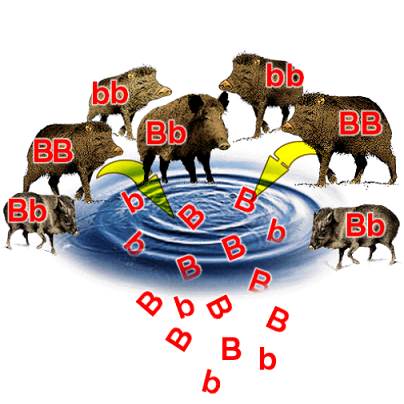
What evolutionary principle can be written as the following formulae?
p+q=1
p2+2pq+q2=1
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
The total genetic diversity found within a population.
Gene pool
This mechanism requires the migration of individual into a population, bringing new alleles with them.
Gene flow
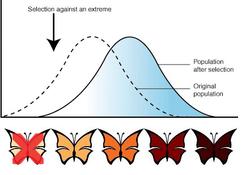
What type of selection does this graph show?
Directional selection
What does p most commonly represent?
Dominant allele
Evolution over a short period of time within a small population or just one species.
Microevolution
This mechanism changes the DNA of an organism, sometimes by random chance or by environmental factors.
Mutation
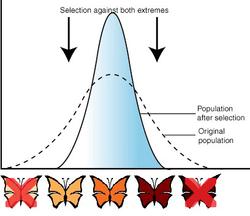
What type of selection does the graph show?
Stabilizing selection
What does q most commonly represent?
Recessive allele
An extreme example of genetic drift; occurs when a population declines to a very low number and then rebounds.
Genetic Bottleneck

This mechanism causes alleles in a population to become more or less common due to chance.
Genetic drift
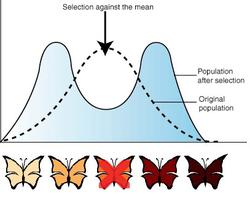
What type of selection does the graph show?
Disruptive selection
What does 2pq represent?
Heterozygous genotype
An extreme example of genetic drift; occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated from the rest of the population.
Founder Effect

This mechanism allows individuals with beneficial traits to survive in a particular environment.
Natural selection
Which is the most common type of natural selection?
Stabilizing selection.

p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
This formula is really just what other genetics tool written mathematically?
Punnett Square
When allelic frequencies remain constant, a population is in genetic equilibrium.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
This mechanism causes some alleles to be more common due to limitations of who and where mates are.
Non-random mating
Selection based on traits capable of attracting mates over traits for survival.
Sexual selection