Identify two challenges of the Growth Stage.
- Dealing with rapid growth
- Avoid getting too comfortable in the market or overextending
- Expanding into new markets that are too small to support all the competing businesses
- Neglecting its current customer base in the pursuit of a new market or a larger market share.
- Competition can come from businesses that are already in the new market or from new businesses entering the established market.
- The owner relinquishing control of some areas to reliable staff, who will contribute to the business according to its goals and objectives.
Define Market Segmentation
Market segmentation refers to the categorizing of customers into groups based on their common characteristics.
Identify the 4 Ps of Marketing
Product
Price
Promotion
Place
Identify the three quality management strategies.
Quality Control is a reactive process that inspects and tests finished products to identify and fix defects after they occur. Its main goal is to ensure products meet specified standards before reaching customers.
Quality Assurance is a proactive approach that focuses on improving production processes to prevent defects from happening. It ensures systems and procedures are in place to consistently meet quality standards.
Total Quality Management is a company-wide strategy aimed at long-term success through continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. It involves all employees and emphasizes quality in every aspect of the business.
How long do you have to complete the exam?
15 minutes planning and 2 hours working time
Explain the difference between Market Share and Market Growth
Market Share measures a company's portion of total sales in a market, showing its competitive position.
Market Growth tracks how much the overall market size is increasing over time, indicating industry expansion.
Define Target Market
A target market is a particular market segment(s) that a business focuses its marketing activities on.
Provide two examples for product extension strategies for businesses.
Change the product’s packaging
Find new uses for product
Add new features to the product
Reducing the price
Selling existing products to new markets
Target a new market segment
Develop new promotional strategies
Identify two of the four subjunction's of materials management.
Inventory Management
Supply Chain Management
Logistics
Capacity utilisation
What is the structure of questions in your exam and which questions are relevant to the stimulus?
2 Explain questions (Knowledge)
1 Describe Business Environment (stimulus)
1 Describe Business Situation (stimulus)
1 Extended Response Report Extract (stimulus) which includes:
Analysis (SWOT Analysis and Relationship and Trend)
Evaluate (One Strategy, Two Criteria, One Decision and Recomendation/s)
Communicating (headings, Introduction, Referencing and Spelling & Punctuation)
Australian Consumer Law is enforced by which national agency?
Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC)
Define differentiation
Differentiation is making a product or service stand out from competitors by offering unique features, quality, appearance, or services that add value beyond price.
Identify and explain two promotional strategies including an example for each.
Advertising is a paid method to promote products through media like TV, radio, or billboards—for example, Crocs could run a fun TV ad during The Voice Australia to showcase a new celebrity-designed collection.
Publicity and Public Relations aim to build a positive brand image through unpaid media or sponsorships, such as Crocs sponsoring Schoolies Week to connect with young Australians and gain media attention.
Sales promotion uses short-term deals to boost sales, like offering “Buy 1, Get 1 50% Off” on Crocs during the back-to-school season to encourage quick purchases.
Personal selling involves face-to-face interaction where a staff member helps a customer choose the right Crocs style and size, making the shopping experience more personal and persuasive.
Digital promotion uses online platforms like social media and websites—for instance, Crocs could run Instagram Reels and YouTube ads to show off new styles to a younger audience.
Social influencers promote products to their followers, such as a popular Aussie TikToker doing a “Crocs outfit of the day” video that inspires fans to buy the same pair.
Explain the production/operating system using examples.
Inputs: These are the resources used in production, including raw materials, labour, capital (like machinery and technology), and enterprise (ideas and risk-taking).
Transformations: The processes that convert inputs into outputs, adding value and improving productivity through efficient operations.
Outputs: The final goods or services produced, which should meet market demands; by-products can be reused in other systems to enhance sustainability and reduce waste.
What are the factors in the internal operating, external operating and Macro Environments that may be asked about in a describe question.
Internal Operating Environment:
Ownership/Management
Employees
Organisational structure
Organisational culture
External Operating Environment:
Customers
Competitors
Suppliers
Interest groups
Macro Environment:
Socio-cultural factors
Technological factors
Economic factors
Environmental factors
Political factors
Legal factors
Ethical factors
Identify two types of primary and two types of secondary research options.
Primary
Surveys
Interviews
Focus groups
Observations
Secondary
Market analyses
Academic journals
Government publications
Media articles
Online content
Identify and explain two of the four marketing objectives including an example for each.
1. Sales
The objective is to increase sales to maintain business growth and momentum during the growth stage.
Example: Achieve an 8% increase in sales revenue for the next quarter.
2. Sales Forecasting
The objective is to predict future sales levels to plan inventory, set realistic goals, and monitor performance.
Example: Forecast monthly sales of 1,200 units based on historical data and seasonal trends.
3. Market Share
The objective is to increase the business’s proportion of total market sales compared to competitors.
Example: Grow market share from 10% to 12% within the next financial year.
4. Brand Awareness
The objective is to improve consumer recognition and recall of the brand to encourage trial and loyalty.
Example: Launch a social media campaign to reach 50,000 new followers in three months.
Identify and explain two different pricing strategies including an example of each.
Price Skimming sets a high initial price for a new product and lowers it over time, such as a tech company launching a smartphone at $1,500 and reducing the price after six months.
Penetration pricing introduces a product at a low price to quickly gain market share, like a streaming service offering subscriptions at $5 per month to attract new users.
Prestige pricing charges a high price to create an image of exclusivity and quality, for example, a luxury brand selling handbags for $3,000.
Competition-based pricing sets prices based on competitors, such as a café pricing its coffee at $4 because nearby cafés charge the same.
Cost-based pricing calculates the price by adding a markup to production costs, like a furniture maker spending $200 on materials and selling the table for $300.
Loss leader pricing sells a product below cost to attract customers, for example, a supermarket selling milk at $1 to encourage more grocery purchases.
Psychological Pricing uses tactics like ending prices in .99 to make them seem cheaper, such as a clothing store pricing shirts at $19.99 instead of $20.
Dynamic Pricing adjusts prices in real time based on demand, like an airline increasing ticket prices during holidays and lowering them in off-peak seasons.
Identify and explain one influence on operations.
Customers: Businesses have shifted their focus from just producing goods to meeting customer needs and expectations. Today’s customers value sustainability, ethical practices, innovation, and community support—not just low prices.
Managing suppliers has become more complex due to global sourcing and outsourcing, making strong, ethical relationships essential. Companies must ensure quality, fair treatment, and sustainability while keeping costs under control.
Technology improves efficiency and productivity by transforming how businesses operate and deliver products or services. Since COVID-19, many businesses have adopted digital tools like online ordering, remote work, and hybrid service models to stay competitive.
Environmental sustainability means using resources responsibly to protect the planet for future generations. Businesses can improve their reputation by using recycled materials, green energy, and ethical suppliers.
Deregulation removes government restrictions to increase competition, reduce costs, and make it easier for businesses to enter markets. In Australia, industries like aviation and telecommunications have seen major deregulation to boost efficiency.
Identify five things you might discuss when talking about business situation in a describe question.
• Stage of the business life cycle (e.g. start-up, growth, maturity, post-maturity)
• Number of stores / locations / online presence
• Revenue and profit trends
• Market share
• Current strategies and operations
• Recent changes or developments (e.g. rebranding, mergers, leadership changes)
• Business goals and objectives
• Key products or services
• Brand image and reputation
• Marketing and promotional activities
• Customer satisfaction and feedback
• Innovation and R&D efforts
• Financial health indicators (e.g. cash flow, debt levels, investment)
• Challenges or internal issues
• Competitive advantage / Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
• Digital transformation or technology adoption (internal focus)
• Organisational capabilities and resources
• Workforce size and skill levels
Identify and explain the three different types of consumer markets.
A mass market is one in which a product is aimed at all consumers, regardless of their age, gender, income or location.
A market segment breaks down the mass market into a more focused portion, typically based on one key characteristic.
A niche market is a business is likely to be highly specialised and to cater for a smaller group of people. Due to its specialised nature, goods and services offered are customised to meet the needs of the market and the business is scaled accordingly.
Identify the four different types of market segment and an example of each.
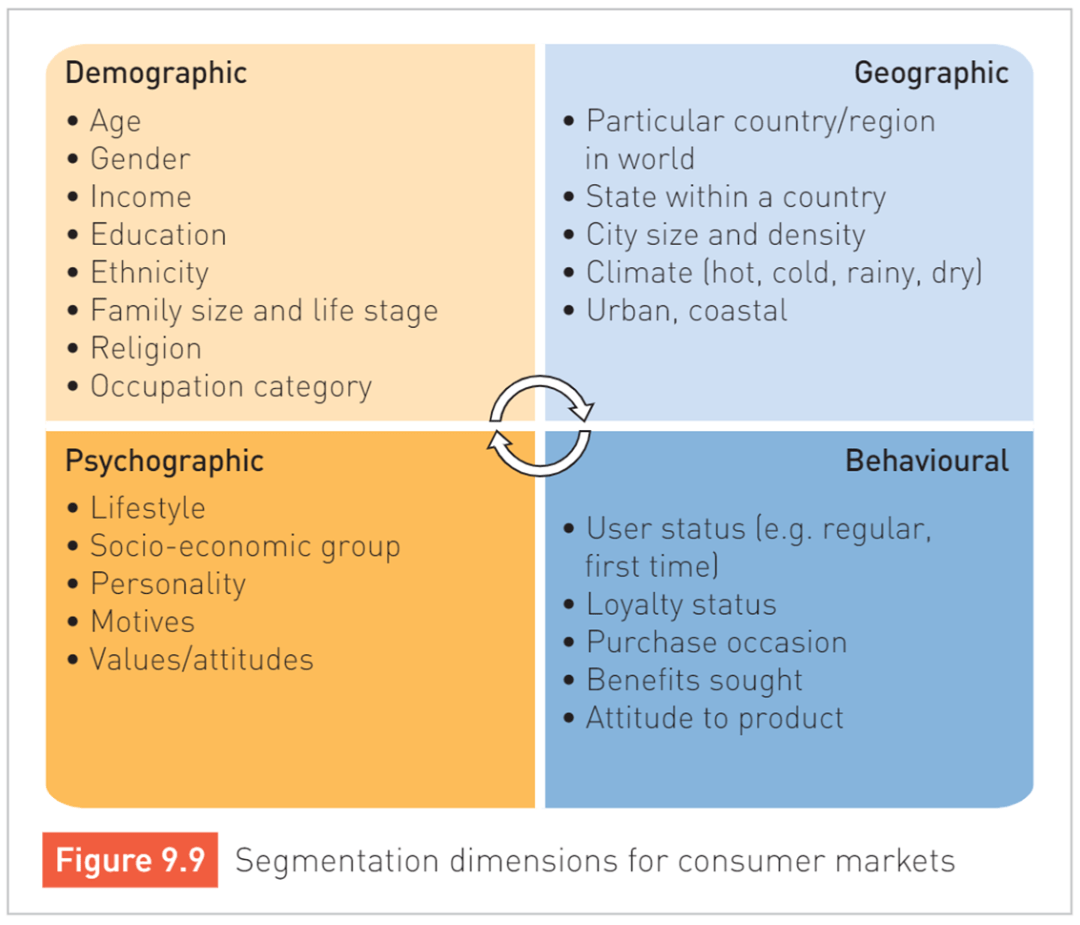
Explain the difference between retailers, wholesalers and distributors including an example for each.
A retailer sells products directly to consumers, like JB Hi-Fi selling headphones to customers in-store or online.
A wholesaler buys large quantities of goods from manufacturers and sells them in bulk to retailers, such as Metcash supplying groceries to IGA supermarkets.
A distributor works with manufacturers to distribute products to wholesalers or retailers, like Coca-Cola Europacific Partners distributing beverages to supermarkets and convenience stores.
Explain why supply chain management is important to a business. Include an example in your response.
Supply chain management is important because it coordinates sourcing, production, and logistics to ensure products move efficiently from suppliers to customers. A well-managed supply chain balances speed and cost-effectiveness, giving businesses a competitive advantage by meeting customer expectations for quality and timely delivery. For example, Coles and Woolworths optimize their supply chains for fast service, while SMEs can gain an edge by sourcing ethical materials and maintaining reliable supplier relationships.
What is the Structure that should be used for an in an extended response question?
