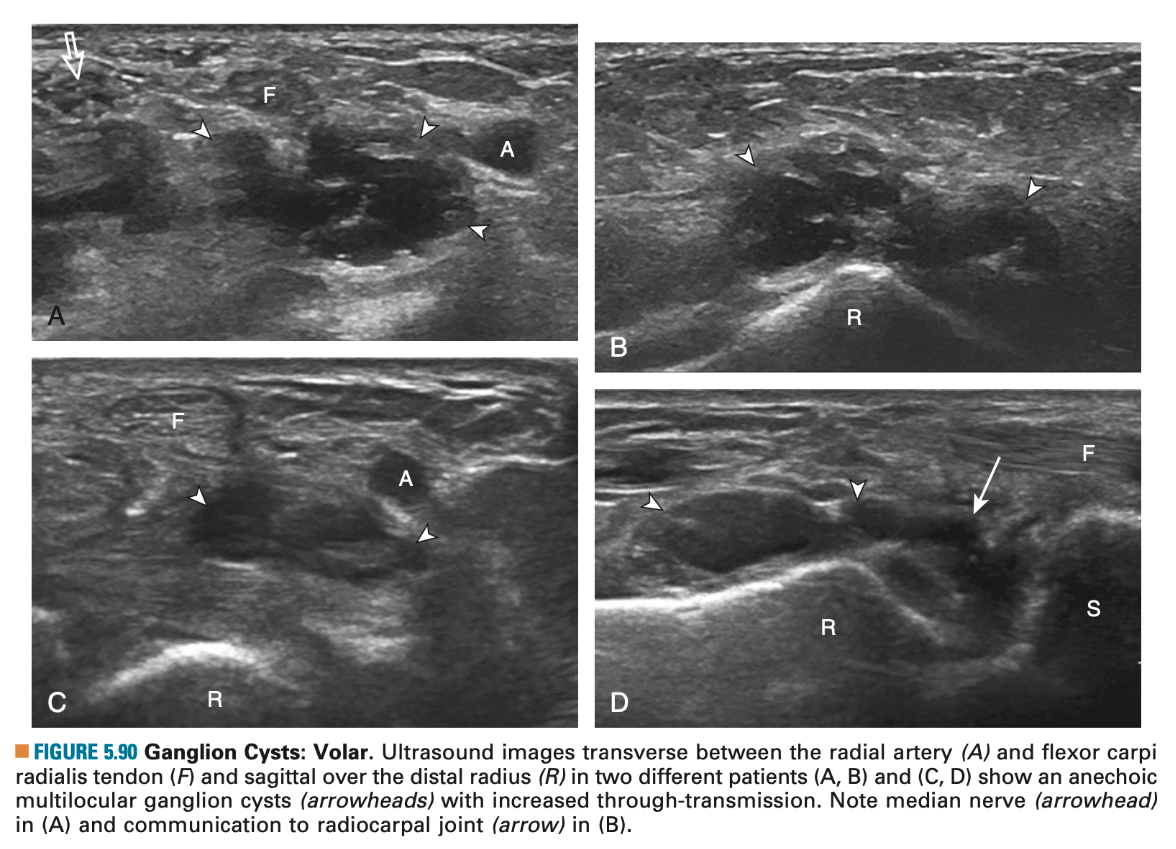
Name the structure occluded below
What is the most common location of ganglion cyst
What is Wrist?
Superficial to scapholunate ligament near the radial artery at the wrist.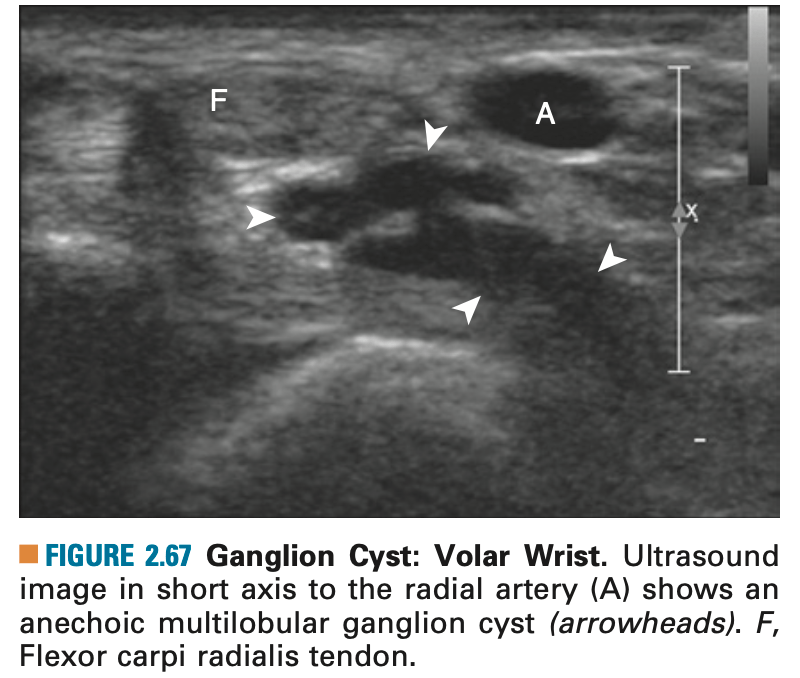
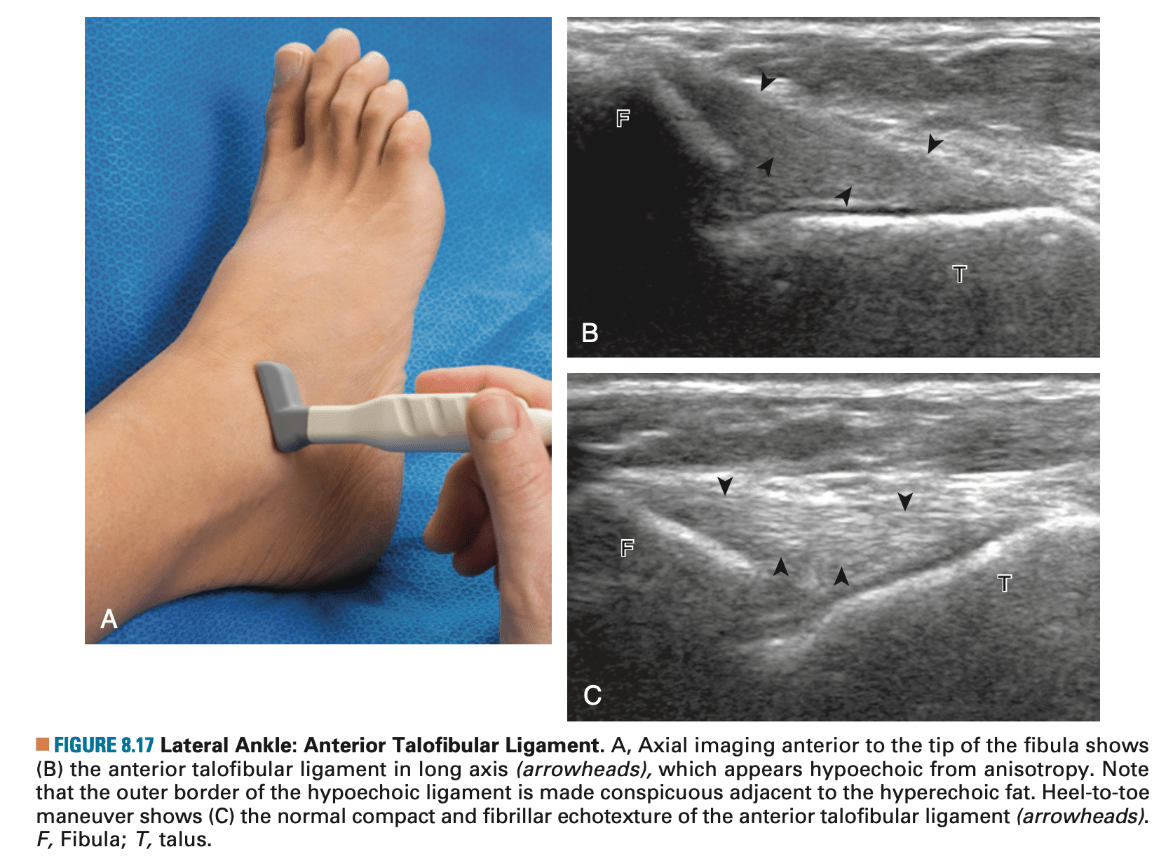
What is the most commonly injured ligament in the foot
What is Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL)?

Protect, and PT once swelling/pain improved
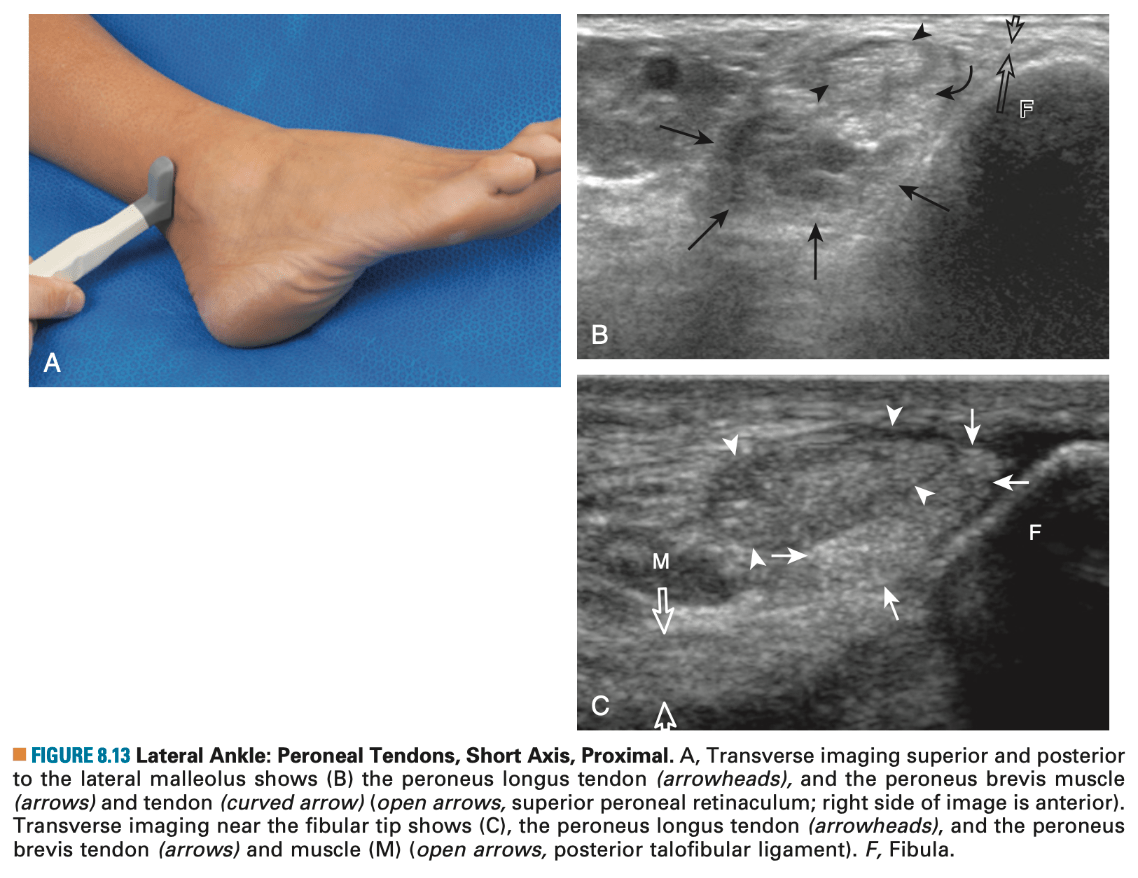
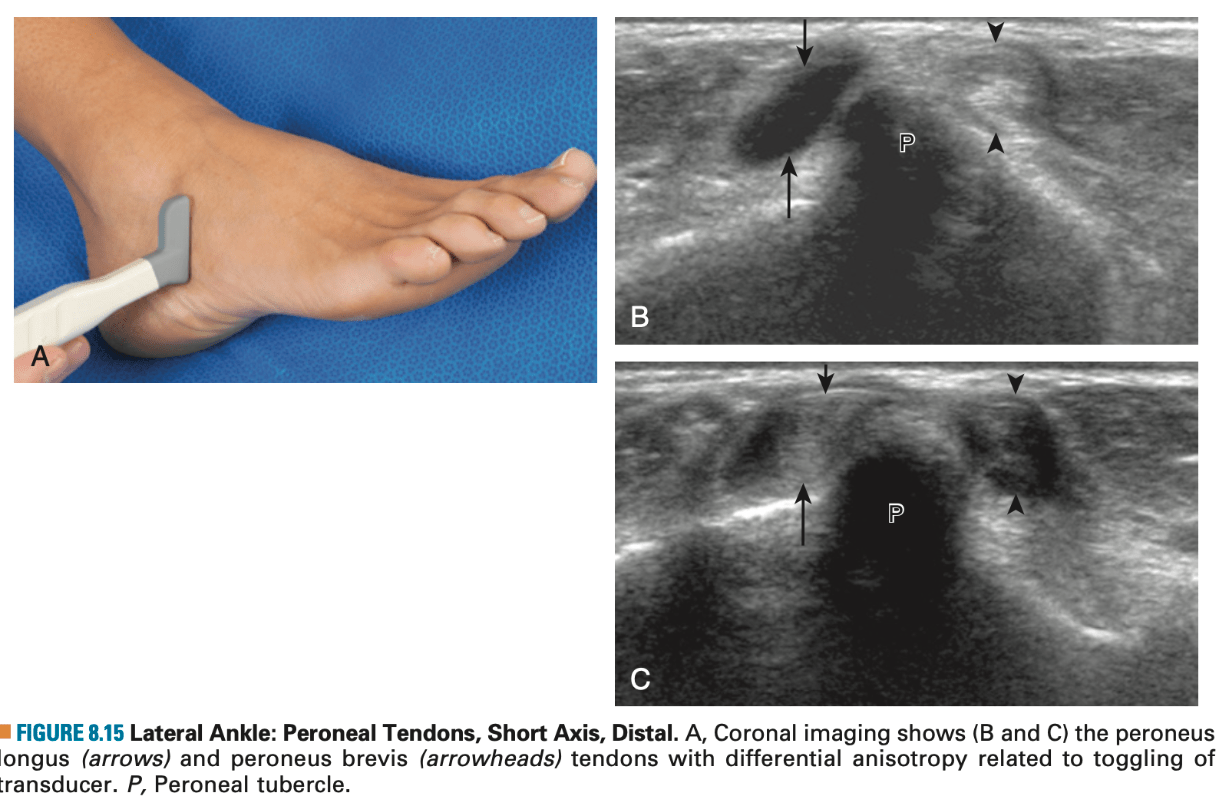
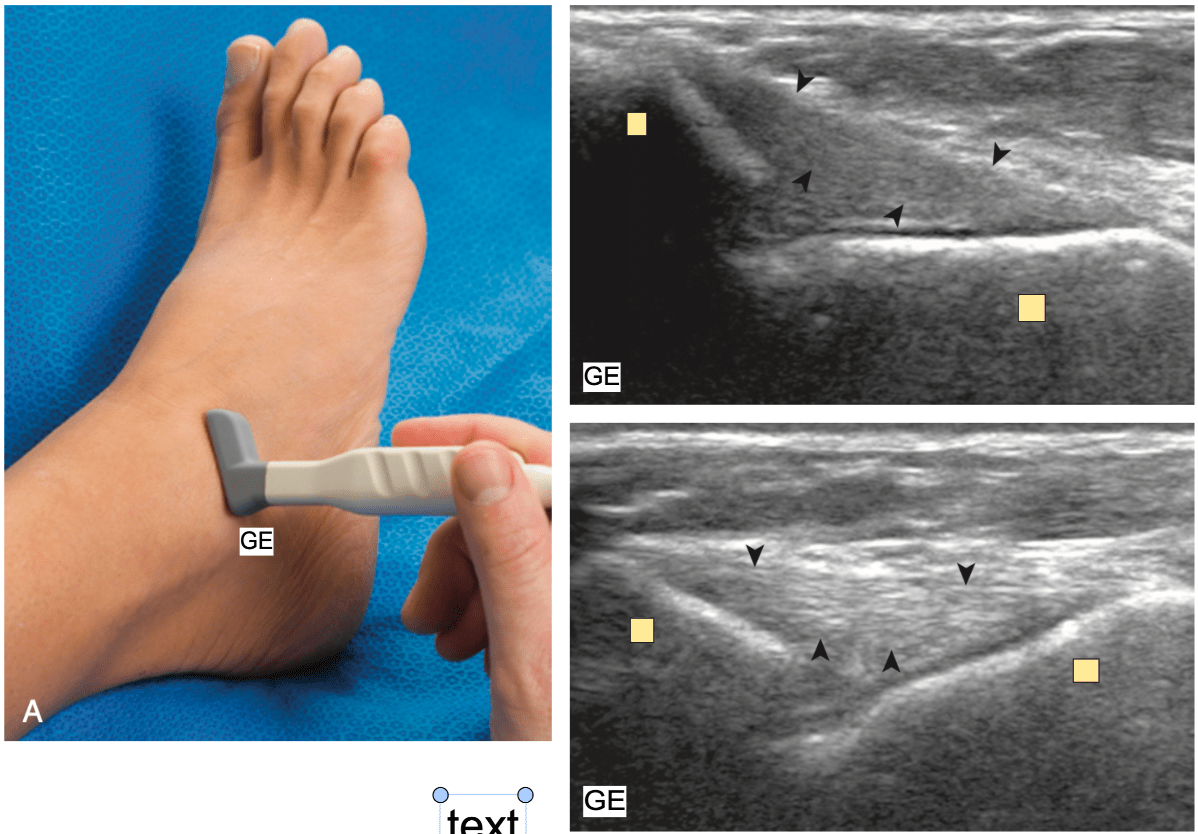
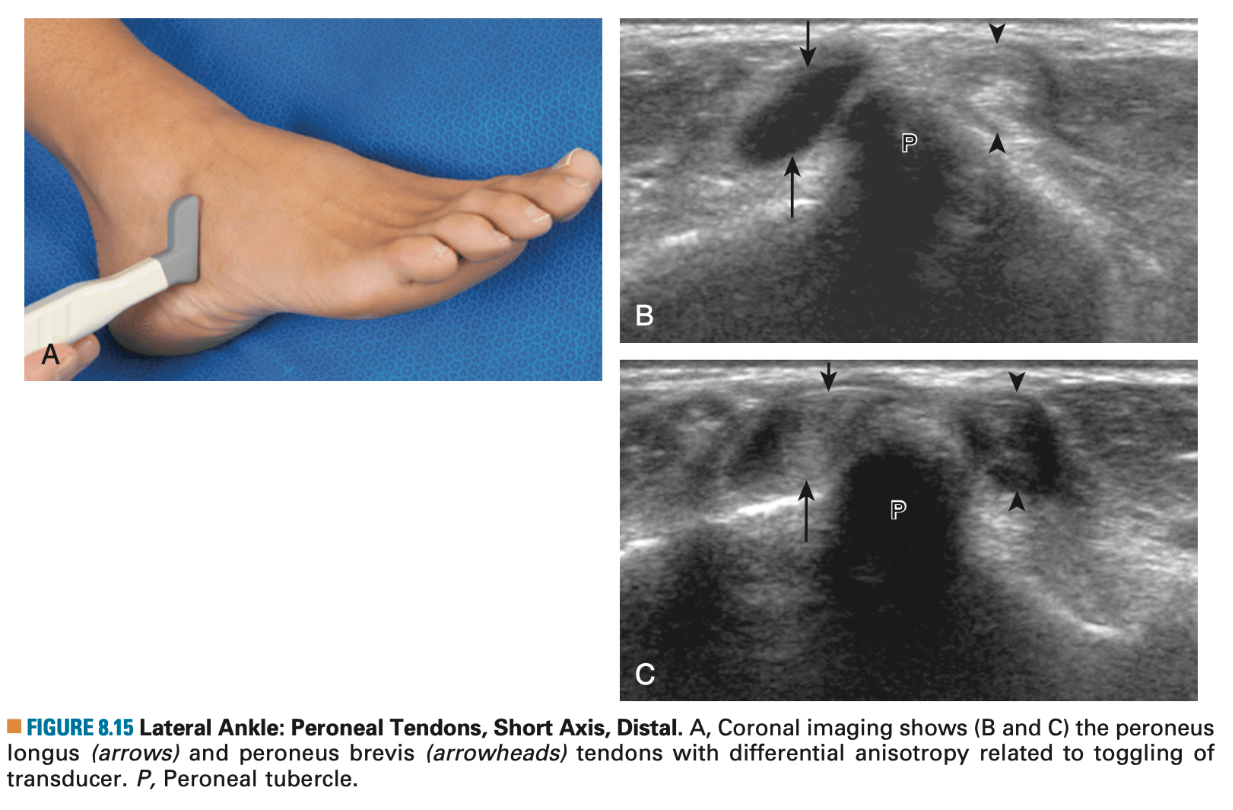
What structure is marked with dark arrowheads.
What is ATFL?
Which way does the fibular head glide with pronation of the foot
What is Anteriorly?
Radial Head: Posterior with Pronation
Fibular Head: Anterior with Pronation
Your hands are parallel with your arm, so think P with P, whereas your feet are perpendicular to your leg, so think they are opposite (A/P).

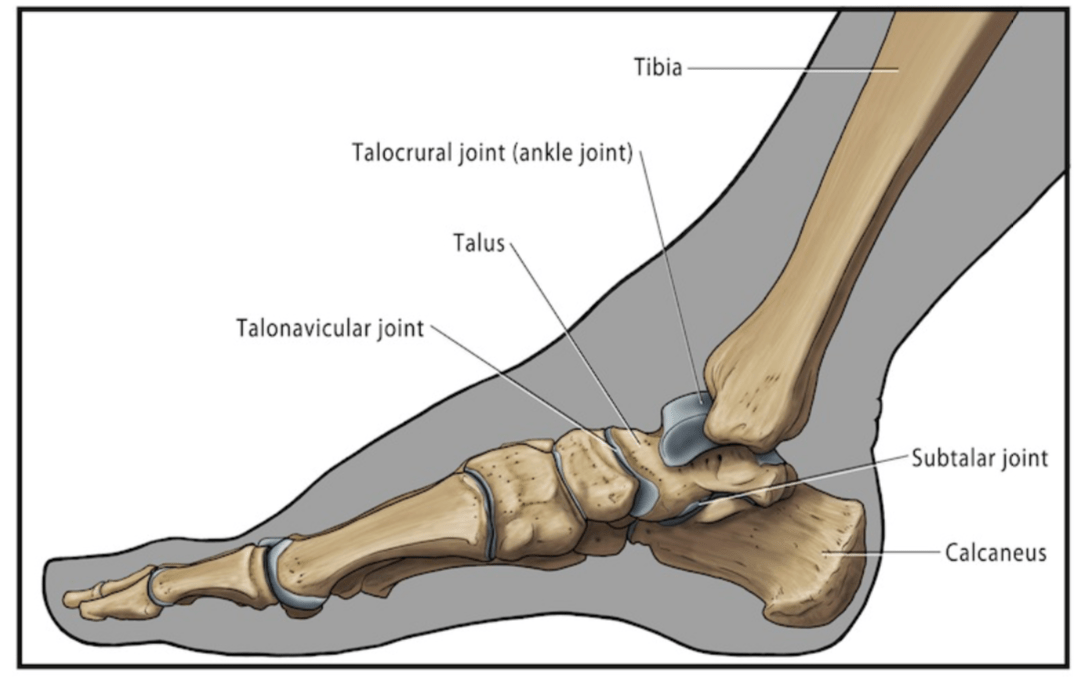
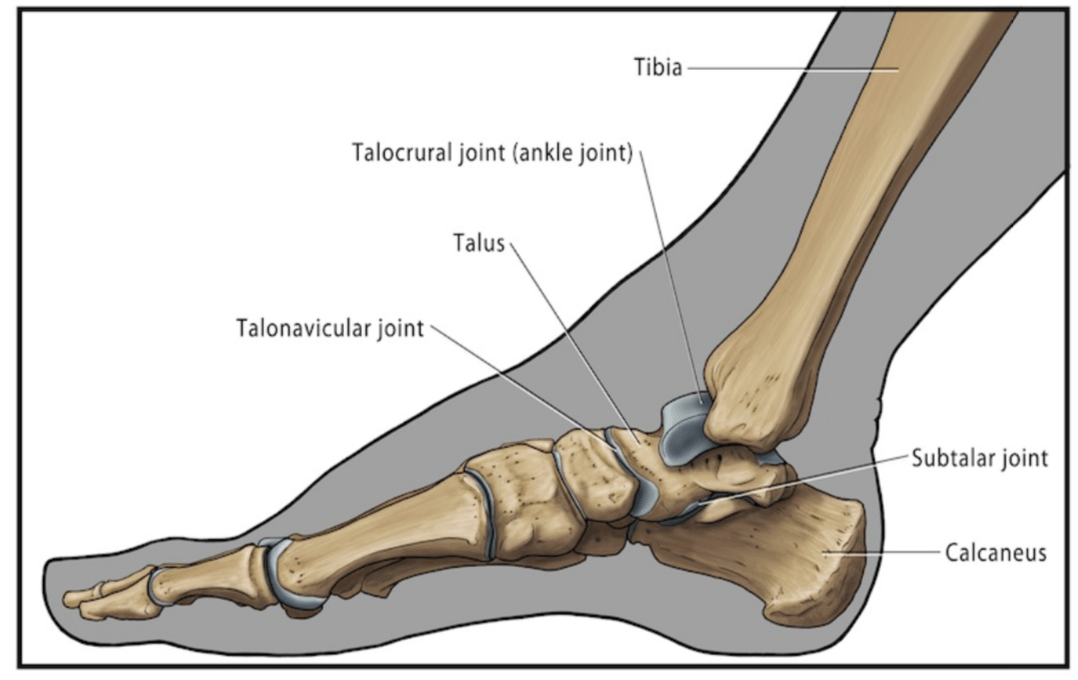
Name the hinge joint that's main motion is plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the foot.
What is Talocrural (Tibiotalar) Joint?
-A hinge joint located between the talus and the medial malleolus, and the lateral malleolus
- Due to the configuration of the talus and the ankle mortise, the ankle is more stable in dorsiflexion than plantar flexion. This is the reason why 80% of ankle sprains occur in plantar flexion.
What is the management for ganglion cysts if observation and conservative management fails
What is Aspiration?

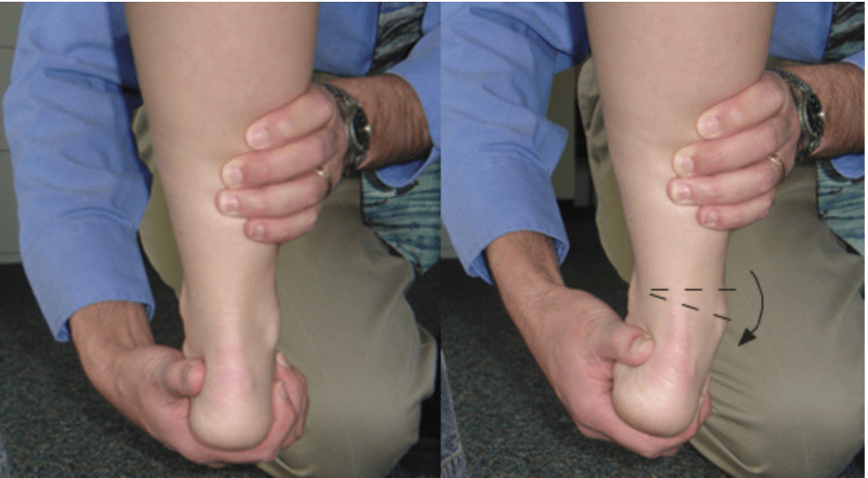
The Talar Tilt Test tests for the integrity of which ligament?
What is CFL?

Excessive anterior displacement of talus relative to tibia (ATFL)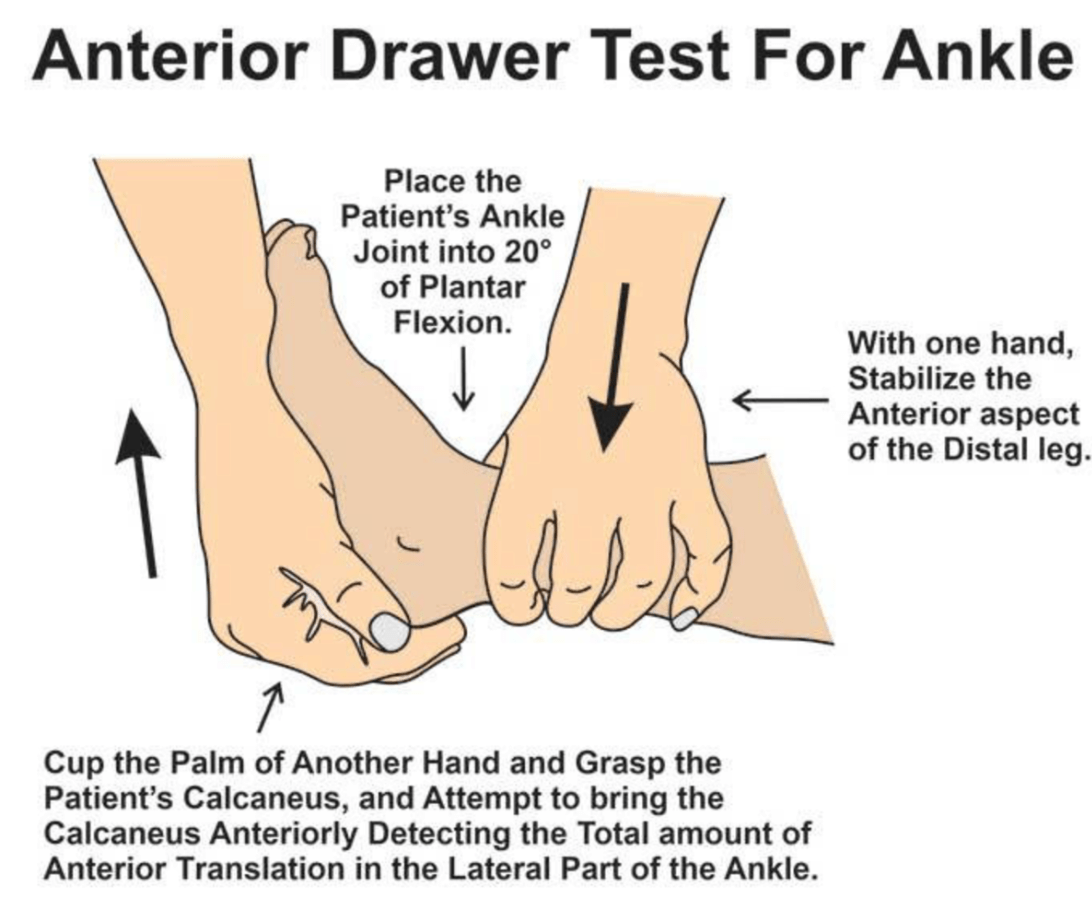
Which of the below is a ganglion cyst on US
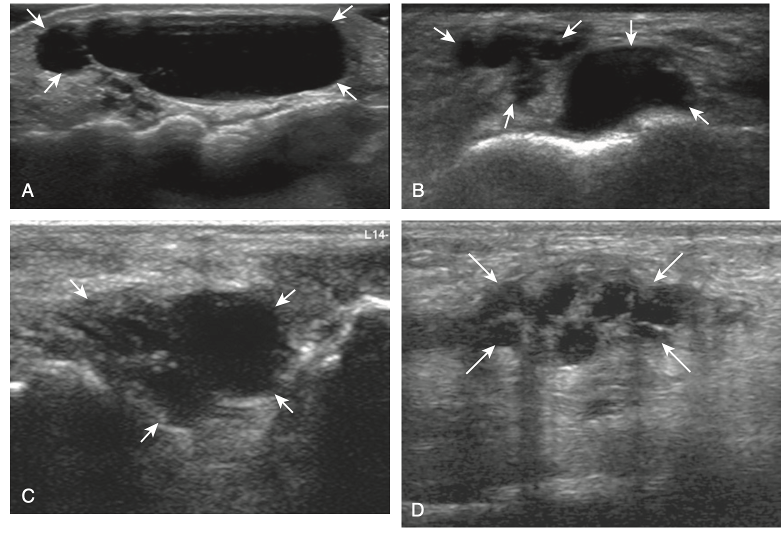
Trick question! All of the above!
Ganglion cysts have several appearances at ultrasound. The most common appearance is that of a hypoechoic or anechoic, multilocular or multilobular, noncompressible cyst that may look complex.
Smaller ganglion cysts are more likely hypoechoic and may show only limited increased through-transmission.
The multilocular appearance of a cyst is specific to both ganglion cysts and fibrocartilage cysts (parameniscal and para- labral); the location of the multilocular cyst assists in this diagnosis. If in contact with fibrocartilage, then parameniscal or paralabral cyst is likely. If located superficial to the scapholunate ligament (Fig. 2.66), near the radial artery at the wrist (a very common site), at the sinus tarsi of the ankle, or within the Hoffa infrapatellar fat pad or at the gastrocnemius tendon origin at the knee, ganglion cyst is likely. The other appearance of a ganglion cyst is a unilocular fluid collection, which can be associated with wrist, hand, ankle, and foot tendons. Unlike a bursal fluid collection, such unilocular ganglion cysts are usually not compressible and not in a location of an expected bursa. Aspiration should only be attempted with a larger diameter needle (such as a 16- or 18-gauge needle), given the high viscosity of the gel-like fluid.

Which way does the fibular head glide with external rotation of the tibia?
What is Anteriorly?
TEA = Tibia, External rotation, Anterior
TIP = Tibia, Internal rotation, Posterior

Name a joint that acts mostly as a shock absorber, and also allows internal/external rotation of the leg while the foot is fixed
What is Subtalar (Talocalcaneal) Joint?
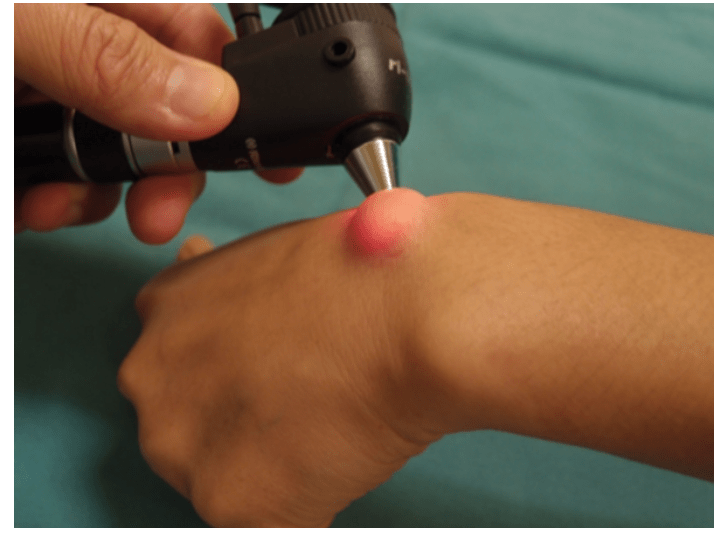
What is an easy way on physical exam to differentiate ganglion cyst from solid tumor
What is Transilluminate?
Ganglion cysts transilluminate while solid tumors do not
- can get US or MRI
Is the ankle is more stable in pronation or supination
What is Pronation?
Pronation is also dorsiflexion, eversion and abduction.
The trochlea of the talus articulates with the ankle mortise. It is wider anteriorly, making the foot more stable in dorsiflexion.

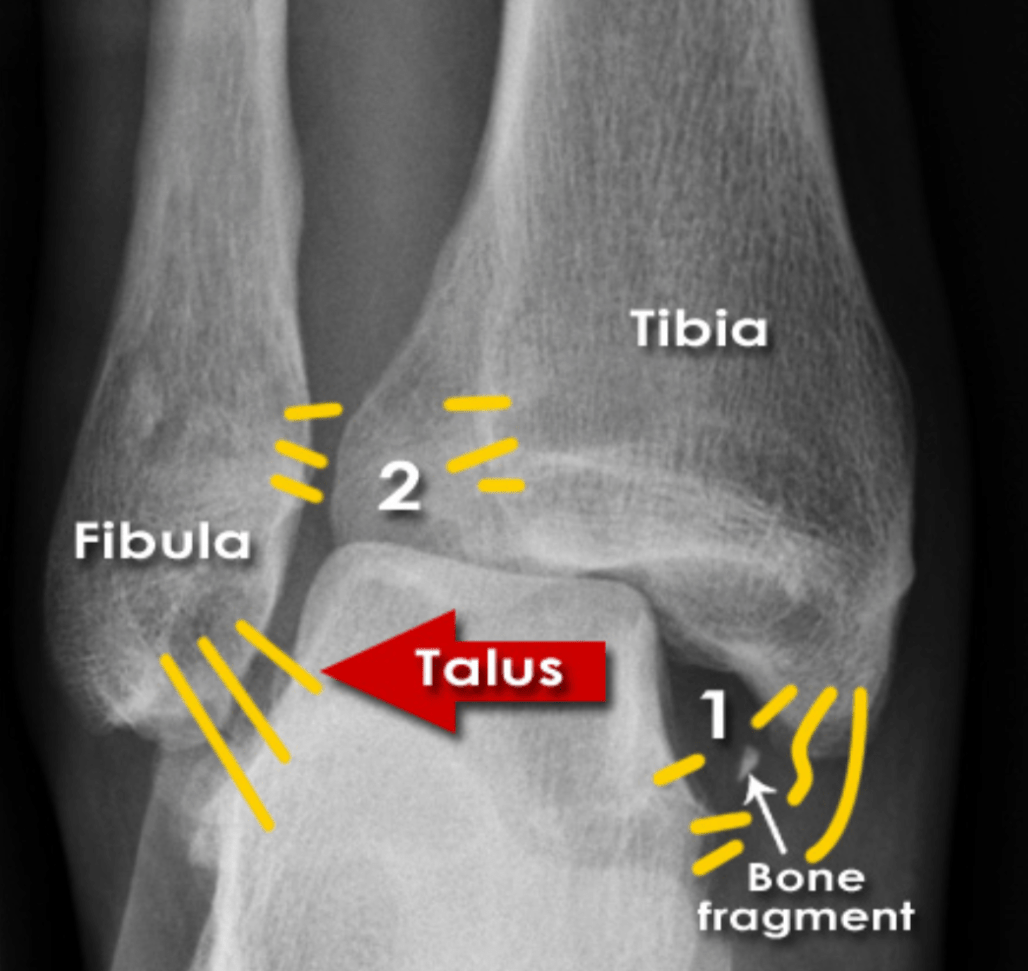
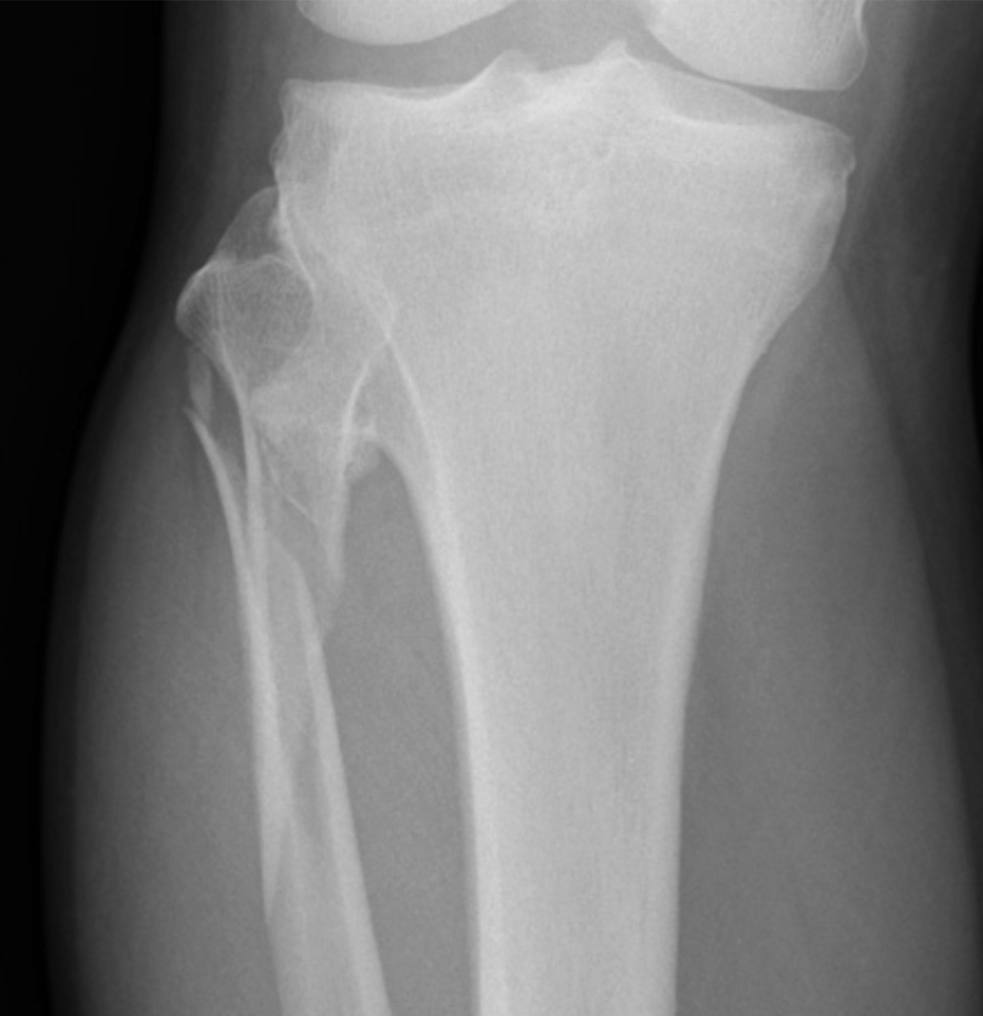
What should you suspect if you see this image?
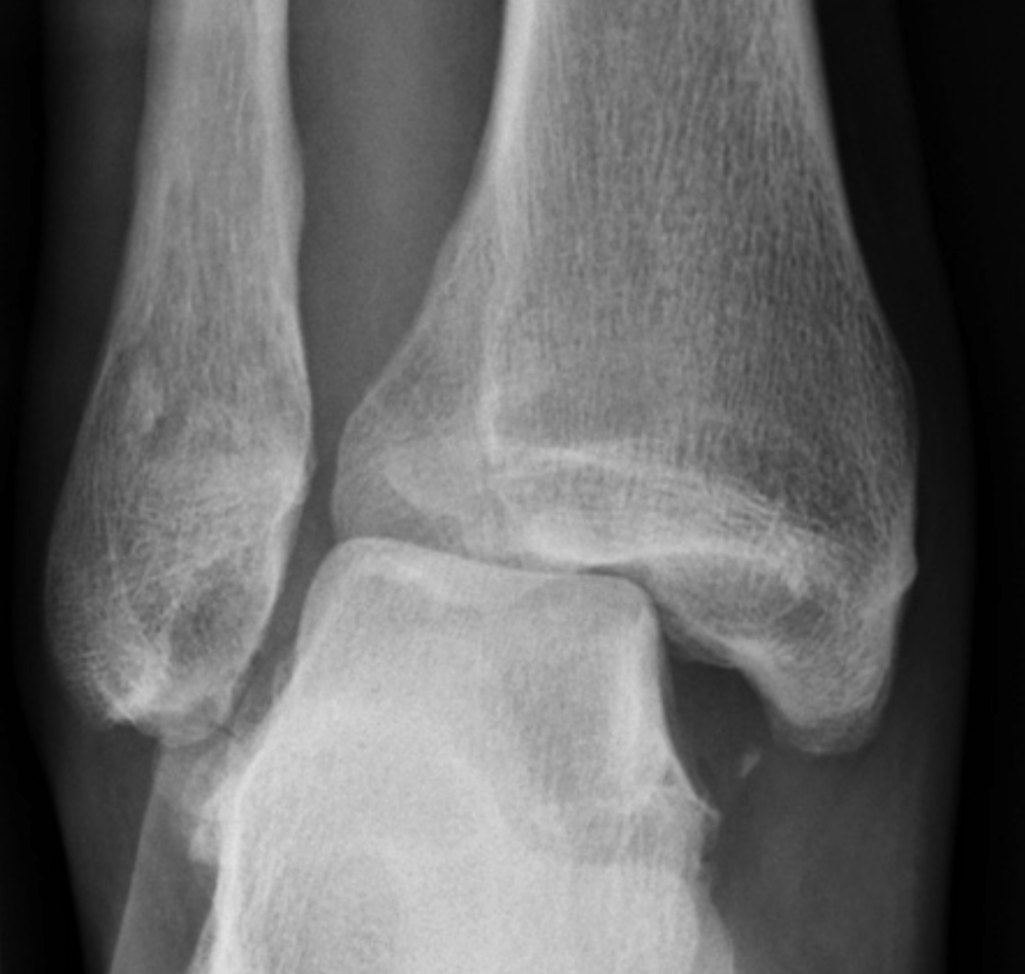
What is Maisonneuve Fracture?
Fracture of the proximal fibula associated with injury to the medial side of the ankle and disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis.
The medial ankle injury may be either a visible medial malleolus fracture or an invisible injury of the medial ligaments.


Describe the movement of ankle joint pronation of the foot
What is Dorsiflexion, Eversion, and ABduction?

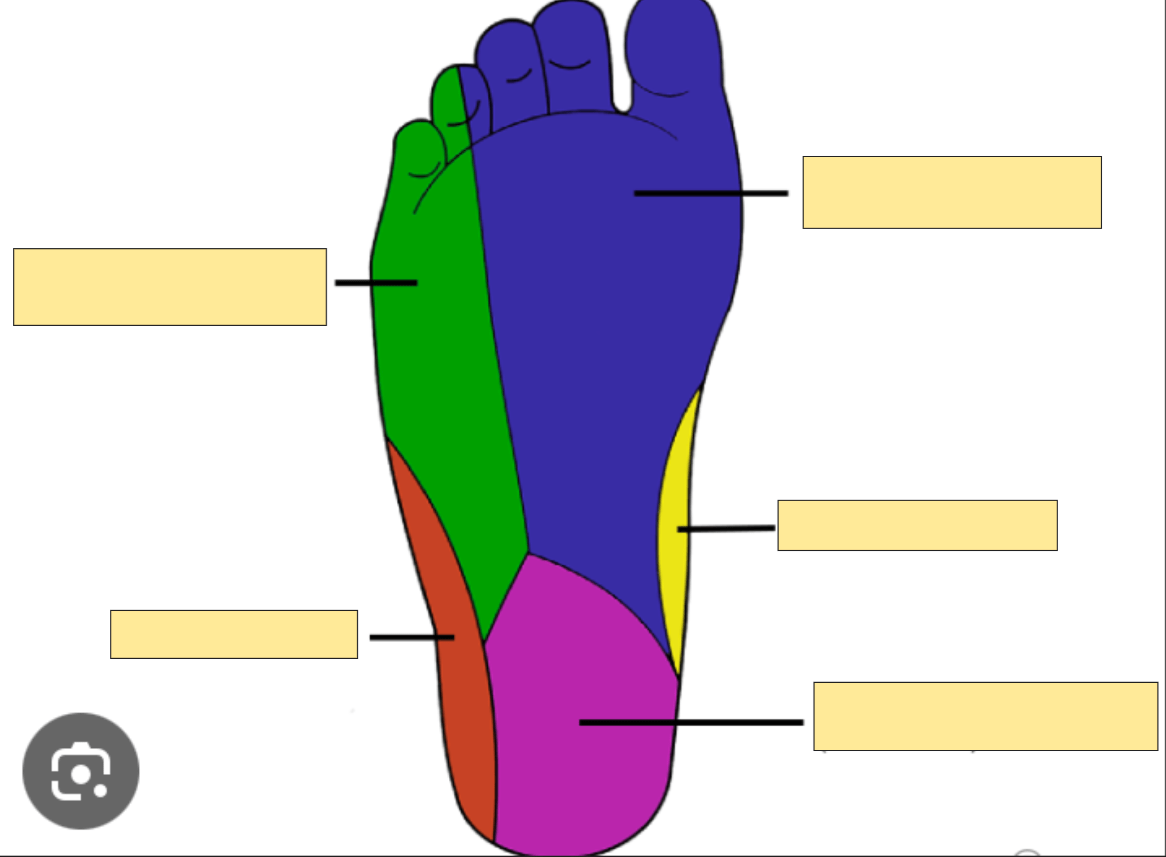
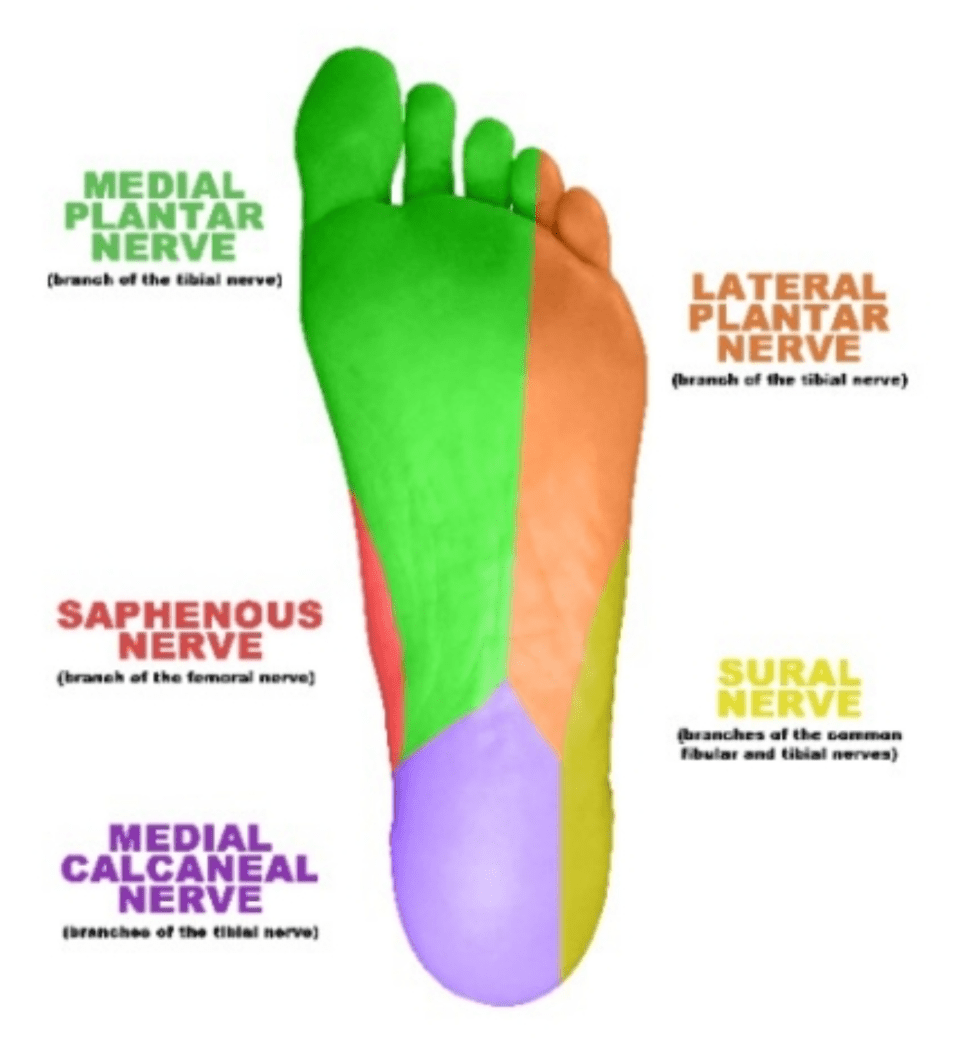
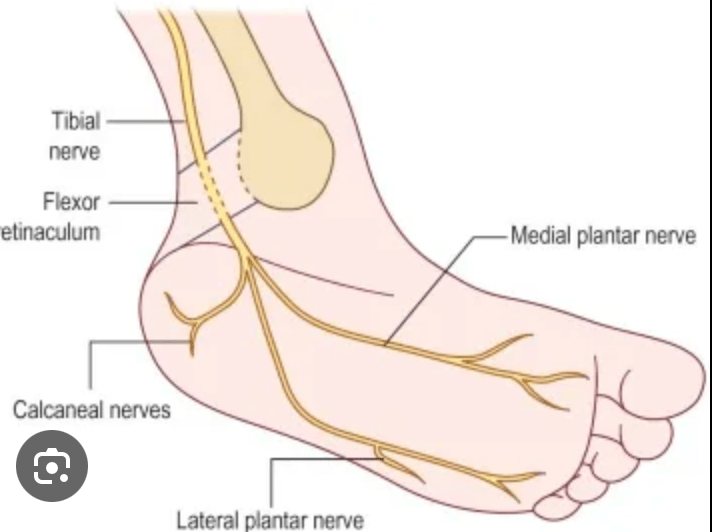
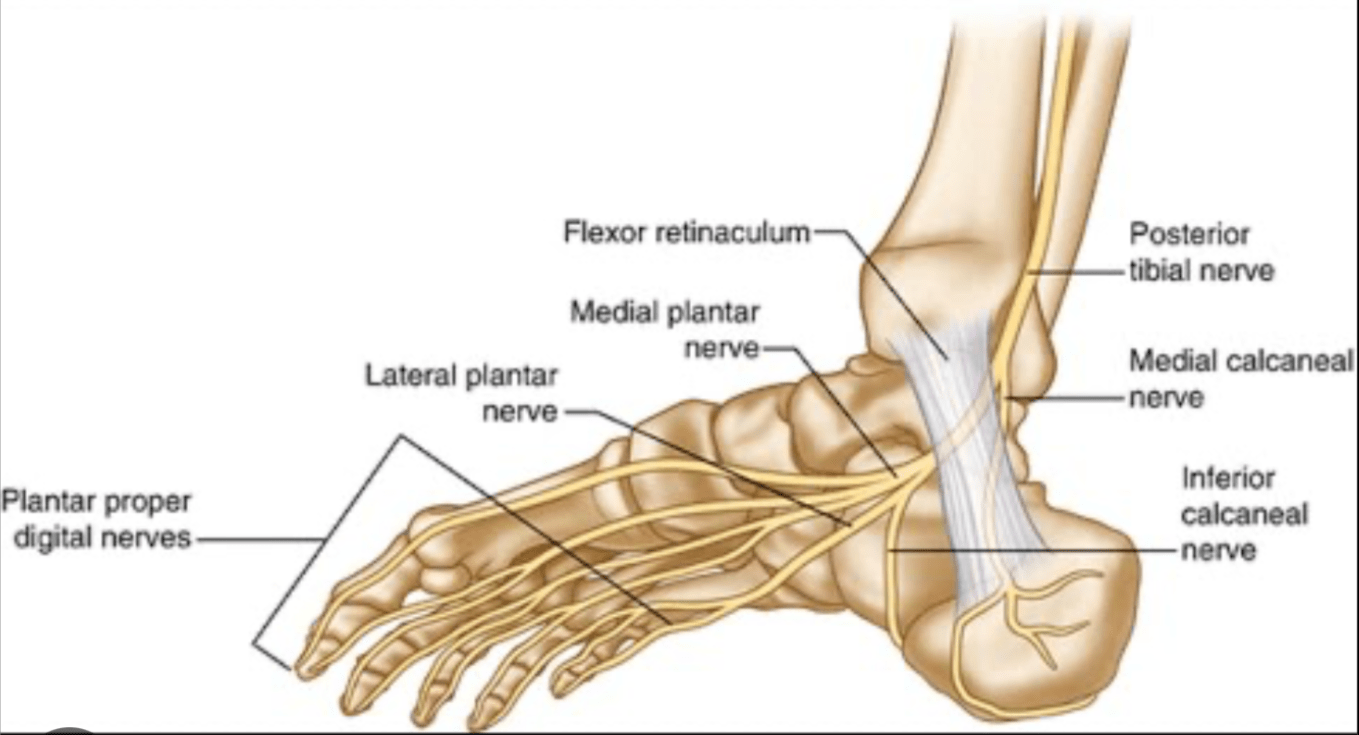
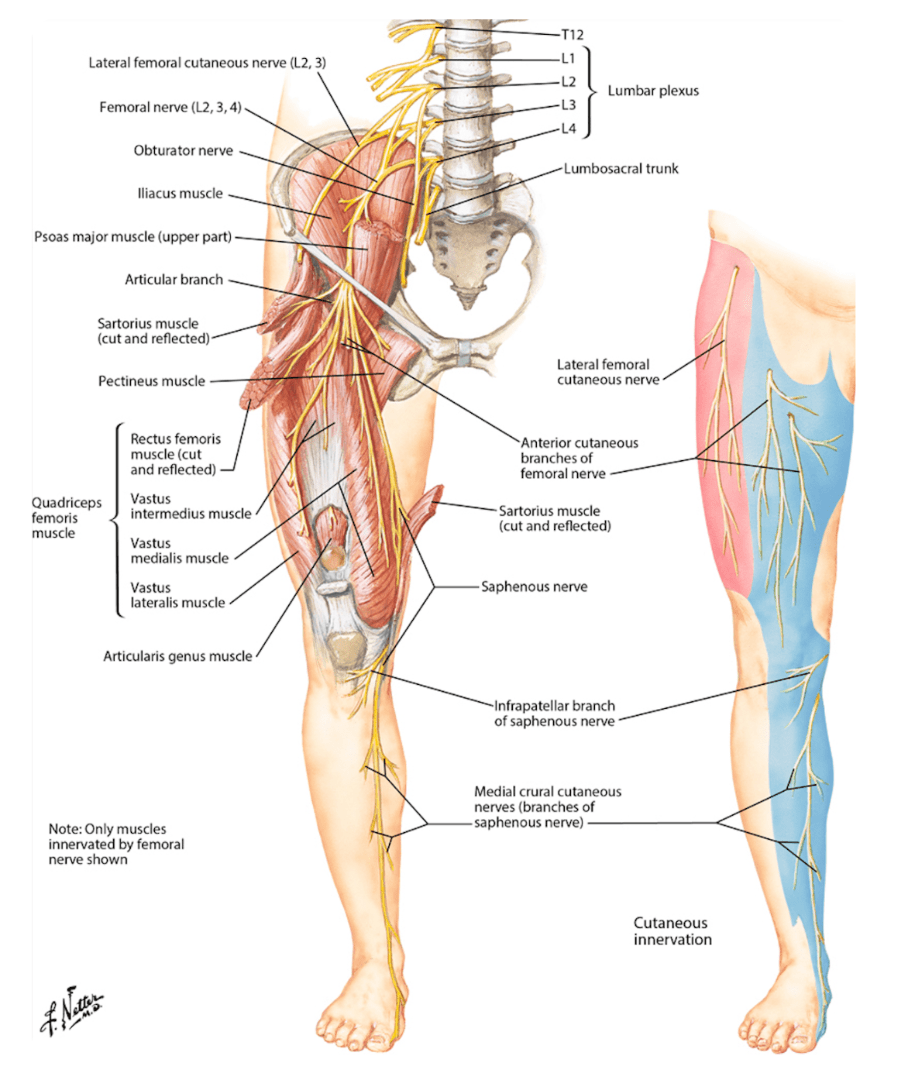
Name the occluded sensory nerves of the plantar foot.
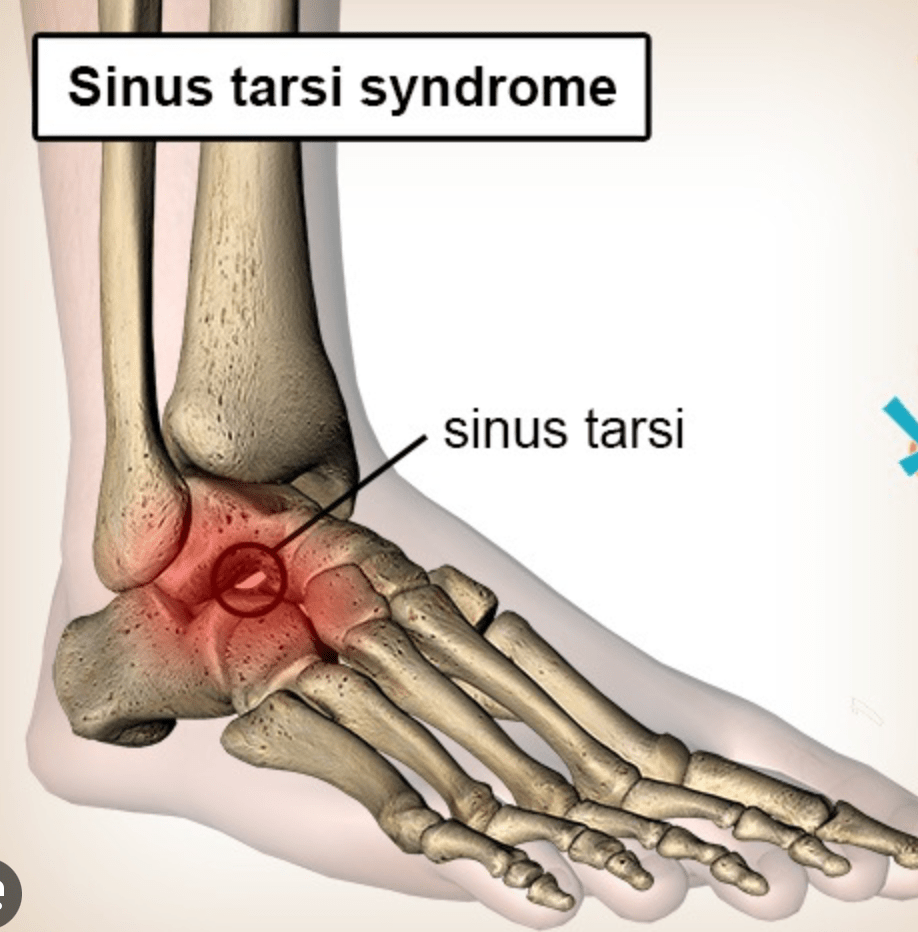
What is the condition that is characterized by synovitis of the lateral aspect of anterior subtalar joint
What is Sinus Tarsi Syndrome?
AKA talocalcaneal sulcas (STS is synovitis of the lateral aspect of anterior subtler joint)
ATFL and CFL first to be injured in inversion injuries, but if severe or recurrent interosseous ligaments of sinus tarsi can be affected.
- Pain with supination
- Acute setting present similar to lateral ankle sprain
- Functional instability of involved ankle and diffuse pain on lateral side of foot and difficulty bearing weight, esp on uneven surface
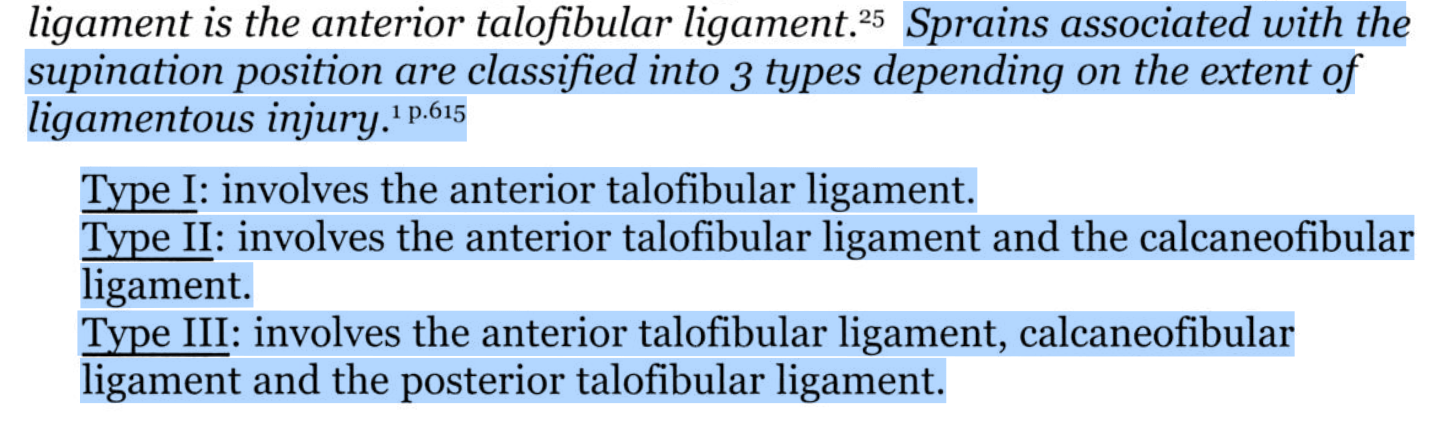
Which ligaments are injured in type II supination ankle sprain
What is ATFL and CFL?
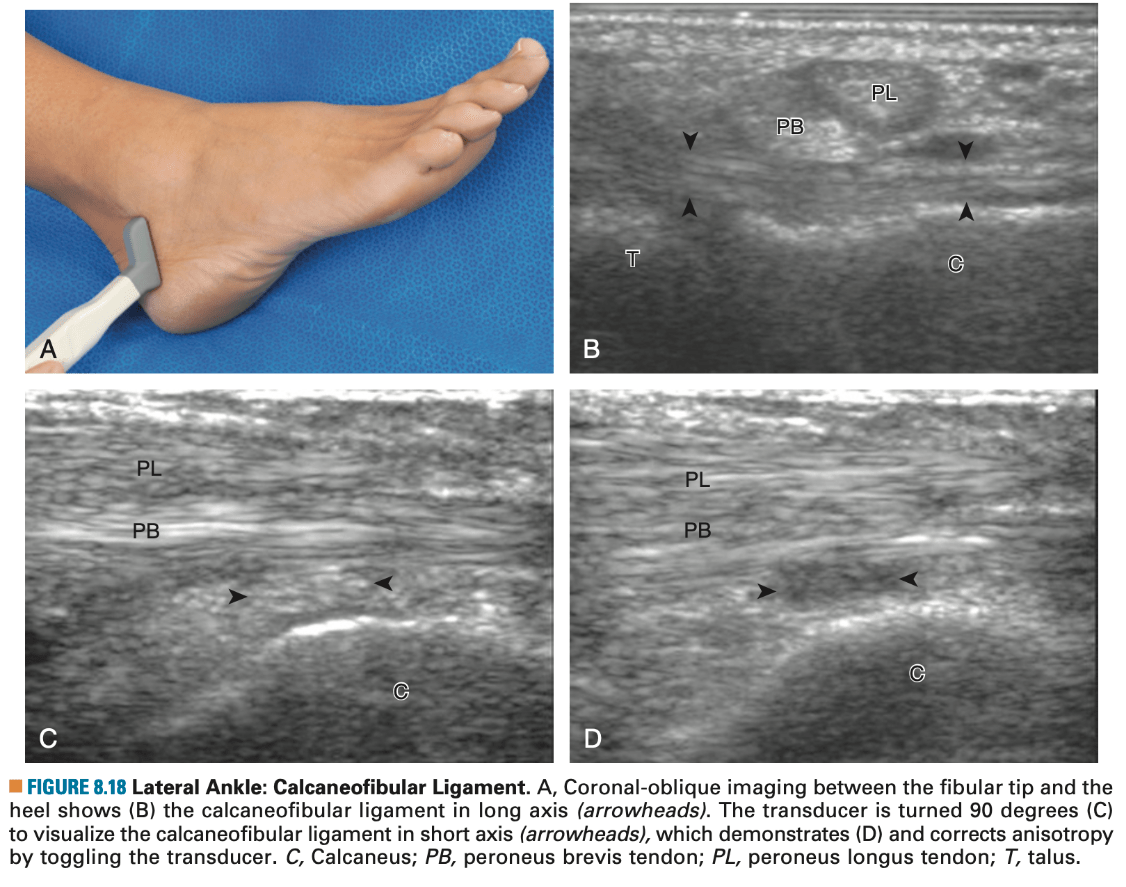
What structure is marked with dark arrowheads.
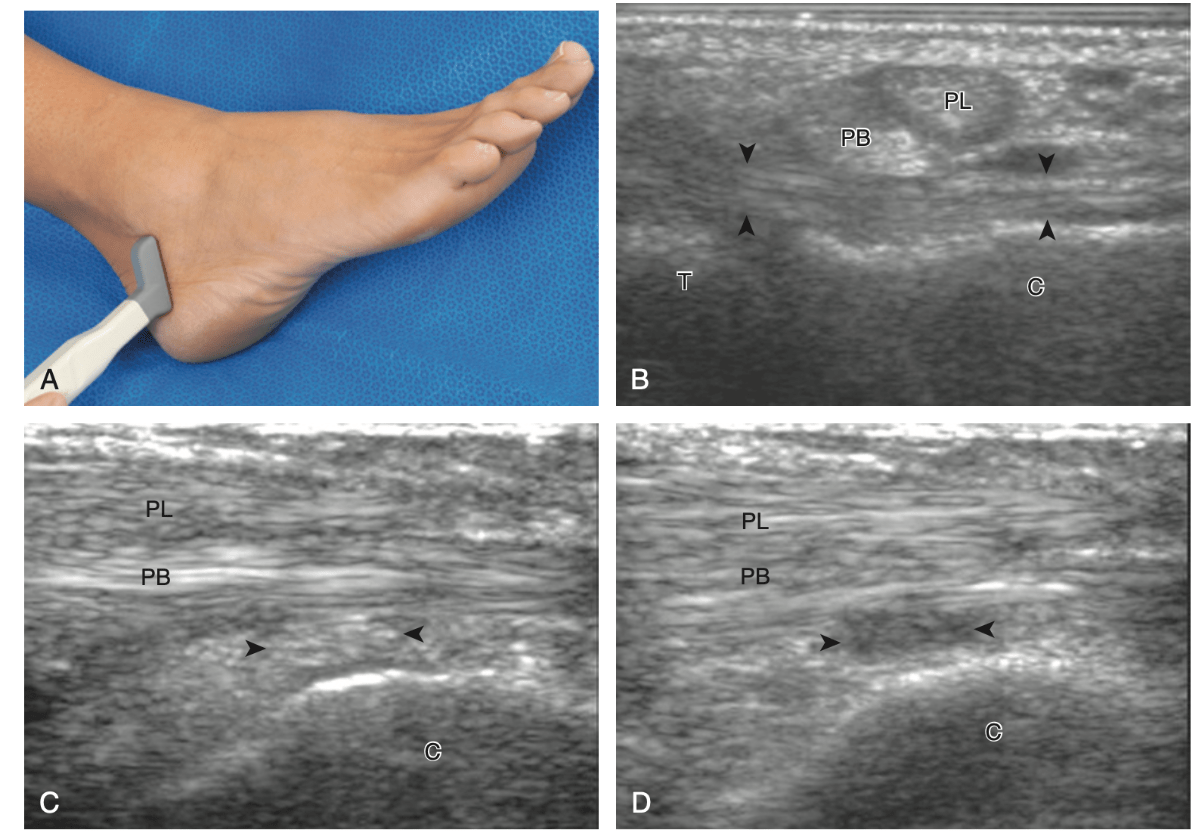
What is CFL?
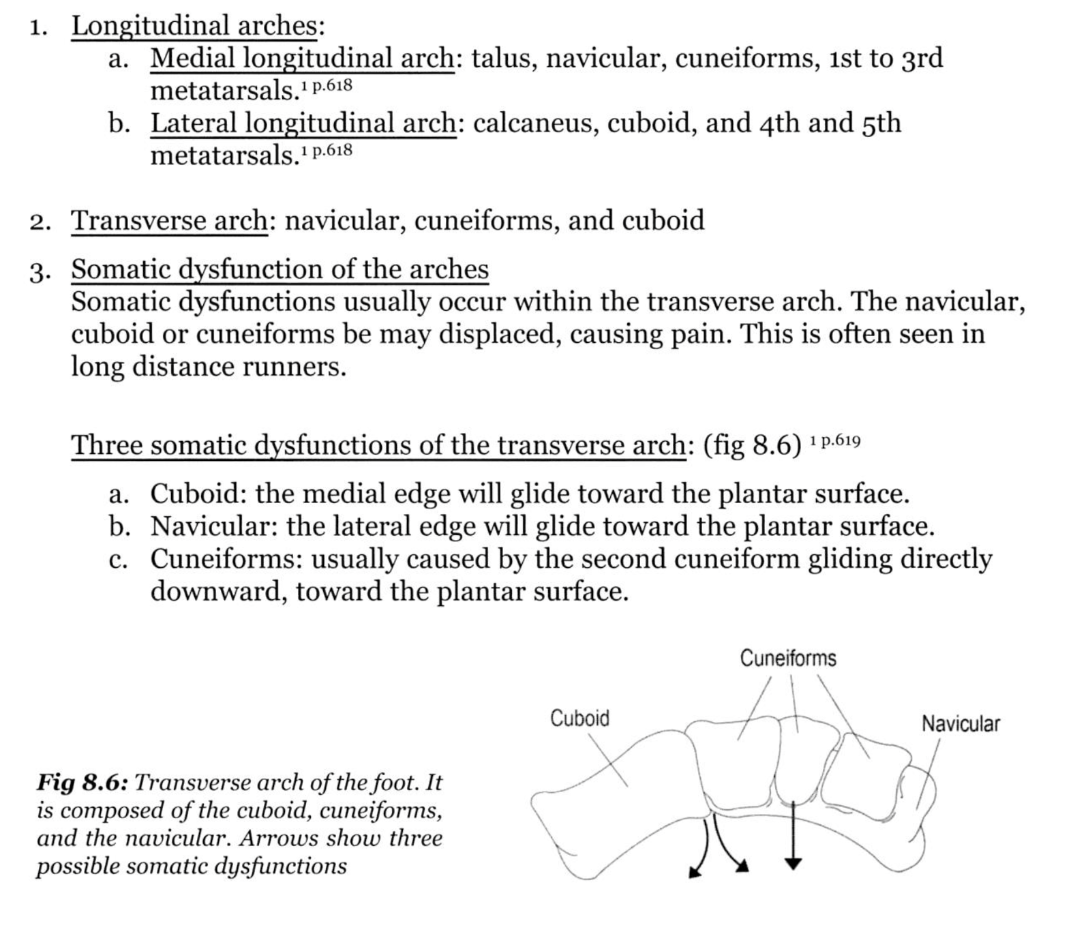
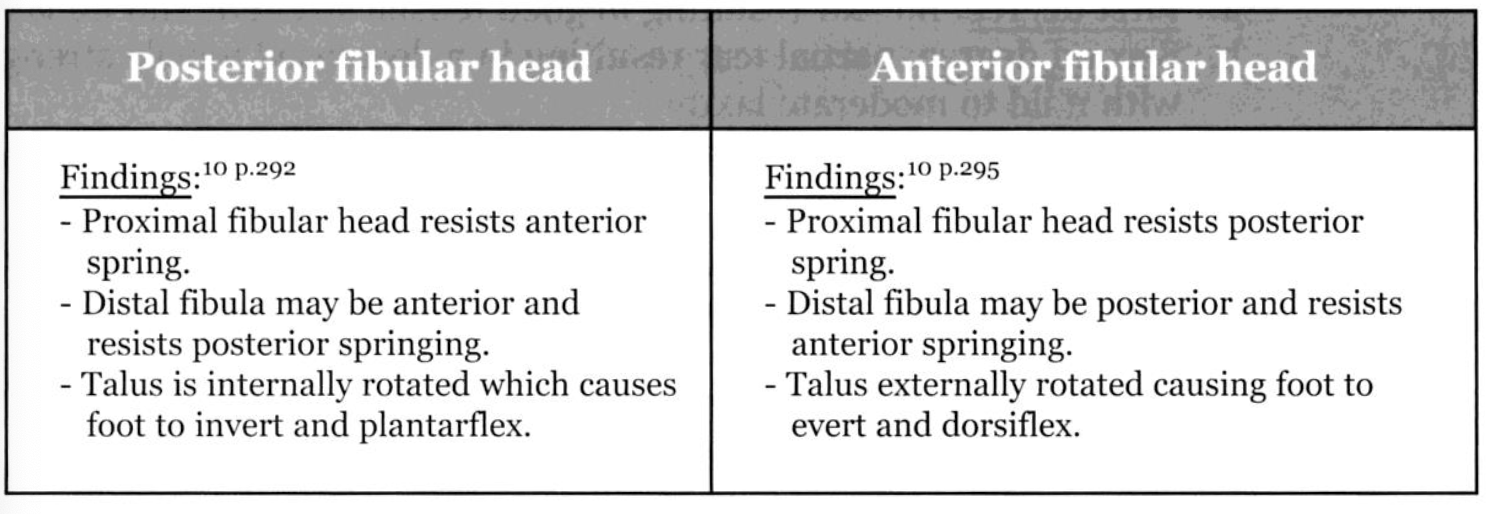
Which bones are part of the transverse arch of the foot
What is Navicular, Cuneiforms, and Cuboid?