Name the neurodegenerative disease associated with the protein misfolding/abnormality:
-Beta-amyloid
-Alpha-synuclein
-Tau
-Huntingtin
-Presenilin
Beta-amyloid: Alzheimer's Dementia
Alpha-synuclein: PD, LBD
Tau: FTD, PSP, CBD
Huntingtin: HD
Presenilin: Early onset Alzheimer's
A 50 yo man presents after a MVA where his head struck the windshield. What is the name of this injury, and explain what happens?
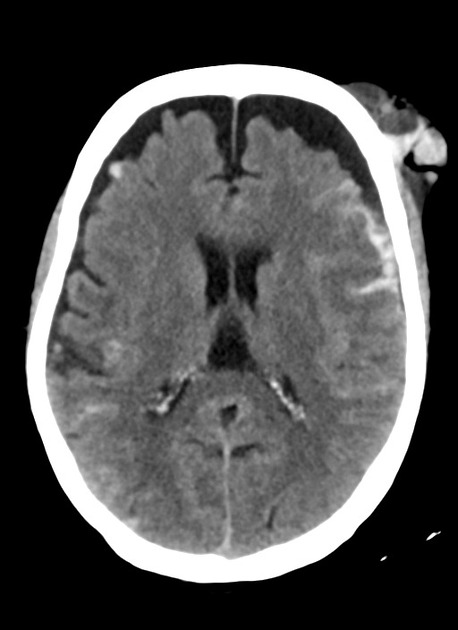
Coup contrecoup injury
Typically traumatic SAH or contusion where injury occurs at the site of external impact as well as the site opposite

A child with absence epilepsy is started on carbamazepine and shortly after presents with confusion and bladder incontinence. What is EEG most likely to show?
Carbamazepine, lamotrigine and phenytoin may trigger status in absence epilepsy and should be avoided
First line agents for trigeminal neuralgia
Oxcarbazepine, carbamazepine
Second line: Baclofen, lamotrigine
First line agents in essential tremor?
Contraindications?
Beta blockers
-Avoid in asthma, hypotension, bradycardia, CHF
Primidone
-Pregnancy, breast feeding, OCP use, liver or kidney disease, history of non-adherence, DOAC use, history of drug dependence
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
MOA: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
MOA of nimodipine
Dihydropyridine class of L-type voltage-gated calcium channel blockers
*Used to decrease mortality and reduce risk of stroke in SAH
How does topiramate increase the risk of kidney stones?
Weak carbonic anhydrase inhibitor:
-Increases urinary pH
-Decreases urinary citrate excretion
Describe hemicrania continua
Indomethacin-responsive headache, one of the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias
Continuous, unilateral head pain with exacerbations of pain associated with parasympathetic symptoms
Response to indomethacin is part of the diagnosis
BONUS - what is the other indomethacin-responsive headache?
Tourette syndrome diagnostic criteria and treatment
At least two motor and one vocal tic for minimum 1 year
First line - CBT
Can also use guanfacine and antipsychotics
Pick Disease is associated with pick bodies (tau-immunoreactive cytoplasmic inclusions) WHERE?
Dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
Also frequent in CA-1, less common in CA-2-4 and the presubiculum
What procedure would this patient most likely benefit from?

Suboccipital decompressive craniectomy
Best chance at reducing mortality; other measures (EVD, other measures to reduce ICP) are only temporizing and are unlikely to affect mortality
Describe the interaction between valproic acid and lamotrigine
Valproate increases lamotrigine blood levels by inhibiting the hepatic glucuronidation of lamotrigine
First line preventative treatments for cluster headache
Verapamil, CGRP inhibitors (specifically galcanezumab)
Describe orthostatic tremor - presentation, diagnosis, treatment
Tremulousness and instability upon standing that improves with walking or sitting
EMG showed high frequency (14-16 Hz) tremor - helicopter sound
First line - clonazepam
Second line - gabapentin, pregabalin, primidone
Refractory - DBS
A 62 yo woman presents with years of progressive vision changes - trouble finding objects on shelves, reading/scanning text, describing objects in a photo scene. VA, fundus exam, eye movements are normal.
Likely diagnosis?
Posterior cortical atrophy
Thought to be a variant of early-onset AD, PCA involves progressive decline of higher level visual processing (simultagnosia, optic ataxia, oculomotor apraxia).
What sensitivity is required to determine electrocerebral silence (ECI) on EEG?
2 uV
Recording must be minimum 30 minutes with minimum 10 cm between leads
**Please note EEG is no longer required or accepted to meet criteria per most recent AAN guidelines
Name the highest risk factors for SUDEP
Sudden unexplained death in epilepsy is a poorly understood phenomenon
Affects ~1 in 1000 adult annually; ~1 in 4500 children
Uncontrolled generalized tonic clonic seizures, higher seizure frequency, multiple ASMs, longer duration of epilepsy, poor medication adherence, male>female
The amygdala regulates the emotional component of stimuli, including pain.
FDA-approved medications for tardive dyskinesia
Valbenazine and deutetrabenazine
(Tetrabenazine is not FDA-approved)
All three medications are type-2 vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitors and reduce dopamine incorporation into vesicles
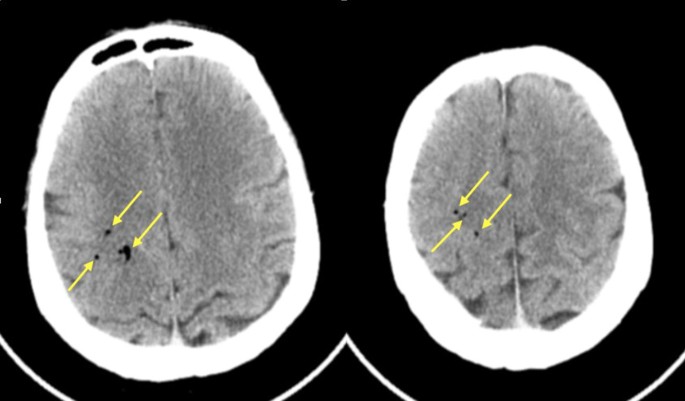
A 78 yo woman presents with acute changes in vision - exam shows right homonymous hemianopsia, CT with left occipital hemorrhage. MRI with scattered microhemorrhages.
Diagnosis and treatment?
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy


Venous air embolism
(central line removal, venous stripping, HD, surgery)
A 37 yo male presents with fever and encephalopathy, CSF studies showing lymphocytic pleocytosis.
Name the EEG pattern and recommended initial treatment?

Acyclovir (as well as ASMs for acute management)
EEG pattern - lateralized periodic discharges (LPDs) over the temporal region
Need to have high suspicion for HSV encephalitis
First line abortive therapy in pregnancy?
Tylenol
NSAIDs avoided especially early; triptans may be relatively safe but use should be limited; not enough data on CGRP inhibitors
A child presents with progressive balance changes, particularly toward the end of the day. In the mornings, he is doing quite well. Family report "stiffness" of the left foot initially that has now progressed to involve both lower extremities.
Dx? Tx?
Dopa-responsive dystonia
AD
Typically starts in a foot and becomes generalized; diurnal variation in symptoms
Classically responsive to low dose levodopa