This term is used to describe the quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to offer at various possible prices during a given time period
Supply
This refers to the value of the next best alternative that is given up to obtain the preferred item.
Opportunity Cost
A government creates this to determine how it will spend its money.
A budget
Name 3 economic indicators:
GDP, Unemployment Rate, Inflation Rate
The ability of a country, individual, company or region to produce a good or service at a lower cost per unit than the cost at which any other entity produces that good or service
Absolute Advantage
The price is said to be at equilibrium when it meets these two objectives.
This is when employees refuse to work until certain conditions are met
A strike
Somaliland would be best described as these 2 kind of economic systems:
Market and Traditional
Economics is broken up into these two subcategories. The first meaning the study of the choices made by economic actors and the second meaning the study of the behavior of entire economies.
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Even if a country has an absolute advantage in producing goods and services they should still trade where another country has this advantage.
Comparative Advantage
This term is used to refer to the combination of limited economic resources and unlimited wants of consumers
Scarcity
What is the main goal of the management of a business?
Maximize profits
What is the main way the government gets money?
Taxation
A product that can be consumed without reducing its availability to anothers and from which no one is excluded; examples are national defense, sewer systems, public parks and basic television and radio broadcasts
A public good
When a party produces only those goods in which it has a comparative advantage.
Specialization
This term is used to describe when the amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at various possible prices during a given period of time
Demand
Three goals of unions
Better wages, better working conditions, better benefits, better hours, job security
Give an example of how a government Corrects for Externalities.
Environmental Protection
This basket of goods helps us determine inflation.
What is the CPI (consumer price index)
Who is the economist who derived the theory of Comparative Advantage?
David Ricardo
A new toy came out before the holidays and they cannot keep enough on the shelves! This is an example of:
High Demand
What is a court orders that order striking employees to get back to work?
An injunction
Name all 6 economic roles of a government.

Explain the difference between exogenous and endogenous variables and name an economic model with which we can use those variables.
Exogenous come from outside the economic model.
Endogenous come from the economic model.
Aggregate supply and demand model.
Which country should specialize in what? Explain.
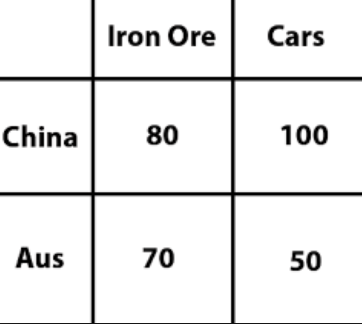
China - Cars
Australia - Iron Ore