What is the photoelectric effect?
When light above a certain frequency strikes a metal surface electrons are emitted.

When an electron moves up energy levels what is happening is it absorbing or emitting energy?
Absorbing - it takes energy to move away from the attractive force of the nucleus.

A particle has 5.2 x 10-16 J of kinetic energy, how much mass would this add to the rest mass of the particle?
m (relative mass) = 5.2x10-16 / (3.00x108)2
m (relative mass) = 5.78 x 10-33 kg (3sf)
Light shines on a metal surface and electrons are emitted. What would happen...
a) If the brightness of the light was increased?
b) If the frequency of the light was increased?
a) The amount of electrons being emitted will increase
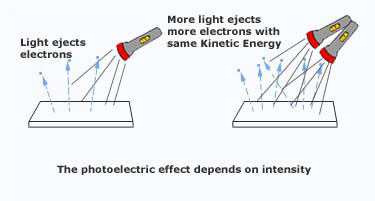
b) The kinetic energy of the electrons would increase
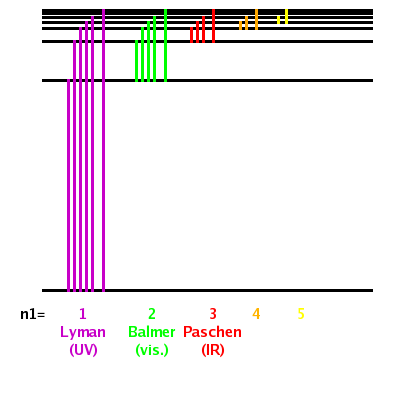
Match up each of these series with the electron transitions associated with the emission spectra of hydrogen and the type of light they emit.
Series --> Paschen, Lyman, Balmer
Electrons drop to --> n=3, n =2, n =1
Emits --> UV light, infra-red light, visible light
Lyman series, electrons drop to n=1, UV light emitted
Balmer series, electrons drop to n=2, visible light emitted
Paschen series, electrons drop to n=3, infrared light emitted

What is the mass number and atomic number of X? What element is X?
2311 Na + 11 H --> X + 10 n

X has a mass number of 23 and atomic number of 12. X is therefore Magnesium-23.

A photon with an energy of 4.87 x 10-19 J hits a metal surface and emits an electron. What is the max kinetic energy that electron could have if the metals work function is 2.61 x 10-19 J?
Ek = E (of photon) - Φ (work function)
Ek = 4.87 x 10-19 - 2.61 x 10-19
Ek = 2.26 x 10-19 J
Which of these is the biggest energy jump and would have to absorb the shortest wavelength of light?
a) 2 to ∞
b) 3 to 10
c) 2 to 3
d) 1 to 2
e) 3 to ∞
d) 1 to 2
The energy it takes to move one energy level away from the ground state (n=1) is greater than any jump from an excited state to a higher level.
What four things are conserved in a nuclear reaction?
Mass number
Atomic number
Mass-energy
Momentum
Yellow light with a wavelength of 570nm hits a metal with a work function of 3.32 x 10-19 J. Will electrons be emitted?
570nm = 5.70 x 10-7 m
f = v / λ = 3.00x108 / 5.70x10-7 = 5.2631579x1014 Hz
E = hf = 6.63x10-34 x 5.2631579x1014 = 3.48947x10-19
E = 3.49 x 10-19 J
The energy of the yellow photons is greater than the work function (minimum energy to release an electron), therefore electrons will be emitted.
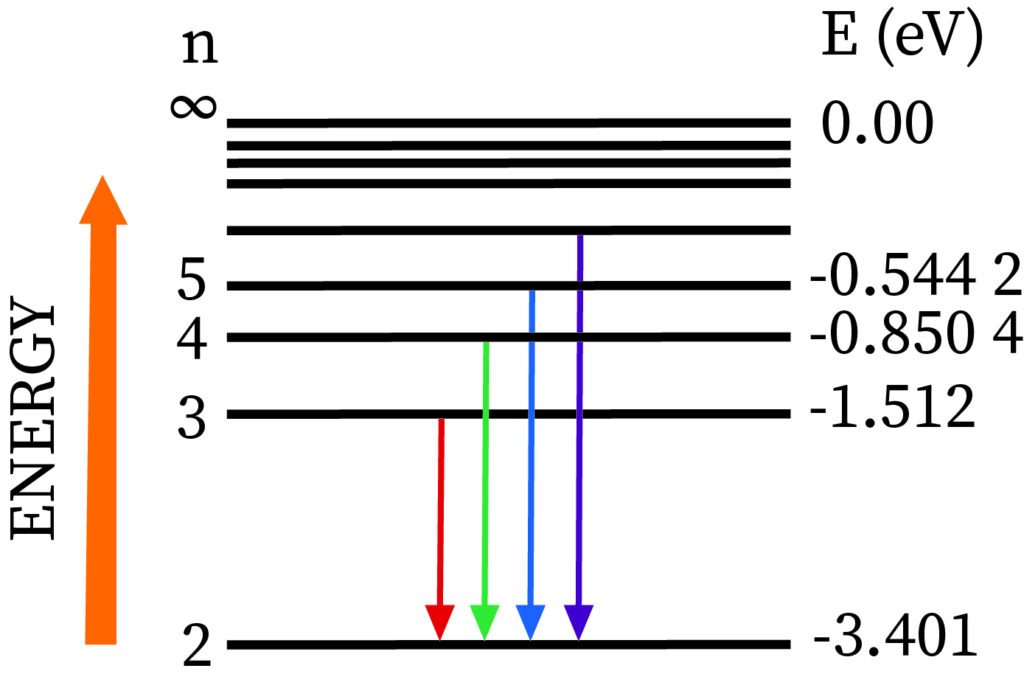
What energy level drop does the emission of a green photon (486nm) correspond to?
It is the second longest wavelength line in the Balmer series, so the second smallest energy jump. Therefore, this must correspond to a drop from energy level 4 to 2.
How much energy is released in this reaction?

m (neutron) = 1.6749×10-27 kg
m (Helium) = 6.6447 x 10-27 kg
m (Argon-40) = 6.6956 × 10-26 kg
m (Calcium-43) = 7.1364 × 10-26 kg
m (reactants) = 6.6956 × 10-26 + 6.6447 x 10-27 = 7.36007 x 10-26 kg
m (products) = 7.1364 x 10-26 + 1.6749 x 10-27 = 7.30389 x 10-26 kg
Change in mass = 7.36007 x 10-26 - 7.36007 x 10-26 = 5.618 x 10-28 kg
E = 5.618 x 10-28 x (3.00 x 108)2 = 5.0562 x 10-11 J
Explain why electrons released by blue light photons leave a metal surface with more speed than those released by green light photons?
(Refer to wavelength, frequency, energy)
Blue light has a shorter wavelength than green light, which means it has a higher frequency (v=fλ) and therefore higher energy as well (E=hf). Because of this, a blue light photon will pass on more energy to an electron than a green light photon. Anything above the work function of the metal will go towards kinetic energy, so electrons released by blue light will have more kinetic energy making them faster.
What is the wavelength of the fourth longest wavelength spectral line in the Paschen series?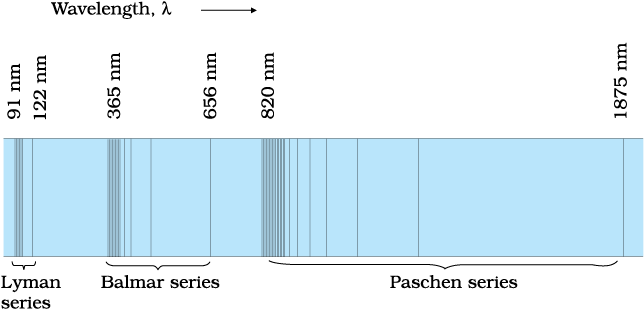
S = 3, L = 7
1/λ = R (1/S2 - 1/L2)
1/λ = 1.097 x 107 (1/32 - 1/72)
1/λ = 995 011.3379
λ = 1/995011.3379 = 1.01 x 10-6 m (3sf)
Find the binding energy of Fluorine-19.
Mass of 199 F nucleus = 3.155 x 10-26 kg
Mass of proton = 1.6726×10−27 kg
Mass of neutron = 1.6749×10-27 kg
Mass of separated nucleons...
9 protons: 9 x 1.6726×10−27 = 1.50534 x 10-26 kg
10 neutrons: 10 x 1.6749×10-27 = 1.6749 x 10-26 kg
Mass of separated nucleons = 3.18024 x 10-26 kg
Mass defect = 3.18024 x 10-26 - 3.155 x 10-26 = 2.524 x 10-28 kg
Binding energy = 2.524 x 10-28 x (3.0 x 108)2 = 2.27 x 10-11 J (3sf)
