Due to a coronary artery spasm, often occuring occurring during periods of rest.
Variant (Prinzmental's) Angina
Given via IV drip for bradycardia
Dopamine
Provides clearer picture of cardiac chambers by passing a small transducer through the mouth and into the esophagus. Used to assess heart failure, valvular disease, and atrial or ventricular thrombi.
TEE
If I am administering 1L of Normal Saline at 75 mL/hour, how long will it take (in hours) to administer the entire bag? Round to the hundredths place.
13.33 hours
A nurse is reviewing lab test results for a group of clients. The nurse should identify that which of the following results indicates the client is at risk for heart disease? (Select all that apply)
A. Cholesterol (total) 245 mg/dL
B. HDL 90 mg/dL
C. LDL 140 mg/dL
D. Triglycerides 125 mg/dL
E. Troponin I 0.02 ng/dL
A C
Symptoms:
-Dyspnea
-Orthopnea
-S3 heart sound (gallop)
-Cough/Bibasilar crackles
-Oliguria or Nocturia
Left-sided heart failure
Medication used to decrease preload.
Diuretics
Indicated for angina, heart failure, an MI, or dysrhythmias. The client exercises on a treadmill to assess the workload of the heart.
Stress test
A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin 250 mcg PO daily. Available are digoxin 0.125 mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer?
2 tablets
A nurse is admitting a client who has a suspected MI with a history of angina. WHich of the following findings will help the nurse distinguish stable angina from an MI?
A. Stable angina can be relieved with rest and NTG
B. The pain of an MI resolves in less than 15 min
C. The type of activity that causes an MI can be identified.
D. Stable angina can occur for longer than 30 minutes.
Life-threatening medical emergency; symptoms include:
-Anxiety
-Tachycardia
-Dyspnea at rest
-Crackles
-Frothy, blood-tinged sputum
Acute pulmonary edema
anticoagulant; reversible inhibitor of factor Xa. Does not affect platelet aggregation directly, but does inhibit thrombin-induced platelet aggregation.
Invasive diagnostic procedure to evaluate the precence and degree of coronary artery blockage.
Cardiac angiography (cardiac cath)
You are administering 60 mg of Lasix. Available is 40 mg/4 mL. The administration rate is 20 mg/min. How many mLs will be administered per minute (mL/min)?
2 mL/min
A nurse is teaching a client with heart failure and a new prescription for furosemide and digoxin. Which of the following information should the nurse include? (Select all that apply).
A. Weigh daily, first thing each morning
B. Decrease intake of potassium
C. Expect muscle weakness while taking digoxin
D. Hold digoxin if heart rate is less than 70
E. Decrease sodium intake
A, E
Symptoms:
-hypotension
-JVD
-Muffled heart sounds
-Paradoxical pulse
Pericardial tamponade
slows ventricular rate and increases force of contraction.
Digoxin (Lanoxin)
Cholesterol test that is the "Bad cholesterol". Normal value is <130
LDL
Drip is running at 20mL/hr. The IV contains 2500 mg in 250 mL.
What is the mcg/min? Round to nearest whole number.
333 mcg/min
A nurse is completing an admission assessment on a client with mitral valve insufficiency. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
A. S4 heart sound
B. Petechiae
C. Neck vein distention
D. Splenomegaly
C
Symptoms:
-Chest pressure/pain worse with inspiration, coughing, and swallowing
-SOB
-Pain relief when sitting and leaning forward
-grating, creaking sound in the chest heard during breathing
Pericarditis
BONUS QUESTION: What is the reversal agent for heparin?
Protamine sulfate
a protein essential for muscle contraction; blood test to determine if myocardial injury is occuring.
Troponin
The MD orders your patient to start an IV Heparin drip at 18 units/kg/hr. You’re supplied with a Heparin bag that reads 25,000 units/500 mL. The patient weighs 172 lbs. What is the flow rate you will set the IV pump at (mL/hr)? Round to nearest tenths place.
28.1 mL/hour
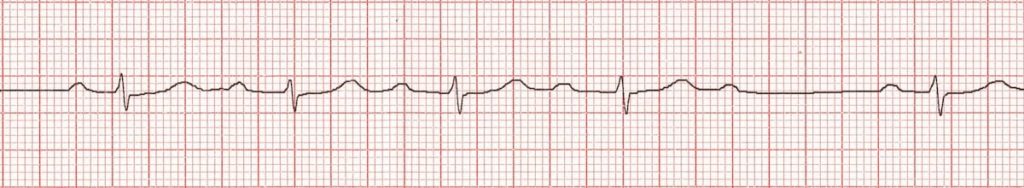
Wenckeback!