What does an EEG measure?
Electrical activity of the brain (brainwaves).
Name one effect of sleep deprivation.
Cognitive, Behaviour/Social, Physical or Emotional
What are the two main types of sleep?
REM and NREM.
What is the main symptom of insomnia?
Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
Which iconic marsupial at Australia Zoo eats eucalyptus and sleeps up to 20 hours a day?
Koala
How does an EMG help differentiate between REM and NREM sleep?
EMG detects muscle tone, which is low in REM but higher in NREM.
How does sleep deprivation impact emotional stability?
Increased irritability, stress, anxiety, and mood swings.
How long does an average sleep cycle last?
About 90 minutes.
How does sleep apnea affect breathing?
Repeated breathing stoppages during sleep.
How long can a saltwater crocodile hold its breath underwater?
Over an hour
Look at this EEG brainwave graph. Is this person in deep sleep or wakefulness?
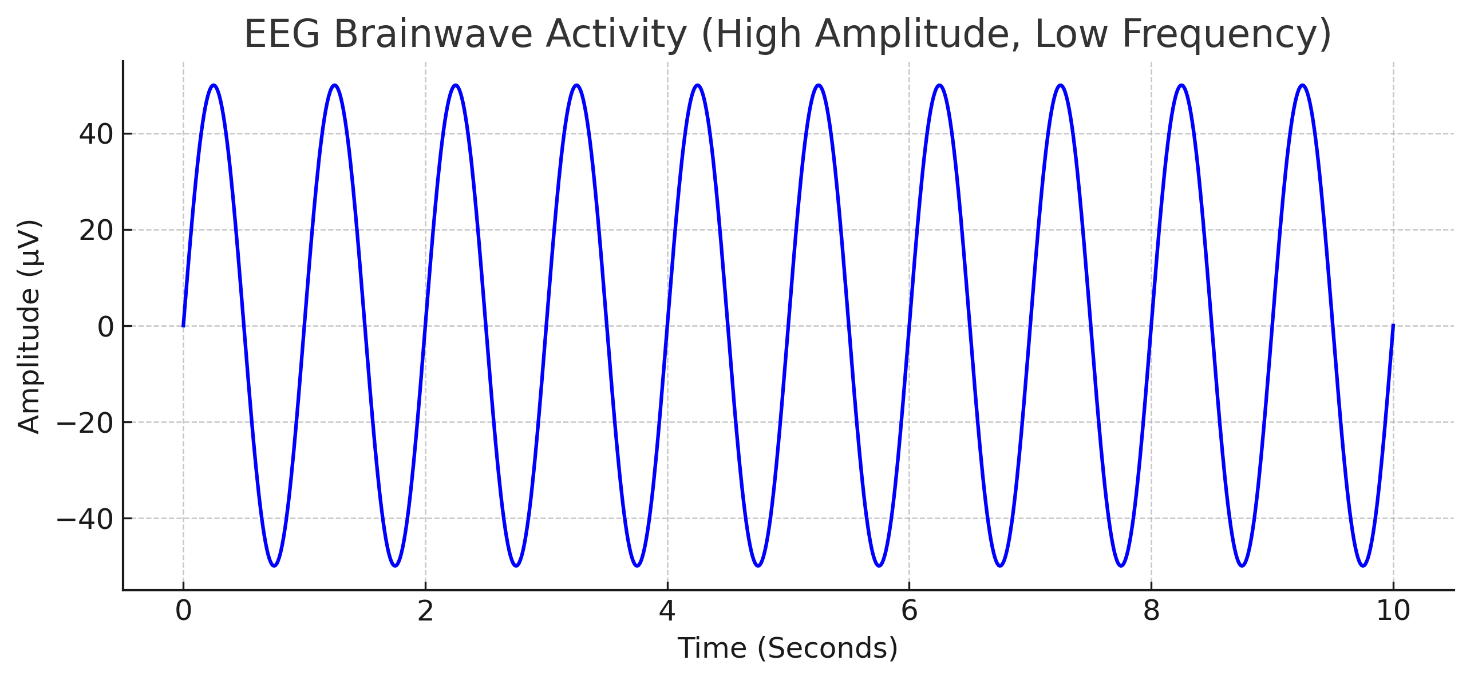
Deep sleep (Waves have high amplitude and low frequency).
Match a case study with its sleep deprivation category (Cognitive, Emotional, Physical, Behavioural).
A shift worker experiences frequent colds and takes longer to recover from illnesses.
Physical: Weaker immune system.
Look at this sleep cycle chart. Identify how many sleep cycles this person went though that night.
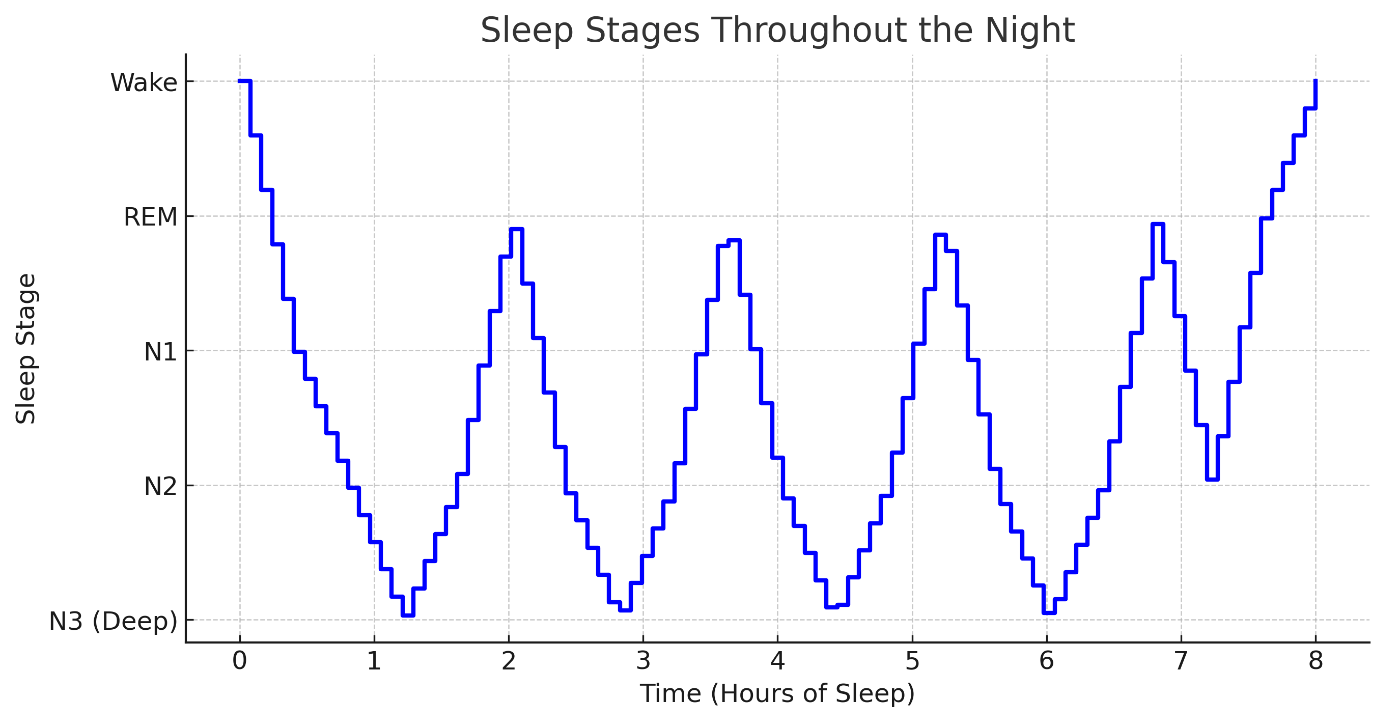
4-5 sleep cycles.
Given a case study, identify the sleep disorder (Narcolepsy, Insomnia, Sleep Apnea).
A 19-year-old university student frequently experiences sudden, uncontrollable episodes of sleep, even during conversations and while eating. Despite getting enough sleep at night, they feel excessively tired during the day and sometimes experience brief episodes of muscle weakness when laughing or excited.
Narcolepsy
Look at this table. Which is the largest reptile at Australia Zoo?
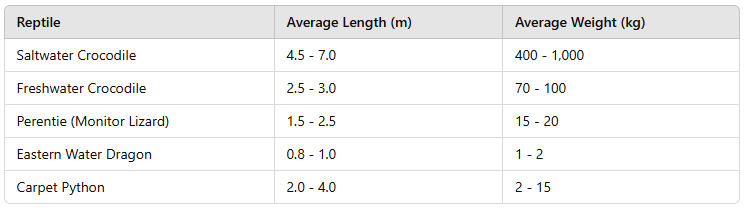
Salt water croc
Explain how EOG recordings differ between NREM and REM sleep.
EOG detects rapid eye movements in REM sleep, but minimal movement in NREM.
Why does chronic sleep deprivation increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease?
Hormonal imbalances lead to weight gain, high blood sugar, and cardiovascular strain.
Explain how NREM Stage 3 is important for physical restoration.
It’s the deepest sleep stage, helping muscle growth, immune function, and recovery.
Why is sleepwalking more common in children than adults?
More time spent in deep sleep (NREM Stage 3), where sleepwalking occurs.
What unique feature distinguishes the cassowary from other birds?
A helmet-like casque and powerful kick!
Given an EEG, EMG, and EOG dataset, interpret the sleep stage. NREM or REM
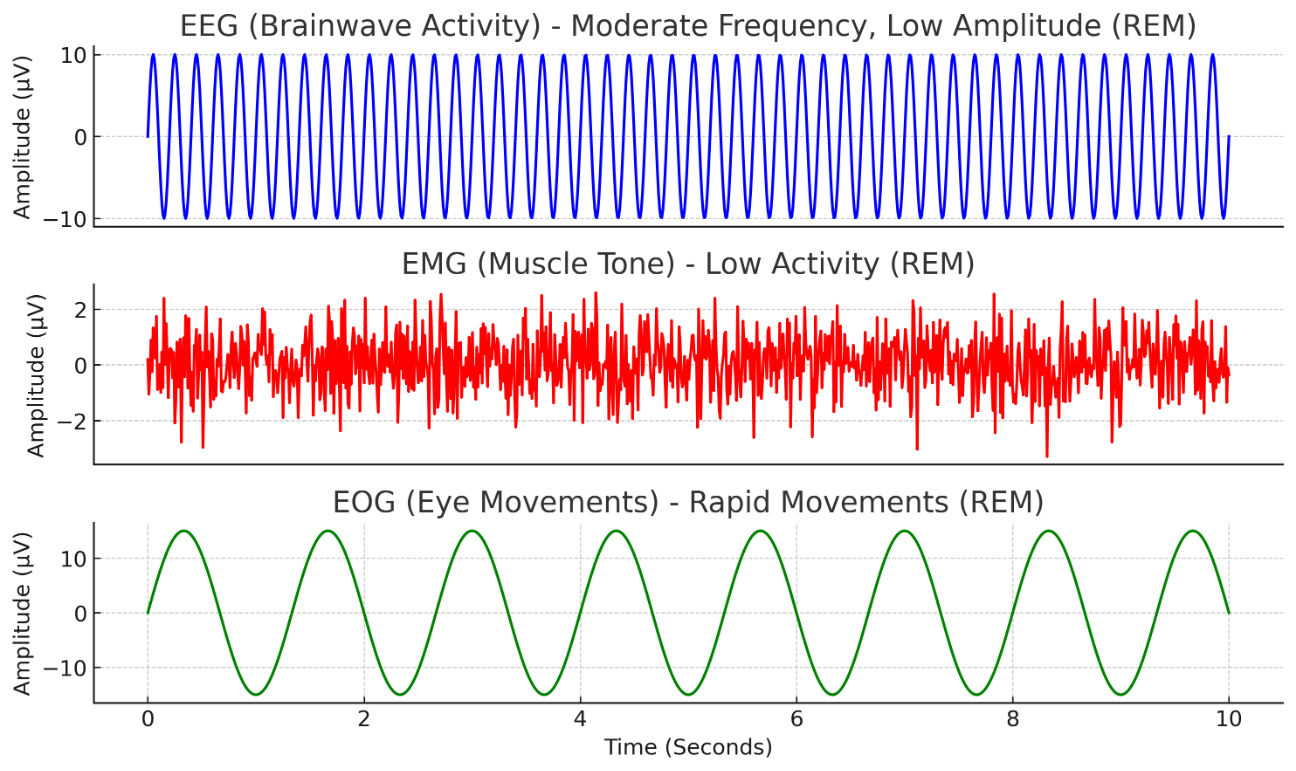
REM sleep (EEG shows high frequency, EOG shows movement, EMG is low amplitude).
Analyse this graph showing reaction time vs. sleep. What does it show?
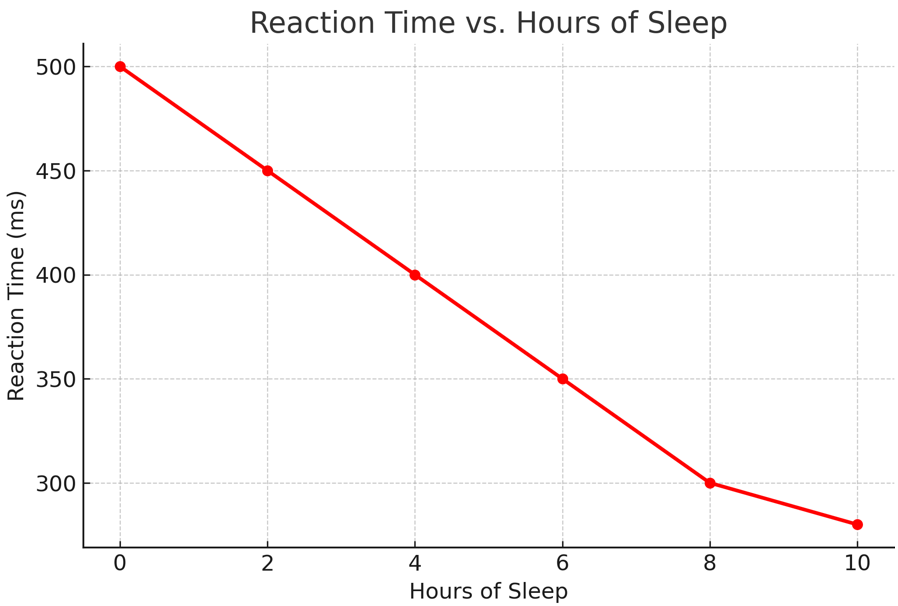
More sleep = Faster reaction times. Sleep deprivation slows cognitive performance.
Analyse a dataset showing REM and NREM cycles. What pattern can you identify?
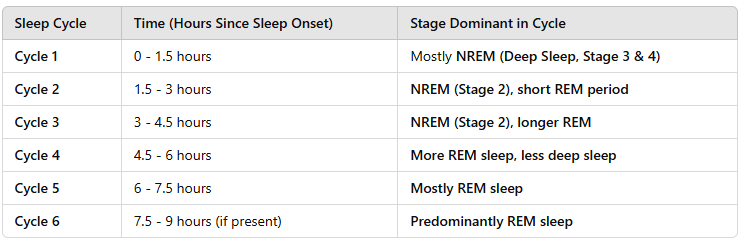
More NREM early, more REM later in the night.
Analyze a dataset linking sleep disorders to health risks. What do you conclude?
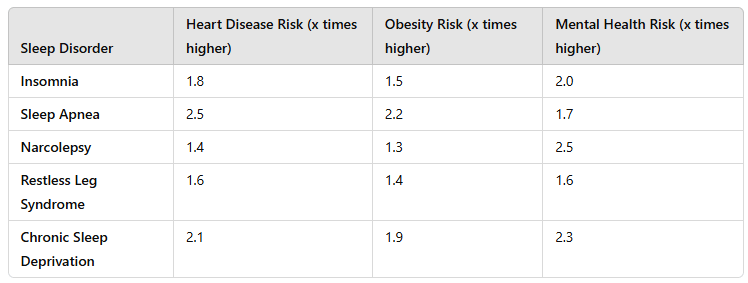
Sleep Apnea has the biggest impacts on physical health while Narcolepsy has the biggest impact on mental health.
Analyze this animal lifespan graph. Which animal lives the longest?
Saltwater Crocodile (up to 70 years).